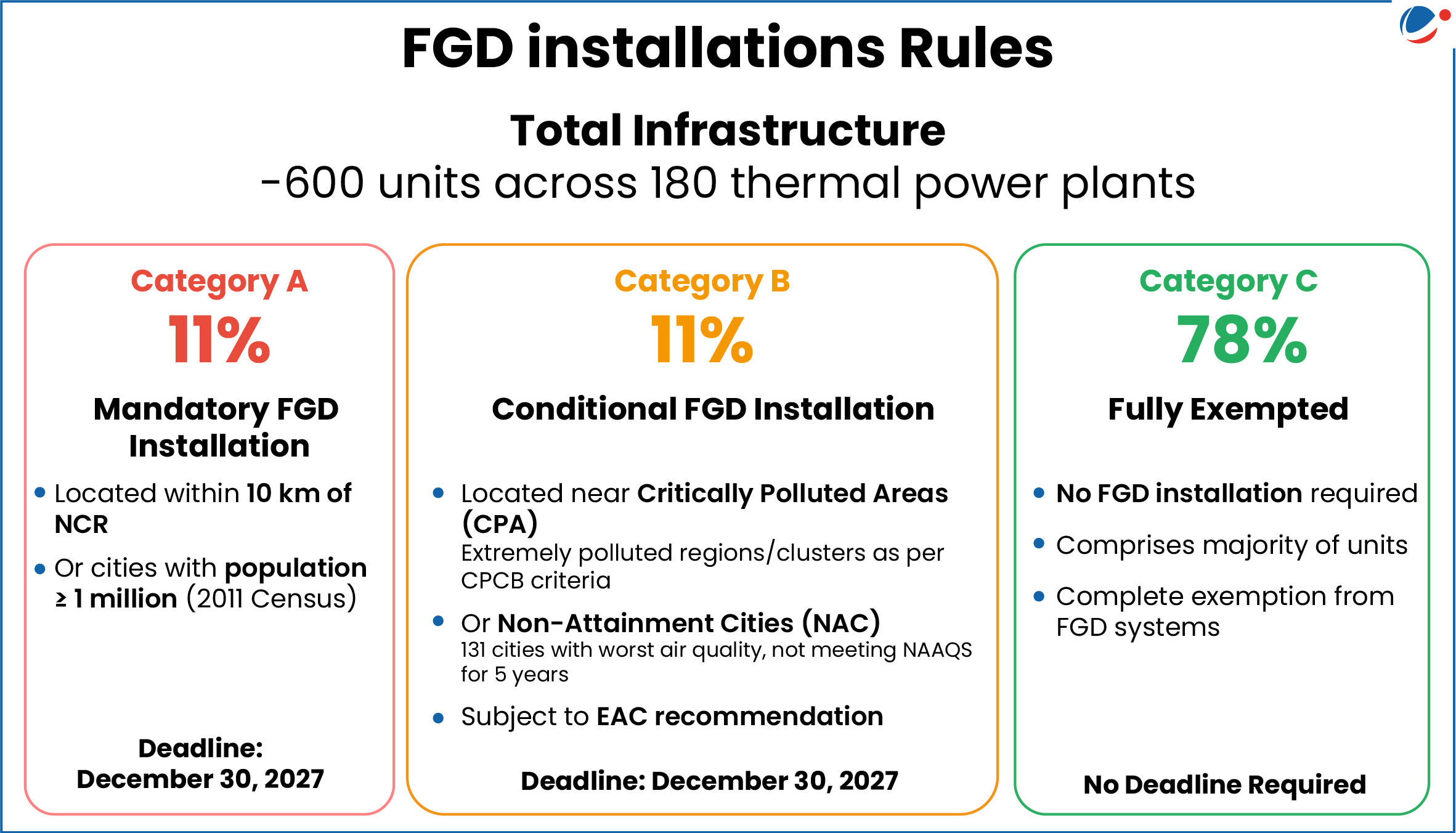
The updated rules (see image) regarding the installation of FGD are in line with the recommendations of an expert committee constituted by Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government.
Rationale for the Ease of FGD Systems Norms
- Ambient SO₂ levels in India range between 10–20 µg/m³, well below the national standard of 80 µg/m³.
- Indian coal is naturally low in sulphur.
- Sulphates have a “beneficial side-effect”: They may suppress global warming by reflecting solar radiation and offsetting the warming effect of greenhouse gas emissions.
- While the IPCC notes that sulphates reduce warming, it never presents this as entirely positive or without downsides.
- Other Reasons: High installation costs, Limited number of qualified vendors; Potential electricity tariff hike.
About Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) Systems
- Definition: FGD is a scrubbing technique that uses an alkaline reagent (typically a sodium- or calcium-based alkaline regent) to remove SO2 from flue gas.
- Flue gas: It is emitted as a byproduct of combustion of fossil fuels. It mainly contains pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, etc.
- FGD units specifically target the SO2 emissions in flue gas.
- SO2 is an acidic gas, and is treated with a basic compound in the FGD unit to neutralise the pollutant.
- There are three types of FGD systems: Dry Sorbent Injection, Wet Limestone Treatment & Seawater Treatment.
About Sulphur Dioxide as a Pollutant
|






