- India’s Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) begins construction phase for contributions to Proton Improvement Plan (PIP-II) project.
- PIP-II is the first particle accelerator on U.S. soil (at Fermilab) to be built with significant contributions from international partners.
- Institutions from India, France, Italy, Poland and UK are part of collaboration. India will contribute $140 million worth components.
- It will power the world’s most high-energy neutrino beam to the under construction Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE) at Long-Baseline Neutrino Facility (LBNF).
- Particle accelerators propel charged particles (Protons, Atomic Nuclei, Electrons etc.) at high speeds, close to the speed of light.
- Accelerators feature four principal components – Source for producing particles, Composite device to speed them up, Metallic tubes in vacuum to allow free movement and Electromagnets to steer the beam particles.
- Some Large Particle Accelerators:
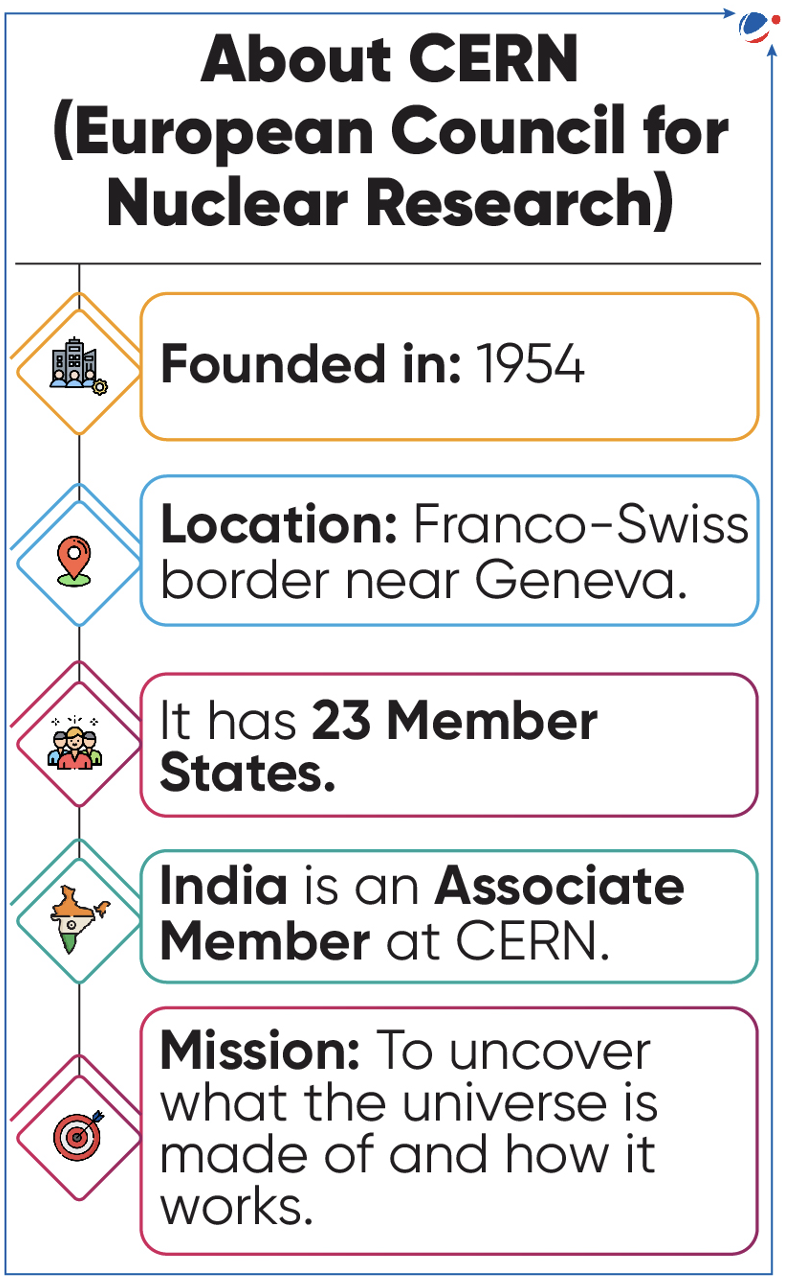
- Large Hadron Collider (LHC): Most powerful accelerator, located at CERN in Geneva. Significant achievements - discovery of Higgs Boson, previously unknown hadrons etc.
- Stanford Linear Accelerator Centre (SLAC), USA: Longest linear particle accelerator in the world. Significant achievements - discovery of quark and tau leptons.
