The report is based on the Global Gender Gap Index (GGGI) which annually benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity based on 14 indicators across four key dimensions.
Key findings
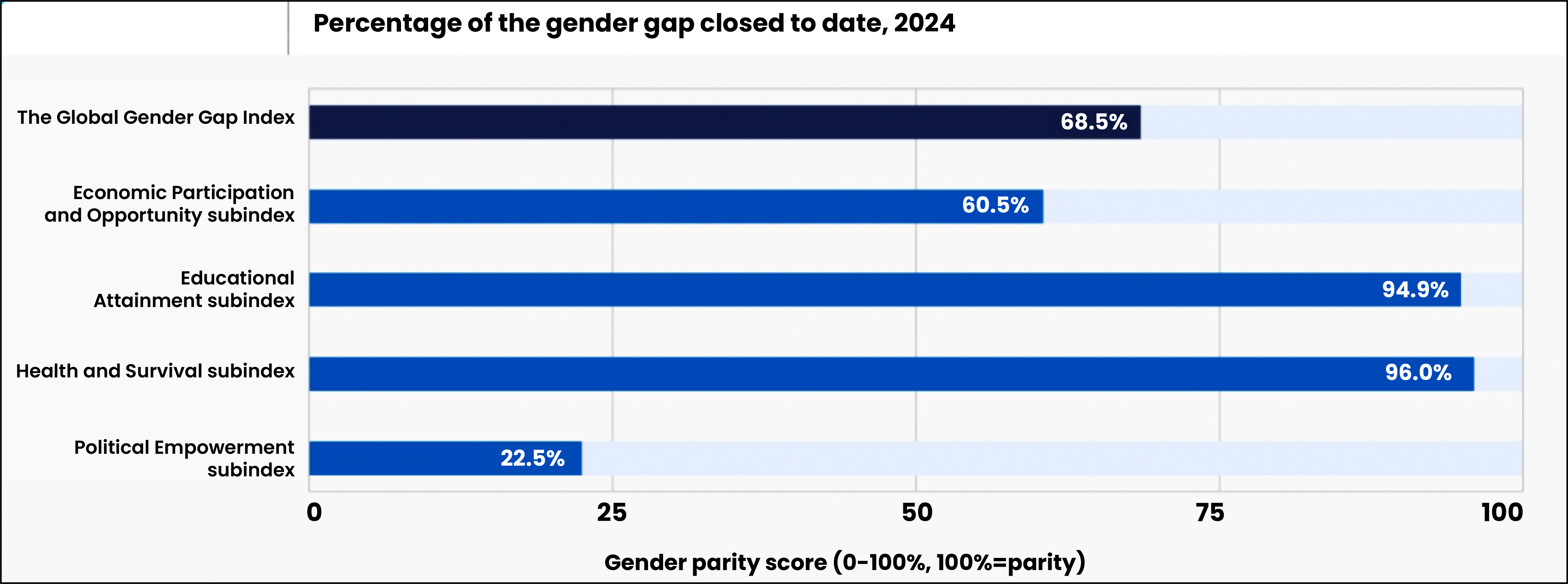
- Global
- Among 146 countries, Iceland, Finland, Norway, New Zealand, and Sweden are the top five countries.
- The share of women in parliamentary positions has shown an almost uninterrupted positive trajectory since 2006.
- At the current rate of progress, it will take 134 years to reach full parity.
- Women constitute 28.2% of the STEM workforce and 47.3% of the non-STEM workforce.
- India
- Overall, India was ranked 129th (ranked 127 in 2023), and 5th in South Asia after Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and Bhutan.
- Saw small declines in Educational Attainment and Political Empowerment while Economic Participation and Opportunity slightly improved.
- Shares of women are high in primary, secondary and tertiary education enrolments.
Recommendation
- Achieving gender parity by 2030 would require a collective investment of $360 billion per year.
- Targeted interventions and ensuring equitable access to emerging technological competencies are needed.
- Businesses need to have effective diversity, equity and inclusion policies and upskilling.
NOTE: Gender Inequality Index (GII), released by UNDP, is also a composite metric of gender inequality based on three dimensions: reproductive health, empowerment and the labour market.






