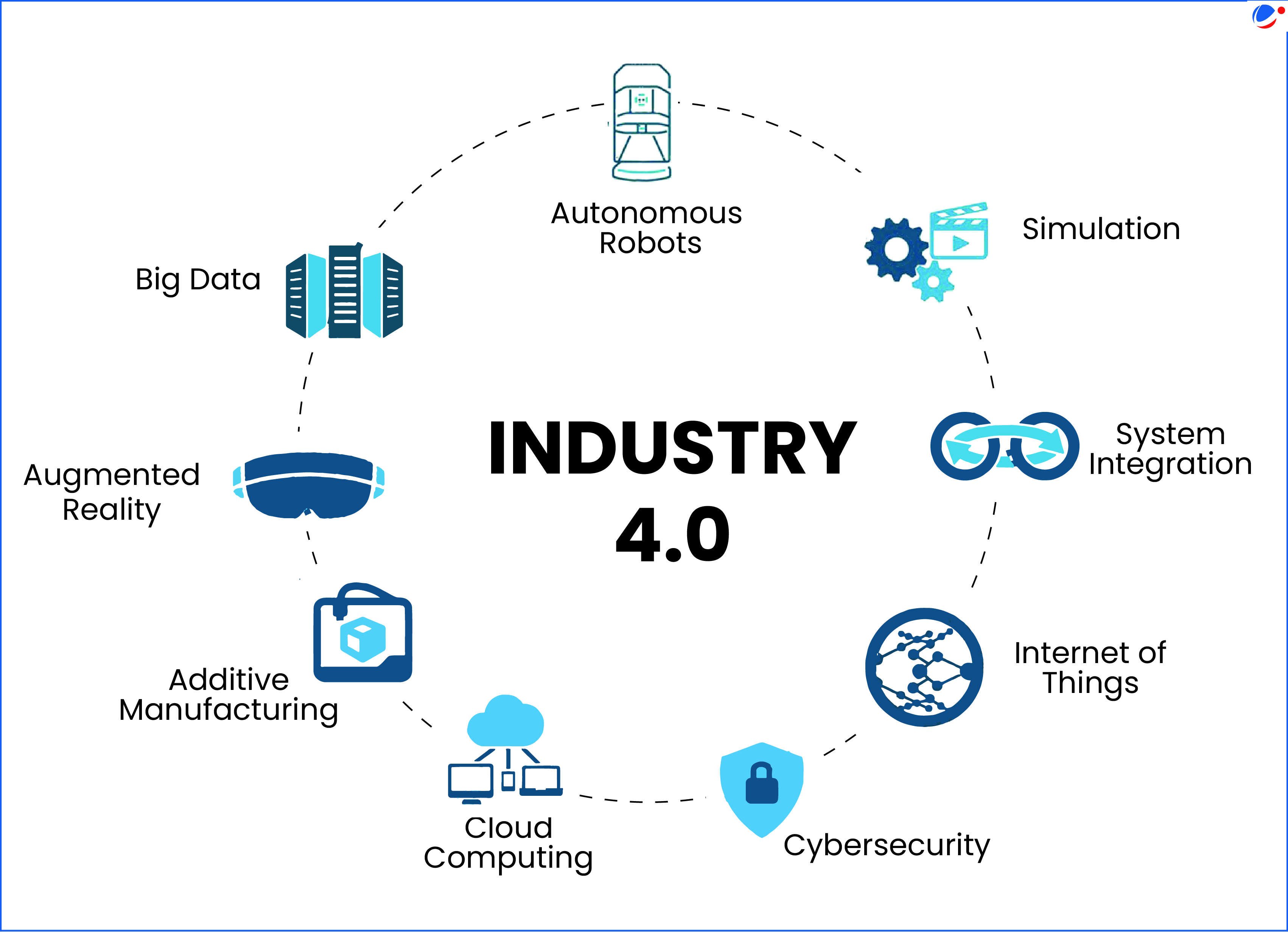
Industry 4.0 refers to “smart” and connected production systems that are designed to sense, predict, and interact with physical world.
Key Highlights of Report
- Industry 4.0 adoption in India: Automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals are frontrunners. In contrast, textiles, metals & mining face significant barriers.
- Key Drivers of Industry 4.0 in India
- Workforce Up-skilling, Digital Infrastructure, Sustainability (To meet global consumer and regulatory expectations for green manufacturing).
- Barriers to Adoption
- Awareness: Many MSMEs lack understanding of Industry 4.0's benefits versus costs.
- Technological Barriers:
- Legacy Systems: Difficult to integrate with modern tech.
- Data Integration: Challenges in handling big data across systems.
- Cyber-security Risks: Increased digital exposure brings higher risks.
- Financial Constraints: High initial investment and ongoing costs, limited access to funding.
- Human Resource Issues: Shortage of skilled workers and cultural resistance to new methods.
- Way forward:
- Harnessing Global Value Chains (GVCs) present immense opportunities for MSMEs to access global markets and enhance competitiveness.
- Develop comprehensive digital strategies and phased implementation roadmaps.
- Other focus areas: Prioritize key technologies such as AI and automation, invest in workforce up-skilling etc.
Government Support and Policy Interventions
|