- European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF): Located in Grenoble, France, and is home to most intense hard x-ray source in the world.

- In a first, CERN Scientists carry out LASER cooling of Positronium.
- An international team of physicists from Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved this breakthrough.
- AEgIS is one of several experiments at CERN’s Antimatter Factory with goal of direct measurement of Earth's gravitational acceleration (g) on anti-hydrogen.
- AEgIS is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- Positronium (Ps), discovered in 1951, is the lightest known atom, consisting only of an electron (e−) and a positron (e+).
- Ps has a very short lifetime, annihilating into gamma rays in 142 billionths of a second.
- Because it comprises just two point-like particles, the electron and its antimatter, it’s a perfect system for experiments under AEgIS, provided it can be cooled enough to measure it with high precision.
- Matter – Antimatter
- Matter comes in many forms—solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas - consisting of subatomic particles that give them mass and volume.
- Sub-atomic particles include protons and neutrons (also known as baryons), electrons and neutrinos (also known as leptons), and other particles.
- All subatomic particles either have their own anti-twins (antiquarks, antiprotons, antineutrons, and antileptons such as antielectrons) or straddle between matter and antimatter.
- Anti-particles can combine to form anti-atoms and, in principle, could even form anti-matter region.
- Matter comes in many forms—solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas - consisting of subatomic particles that give them mass and volume.
- ISRO successfully launched the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) funded INSAT-3DS weather forecasting satellite.
- GSLV-F14 placed INSAT-3DS into the intended geosynchronous transfer orbit and then to a Geo-stationary Orbit .
- It was launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota (Andhra Pradesh).
- INSAT-3DS Satellite
- It is a follow-on mission of Third Generation Meteorological Satellite.
- It will aid presently operational INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR which are dedicated meteorological geostationary satellites.
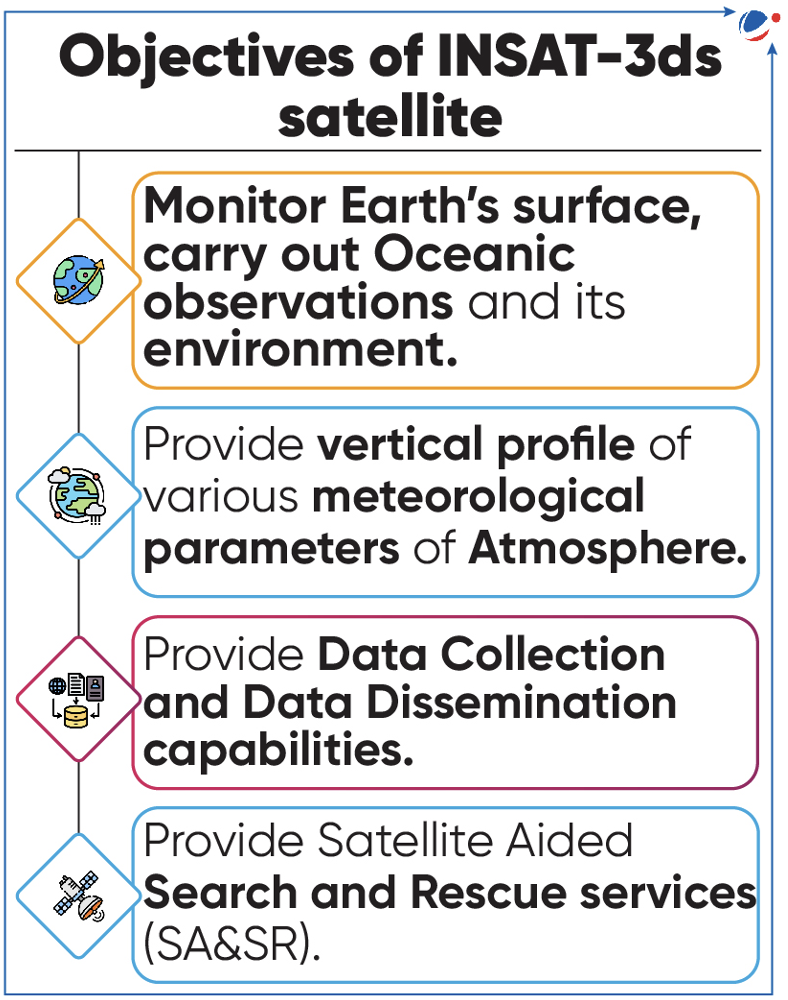
- Onboard payloads: Imager Payload, Sounder Payload, Data Relay Transponder, and SA&SR transponder.
