Starlink is the world’s first and largest satellite constellation that uses Low Earth Orbit (LEO) to provide high-speed, low-latency broadband internet.
Satellite Internet
- It is a wireless internet through communication satellites orbiting the Earth and is location independent, providing global coverage.
- Satellites communicate with each other using lasers, reducing dependence on ground stations.
Starlink Satellite Internet Service
- Presently, there are around 7,086 starlink satellites in orbit.
- Each starlink satellite:
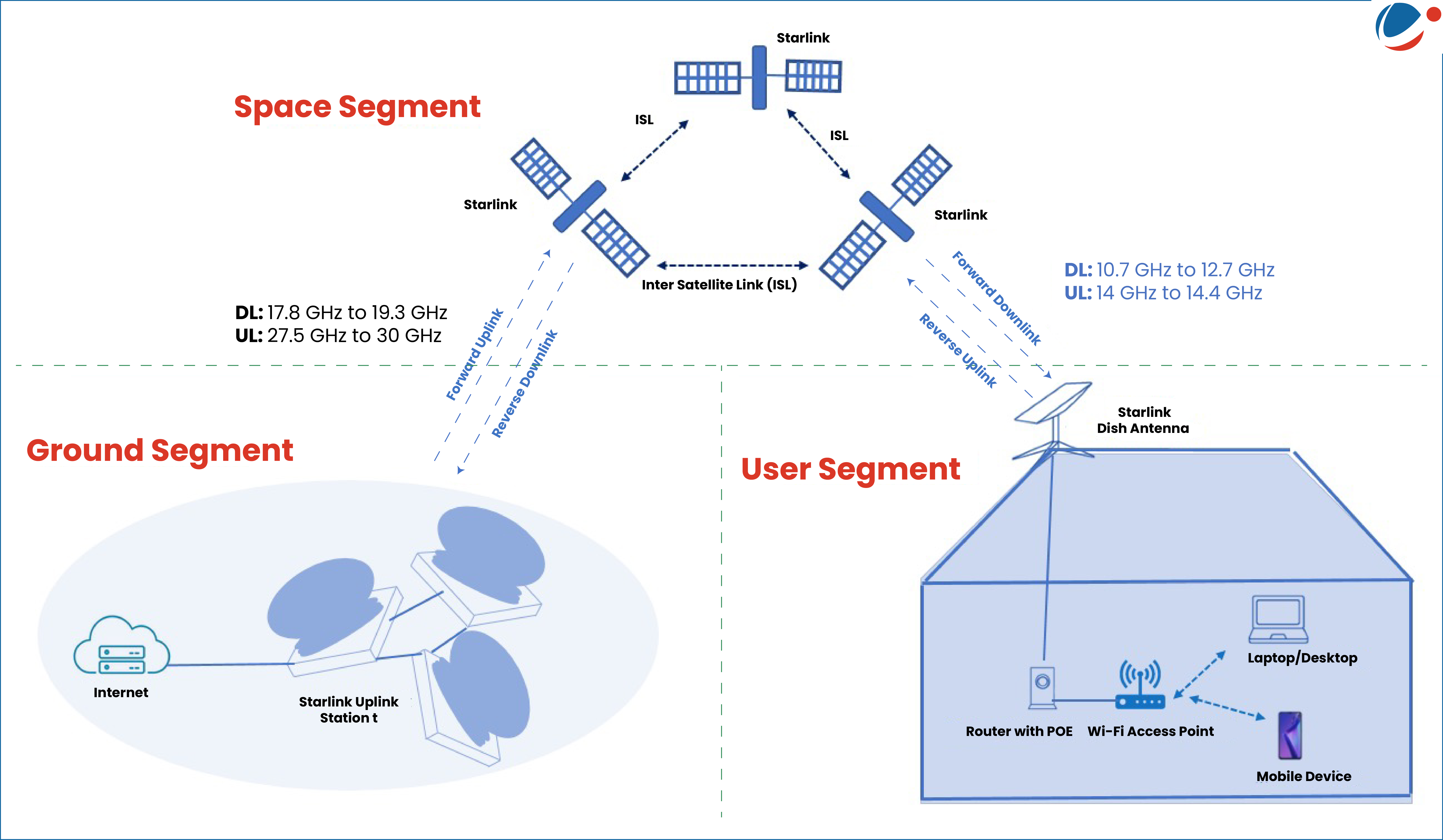
- Contains 3 space lasers (Optical Intersatellite Links or ISLs) operating at up to 200 Gbps, which together across the constellation form a global internet mesh.
- Uses 5 advanced Ku-band phased array antennas and 3 dual-band (Ka-band and E-band) antennas to provide high-bandwidth connectivity.
Significance of Satellite Internet
- Improving access: Suited for unconnected areas or areas with unreliable connectivity.
- Connectivity during Disasters: Starlink provided connectivity to Tonga after a massive volcano eruption and tsunami.
- Military applications: Provides connectivity between military bases and military planes, ships, drones etc.
Concerns
- Astronomical Interference: Bright light emitted by satellites in the night sky could interfere with astronomical observations.
- Atmospheric changes: Plan to steering out of service starlink satellites into Earth’s atmosphere risks altering the atmospheric chemistry.
- Technical limitations: Disruptions by extreme weather conditions and geomagnetic storms.







