Why in the News?
Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) has sought public comments on the proposed Draft Guidelines on Prevention and Regulation of Greenwashing issued under Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
More on the News
- Green washing involves making a product or policy seem more environmentally friendly or less damaging than it is in reality
- Key highlights of the draft guidelines
- Defines and also prohibit greenwashing.
- Applicability: Applies to all advertisements, service providers, advertisers, endorsers, etc. whose service is availed for the advertisement.
- Information disclosure: Prohibits selective presenting of data and calls for fully disclosing environmental claims including vague terms like 'green', 'eco-friendly', 'eco-consciousness' used in advertisements.
- Verification of claims: Requires substantiating environmental claims with credible certification, reliable scientific evidence, and independent third-party verification.
- Conditions for futuristic environmental claims: Mandates making of futuristic environmental claims only when clear and actionable plans have been developed for achievement of objectives.
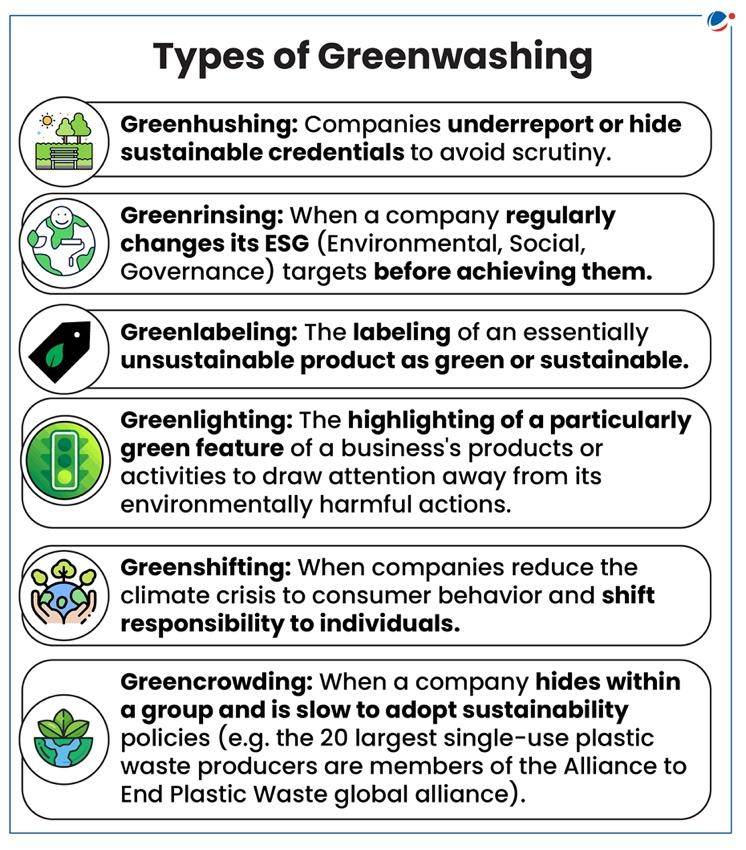
Need for regulating green washing
- Erosion of Public Trust: Deceptive marketing and false claims of sustainability. Also making it difficult to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Example, in 2015, the US Protection Agency exposed Volkswagen for using software to manipulate emission tests in its Clean Diesel cars.
- Obstacle in tackling climate change: False environmental claims delay the genuine solutions to the climate change, while also making consumers to choose for the unsustainable products.
- Impact on Innovation: Redirecting resources towards the appearance of environmental friendliness may come at the cost of innovation for substantial and lasting benefits.
Initiatives taken to prevent Greenwashing
- India
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): The BIS has developed a standard for eco-labelling of products and services called IS/ISO 14024:1999.
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: Establishes Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) to regulate matters relating to violation of rights of consumers, unfair trade practices and false or misleading advertisements.
- Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI): The ASCI guidelines requires that advertisements making environmental/green claims be specific, accurate, and not misleading.
- Green Rating Project (GRP): GRP of the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) rates industrial units within a specific sector on the basis of their environmental friendliness.
- Indian Green Building Council (IGBC): The IGBC is a nonprofit organization that has developed a rating system for green buildings.
- Global
- UN’s High-Level Expert Group on Net-Zero Emissions Commitments of Non-State Entities: It was established in 2022 by the UN Secretary-General.
- Expert Group in its report ‘integrity matters’ outlined ten recommendations for accountable net-zero pledges by companies which included announcing Net Zero Pledge, setting Net zero target, creating a transition plan, etc.
- Greenwashing TechSprint: It was organized by the Global financial innovation network to develop a tool to help regulators more effectively tackle greenwashing in financial services. Reserve Bank of India was also one of the participants.
- UN’s High-Level Expert Group on Net-Zero Emissions Commitments of Non-State Entities: It was established in 2022 by the UN Secretary-General.
Way-Forward
- Increase transparency and accountability: Annual publication of each organization’s greenhouse gas emissions alongside baseline data and Third-Party certification.
- Media Campaigns and Consumer Awareness: Understanding the common greenwashing tactics is crucial to recognizing and avoiding greenwashing.
- Harness new technologies: AI, natural language processing, Machine Learning can increase speed and intelligence of tackling greenwashing while also measuring impact of a project.
- Cross-border cooperation and collaboration: Collaboration between companies, governments, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders can help to promote sustainability and reduce Greenwashing.
- Phase out fossil fuels and scale up renewable energy: Will lead to real environmental benefits and achieving just transition.





