This is the first time that boot-strap mode starting of a gas-generator cycle cryogenic engine is being done without any auxiliary start-up system enhancing the restart capability and mission flexibility of future LVM3 flights.
- Currently, it required an additional start-up gas bottle and associated systems, leading to a reduction in vehicle payload capability.
About Cryogenic Engines
- Meaning: Last stage of space launch vehicles which makes use of Cryogenics.
- Cryogenics involves the study of production and behaviour of materials at extremely low temperatures (below -150 degree C).
- Propellants Used: Liquid Hydrogen and liquid Oxygen.
- Significance: More efficient and provides more thrust for every kilogram of propellant burned.
- Earth storable liquid and solid propellants used in liquid and solid stages are less efficient and gives small payload advantage.
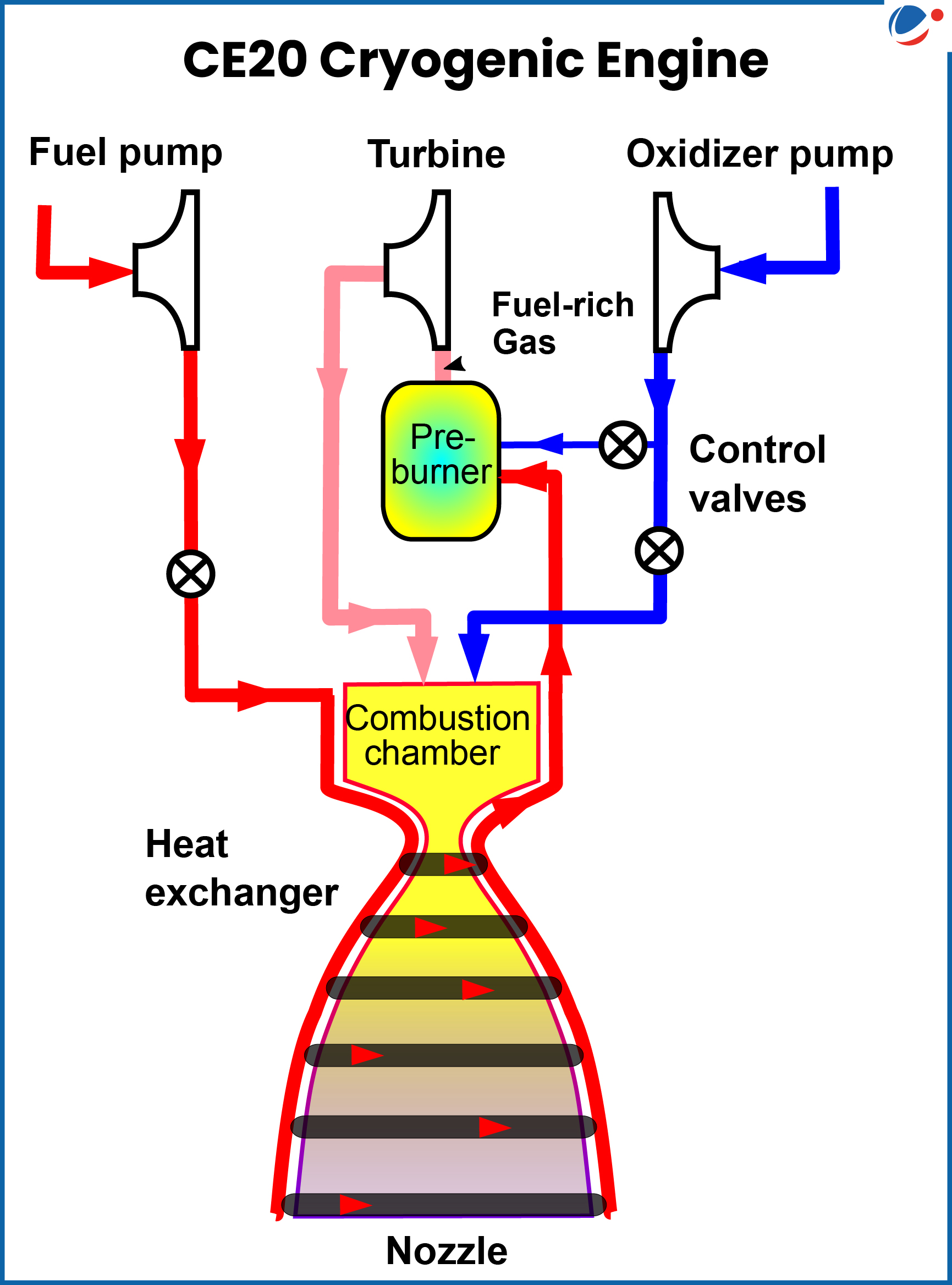
- CE20: India's largest cryogenic engine developed by Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre, Valiamala, Kerala.
- CE20 Cryogenic Engine powering the LVM3 upper stage, has been qualified for Gaganyaan missions.
About LVM3
- New heavy lift launch vehicle of ISRO for achieving a 4000 kg spacecraft launching capability to GTO (Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit).
- Three Stages Involved:
- Two solid propellant S200 strap-ons.
- The liquid L110 stage.
- Largest liquid Stage realized by ISRO.
- Core Stage of GSLV-Mk III which uses two high thrust Vikas engines.
- Recently, Godrej Enterprises delivered the first human-rated L110 stage Vikas engine for Gaganyaan project to ISRO.
- C25 cryogenic stage: Powered by CE-20 Engines.





