This warfare threatens the security of global connectivity and could reshape the geopolitical landscape.
About Seabed Warfare
- It encompasses military operations conducted on, from, or targeting the ocean floor, focusing on critical undersea infrastructure.
- Tools used: Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), Submersibles, etc.
Reasons for the Rise
- Increased Reliance on undersea infrastructure: Like communication cables, energy pipelines, etc.
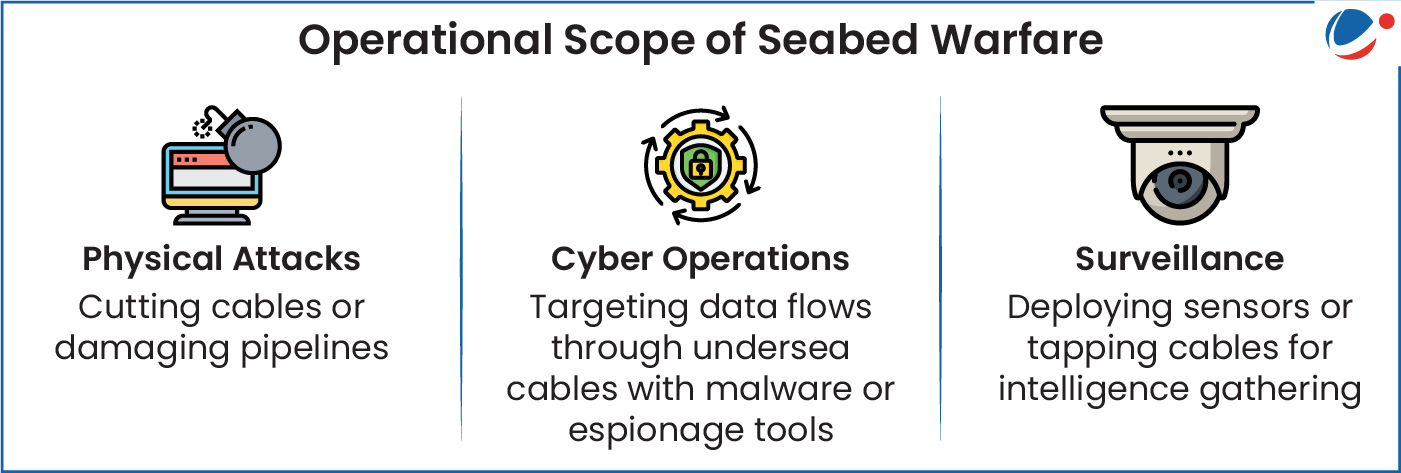
- Advancement of deep-sea technology: It has enhanced the scope of seabed warfare from cable-cutting and censorship to sophisticated operations like surveillance, reconnaissance, and cyber warfare.
- Potential of Ocean Economy: As per Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), it has the potential to reach $3,000 billion by 2030.
- Several activities like oil and gas exploration, submarine cables for fibre optic communication etc., hold immense future potential.
Need for Building Seabed Warfare Capability
- Increased geopolitical interests: French Navy unveiled its strategic seabed warfare doctrine in 2022 with other countries like USA, UK, China, etc., showing similar interest.
- Security of Indo-Pacific: Region is home to critical undersea cables, essential pipelines, energy routes, etc.
- Growing China’s influence in the region has raised concerns for its security.
- Rising Tensions: Evident in the form of recent incidents like explosions on Nord Stream 1 and 2 gas pipelines (2022); sabotage incidents against undersea cables in the Baltic Sea (2023, 2024), etc.
- Building Seabed Surveillance: To track submarine movements laying the foundation for modern naval strategy.





