SC in the Nandini Sundar & Ors. Vs. State Of Chhattisgarh, held that enacting a law by legislature contradictory to previous Court orders cannot be viewed as CoC.
- The court further held that a legislature has the powers to remove the basis of a judgment or, validate through an amendment a law which has been struck down.
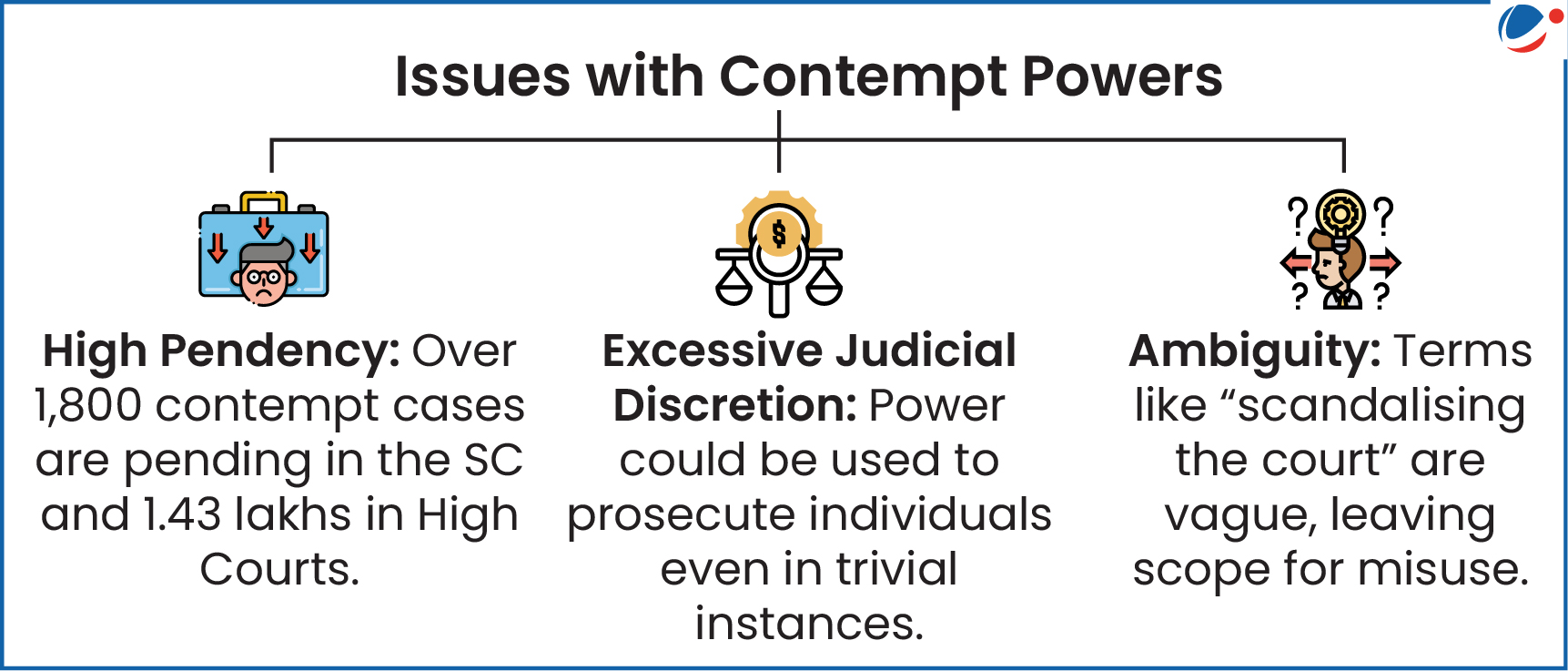
About Contempt of the Court
- Meaning: It refers to disobeying or disrespecting a court, lowering its authority and dignity.
- Legislative Framework: The Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 and the Rules to Regulate Proceedings for Contempt of the Supreme Court, 1975.
- Types of Contempt
- Civil Contempt: Wilful disobedience of court orders or undertakings.
- Criminal Contempt: Publishing or doing anything (spoken, written, signs, etc.) that:
- Scandalises or lowers court’s authority .
- Prejudices or interferes with any ongoing proceedings
- Obstructs the administration of justice in any manner.
- Major Exceptions (Contempt of Courts Act, 1971): Innocent publication; fair and accurate reporting of judicial proceedings; fair criticism of the judicial act, etc.
Related Constitutional Provisions
|






