Why in the News?
Neuralink, an Elon Musk company has successfully installed a wireless brain-computer interface (BCI) implant in a human patient.
More about News
- In 2023, Neuralink was granted permission by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human trials.
- It aims to build a next-generation brain implant with at least 100 times more brain connections than devices currently approved by FDA.
- Initial results of trial showed promising neuron spike detection.
- Spike refers to use electrical and chemical signals to send information around the brain and to the body.
- Neuralink also announced that their first product will be named Telepathy.
About Brain–Computer Interface (BCI)
- It is a system that determines functional intent - the desire to change, move, control, or interact with something in our environment - directly from brain activity.
- In other words, BCIs allow controlling an application or a device using only our mind.
- Using a BCI skips over the need to have voluntary control of your muscles to interact with devices around you. It replaces the execution of a physical movement.
- It has three main parts:
- A device to detect and record signals coming from the brain.
- A computer to process and analyze the recorded brain activity.
- An application/device to control.
- Another important part of a BCI is feedback: The system must somehow let the user know what decision or intended action the computer was able to interpret.
- Types of BCIs:
- Non-Invasive: In it, sensors are placed on the scalp to measure the electrical potentials produced by the brain.
- E.g. Electroencephalography (EEG), Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) etc.
- Semi-invasive: The electrodes are placed on the exposed surface of the brain.
- E.g. Electrocorticography (ECoG) which is the process of recording electrical activity in the brain by placing electrodes in direct contact with the cerebral cortex or surface of the brain.
- Invasive: Chips/Sensors are placed directly into the cortex, measuring the activity of a single neuron.
- E.g. Neuralink’s Implant.
- Non-Invasive: In it, sensors are placed on the scalp to measure the electrical potentials produced by the brain.
About Telepathy
|
Applications of BCI
- Helping people with physical disabilities and ageing: BCIs can enable precise control of prosthetic limbs, giving amputees natural motor skills. It can also help older people train their motor and cognitive abilities.
- Treatment for diseases: Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy and spinal cord injuries etc. can be treated.
- Facilitate brain research: Scientists could use BCIs to improve understanding of the brain. Some researchers have used a BCI to detect the emotions of patients in a vegetative or minimally conscious state.
- Improving human performance: BCIs can now be used as a neurofeedback training tool to improve cognitive performance, augment human capabilities and human-computer interactions.
- BCI could be used to affect alertness and to improve subjects’ performance in a cognitively-demanding task.
Concerns related to BCI
- Technical and user challenges: Each person generates unique brain signals, which are difficult to measure clearly. Also, Translation of brain signals to speech by a BCI could cause harm if it is not accurate.
- Data Privacy and Security: BCIs are vulnerable to cyberattacks as hackers could use malware to intercept brain-wave data generated by the device.
- Social impact: Reported costs of wearable BCIs range from hundreds to thousands of dollars, which may result in unequal access.
- Ethical issues: BCIs may raise questions about what constitutes consent and about potential unfair advantages conferred by certain human enhancements.
- Medical issues: Potential for implants’ tiny wires to migrate to other areas of the brain and thus may unintentionally influence other brain functions, or cause any unwanted side effects such as seizures, headaches, mood changes, or cognitive impairment.
Conclusion
Over the next few decades, BCI research and development is likely to continue to grow and we may see greater widespread use of BCIs in people's daily lives. Also, there is a need to improve the accuracy, reliability and efficiency of BCIs so as to realise its full potential.
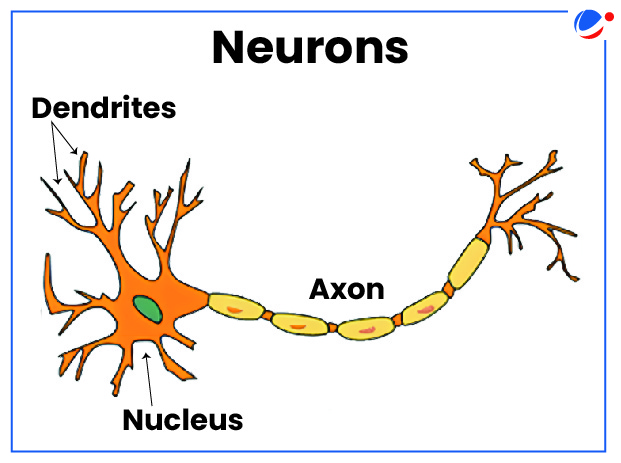 About Neurons
How neurons work?
