The report released by the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) under the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy provides a policy-linked, investment-ready framework to guide project siting, infrastructure development, and private sector participation.
- The report aims at realizing India’s Panchamrit commitments, support goals of energy independence by 2047 and net-zero emissions by 2070.
Key Highlights of the Report
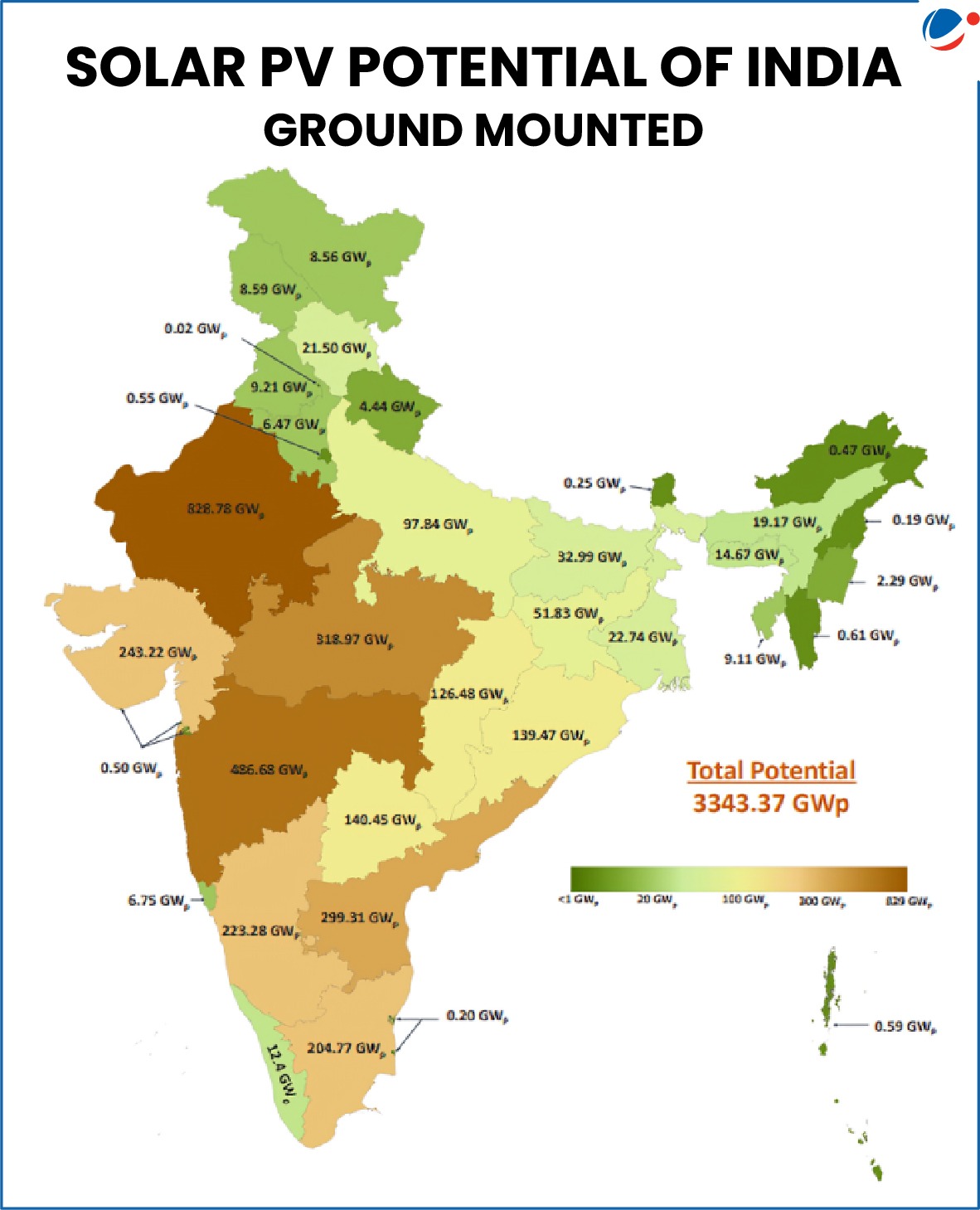
- Updated National Solar Potential Assessment: To approximately 3,343 GWp from 749 GWp in 2014.
- Geographic Distribution: Other than Rajasthan and Maharashtra, many other states too have very high potential. (Refer image)
- Approximately 6.69% of the total identified feasible wasteland in the country can be utilized.
Challenges to full realization of solar energy in India
- Land Acquisition: Large-scale solar parks require significant land, often in ecologically sensitive or agriculturally important areas.
- E.g. Rajasthan and Gujarat face conflicts over grazing land and biodiversity-rich desert ecosystems.
- Grid Integration: Lack of affordable large-scale energy storage technologies limits the integration of weather- dependent solar power.
- High Initial Capital Cost: Despite declining module prices, upfront project costs remain high.
- Other: Financial stress in DISCOMs; Import dependency for solar modules (~80% from China); policy and regulatory uncertainty, shortage of skilled workforce, etc.
Initiatives Launched
|






