This is the first dual frequency Radar Imaging mission marking a major milestone in Indo-US space collaboration.
About NISAR
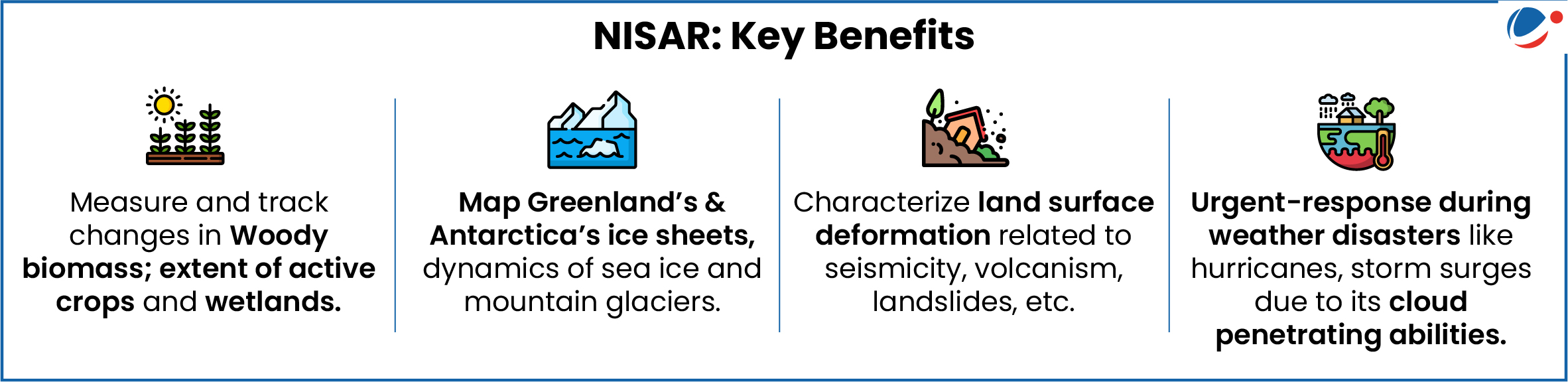
- Earth Observation Satellite (EOS): Images global land and ice-covered surfaces including islands and selected oceans every 12 days (orbits Earth every 97 minutes).
- Weight: 2,392 kg.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)-F16.
- Placing Orbit: Sun Synchronous Polar Orbit.
- It is the first time a GSLV rocket is used to place a satellite into Sun-Synchronous orbit.
- GSLV is typically used for placement in Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit/GTO (35 786 km).
- It is the first time a GSLV rocket is used to place a satellite into Sun-Synchronous orbit.
- Key Features
- Built around ISRO’s I-3K spacecraft bus.
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): Dual band SAR operating on both L (by NASA) and S (By ISRO) bands.
- SAR sends out a pulse of energy and then records the energy reflected back after its interaction with Earth creating high resolution images through radar motion.
- Processes radar signals received from different positions along the path, creating a larger "synthetic" aperture.
- SweepSAR technique: For high-resolution, wide-swath images across broad range of terrain.
- Expected Mission Life: At least 5 years.
- Open-Data Policy: Information collected will be freely available to global scientific community benefiting developing countries.
About Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO) and Polar Orbit
|




