Their findings indicate that while the AMOC experienced natural fluctuations, it largely remained stable during this time i.e. Holocene Epoch.
- However, future projections suggest human-caused climate change could lead to an unprecedented weakening of the AMOC.
About AMOC
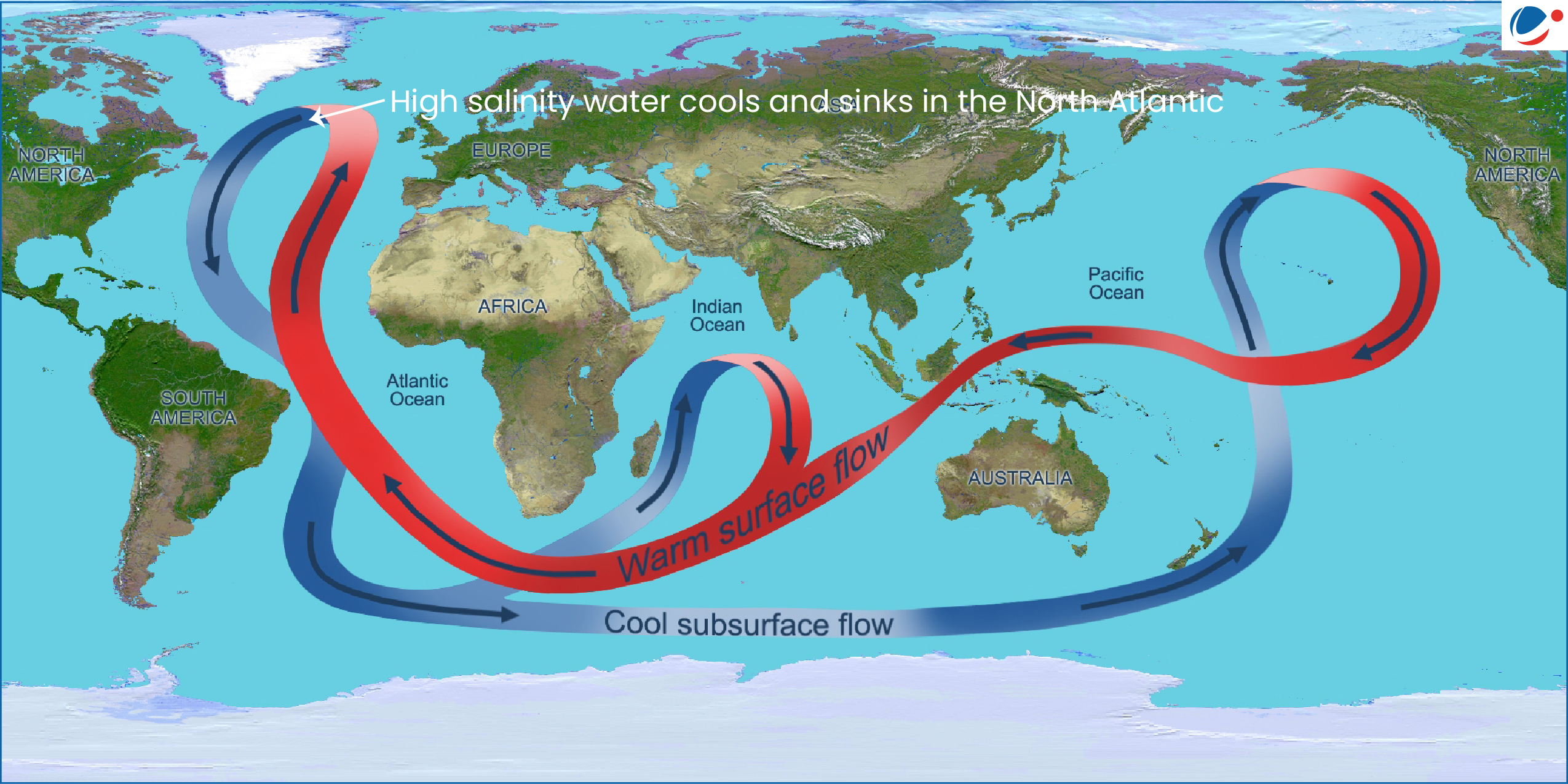
- A system of ocean currents that circulates water within the Atlantic Ocean, bringing warm water north and cold water south.
- Driving Force: Differences in water temperature and salinity.
- The warm tropical water moves towards the poles, becomes cool & dense, sinks in the North Atlantic and flows south before warming and resurfacing thus restarting the cycle.
- Significance:
- Weather and Monsoon: Influences rainfall patterns, including Indian monsoon and rainfall in Sahel region of West Africa.
- Heat Transport: From the tropics to higher latitudes, moderating Europe’s climate.
- Carbon uptake: It transports dense and carbon-rich water masses from the surface to the deep ocean.
- Concerns: Potential slowing down of AMOC due to increased influx of freshwater from melting Greenland ice sheet and Arctic amplification due to global warming.
- Freshwater reduces density of North Atlantic waters, hindering their ability to sink and drive the circulation.
Potential Impacts of AMOC Slowdown:
- AMOC carbon feedback: Reduction of ocean carbon uptake, which leads to more atmospheric CO2 and more global warming.
- Extreme events: E.g. Colder temperatures in Europe, Could shift South Africa’s rain belt (triggering droughts for millions), Sea level rise (e.g. across the U.S. East Coast).
- Fewer nutrients transport: Could affect all kinds of sea life, from plankton and sea birds to fish and whales.