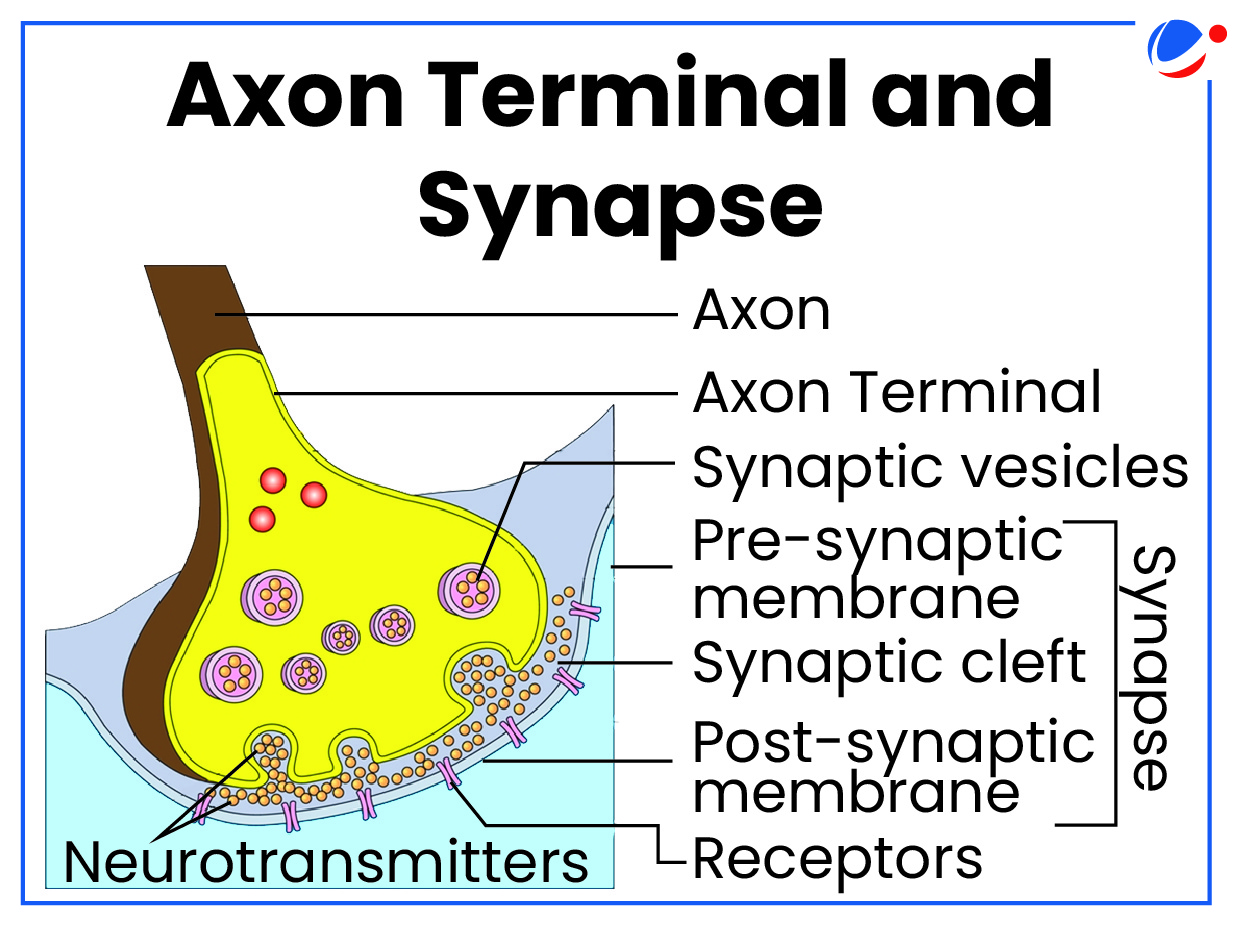
|




