Produced by UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC), the report highlights progress made since the launch of Global Methane Pledge.
Key Highlights of the Report
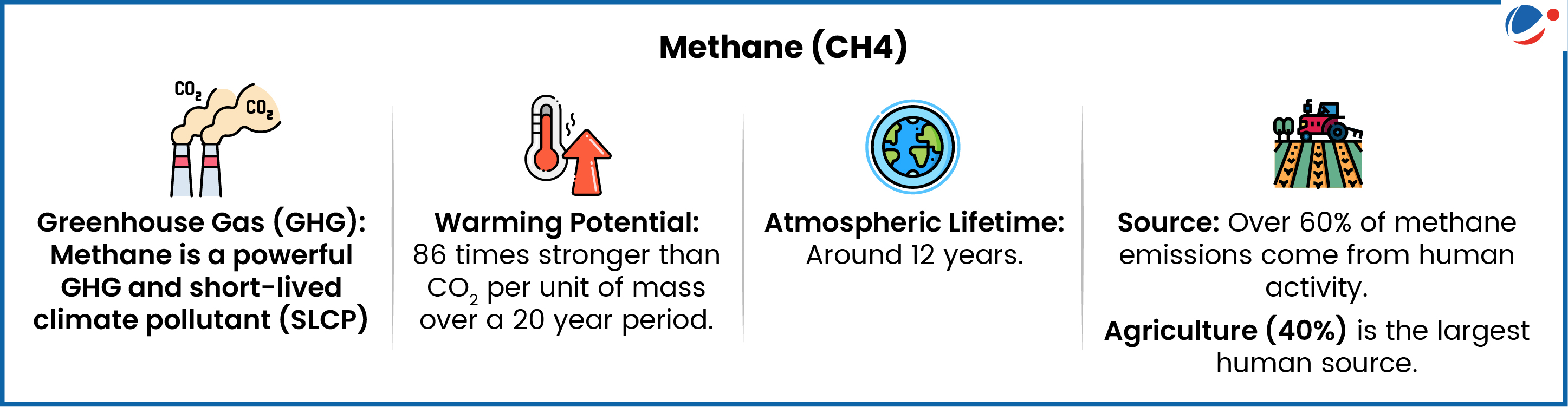
- Methane’s atmospheric Concentrations: More than doubled since pre-industrial times reaching approximately 352 million tonnes (Mt) per year in 2020 and is expected to rise further by 5% by 2030.
- Impact of Rising Global Emissions: Contribute to 24,000 additional premature deaths and 2.5 Mt of crop losses annually by 2030 relative to 2020.
- Case of India: India is the world’s third-largest methane emitter (primarily driven by Stubble burning) after China and the United States, producing around 31 million tonnes a year.
Major Initiatives taken to tackle Methane Pollution
Global
- Global Methane Pledge (GMP): Voluntary framework to reduce methane emissions by 30% from 2020 levels by 2030. (Not signed by India)
- Launched on the sidelines of COP26 (Glasgow) in 2021 by Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC).
- International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO): Led by UNEP.
India
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Technologies for Mitigation of Methane Pollution from Rice: System for Rice Intensification; Direct Seeded Rice (does not maintain standing water while transplanting paddy); Crop Diversification Programme, etc.