- Indian Industries have significantly contributed to its making.
- GSLV-F14: GSLV-F14 is 16th flight of India’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) and 10th flight with Indigenous Cryogenic stage.
- GSLV is a three-stage launch vehicle having a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage comprises a solid propellant motor.
- Second stage comprises earth-storable liquid propellants.
- Third stage is a cryogenic stage.
- GSLV can launch spacecraft capable of performing communications, navigation, earth resource surveys, and any other proprietary mission.
- GSLV is a three-stage launch vehicle having a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO): Transfer orbits are a special kind of orbit used to get from one orbit to another.
- To attain geosynchronous (and also geostationary) Earth orbits, a spacecraft is launched into an elliptical orbit with an apoapsis altitude (point at which an orbiting object is farthest away from the body it is orbiting) of around 37,000 km. This is called a GTO.
- Geostationary orbit (GEO): Satellites in GEO circle Earth above the equator from west to east by travelling at the same rate as Earth.
- This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position.
- ISRO confirmed successful de-orbiting and atmospheric re-entry of Cartosat-2 at its end-of-life.
- About Cartosat-2
- Launched in 2007.
- Placed in Sun-synchronous orbit.
- Advanced remote sensing satellite capable of providing scene-specific spot imagery.
- De-orbiting of Cartosat-2: ISRO lowered its perigee (point in the orbit of a satellite at which it is nearest to the earth) using leftover fuel to comply with international guidelines on space debris mitigation.
- De-orbiting of Cartosat-2 represents a significant step for ISRO in ensuring long-term sustainability of outer space activities.
- Asteroids named Iris and Massalia (rich in silicate) were found to emit the unique wavelength that “unambiguously” indicated the presence of water molecules.
- Discovery was made by studying SOFIA's observations.
- SOFIA was NASA’s airborne astronomical observatory that was retired in 2022.
- Discovery was made by studying SOFIA's observations.
- Asteroids
- They are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun. They are much smaller than planets.
- Significance of water on asteroids
- Can shed light on how water was delivered to Earth.
- Could be helpful in search for extraterrestrial life.
- SpaceX has recently launched NASA’s PACE satellite to monitor ocean, atmosphere, and climate.
- PACE was placed in a sun-synchronous orbit, which means that it will always be synced to the same position relative to the Sun.
- Objectives
- Will help in understanding how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide.
- Will reveal how aerosols might fuel phytoplankton growth in the surface ocean
- Will contribute to new global measurements of ocean color, cloud properties, and aerosols.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is organizing a special program for School Children called "Young Scientist Programme" or YUVIKA.
- Key objectives:
- Impart basic knowledge on Space Science, Space Technology, and Space Applications to the younger students.
- Encourage more students to pursue Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) based research and aligned careers.
- Program envisages classroom training, practical demonstration of experiments, model rocketry interactions with ISRO scientists, and field visits.
- Eligibility: Students studying in Class 9 within India are eligible to apply.
- World Health Organisation (WHO) awards countries for progress in eliminating industrially produced trans-fatty for first time.
- WHO has awarded first-ever validation certificates to Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Saudi Arabia, and Thailand in eliminating industrially-produced trans-fatty acids iTFA.
- Total of 53 countries have now best practice policies in effect for tackling iTFA in food, improving food environment for 46% of world’s population.
- To be validated for trans-fat elimination, countries should demonstrate:
- A best-practice for iTFA elimination policy is in effect in country; and
- Applicant country has adequate monitoring and enforcement systems in place.
- WHO criteria for Best practices in iTFA elimination policies
- Mandatory national limit of 2 grams of iTFA per 100 grams of total fat in all foods;
- Mandatory national ban on production or use of Partially Hydrogenated Oils (PHO- major source of trans-fat) as an ingredient in all foods.
- Combination of PHO ban and iTFA 2% limit.
- Trans-fats are unsaturated fats produced from vegetable oils.
- There are two forms of trans-fat i.e. Naturally-occurring trans-fats (dairy and meat products), Industrially produced trans-fat (packaged foods, cooking oils etc.).
- They are source of non-communicable disease and associated with increased risk of heart attacks.
Steps taken to regulate TFA
|
- The initiative was earlier announced at the G20 Health Ministers meeting in India.
- The GIDH will be a WHO Managed Network of stakeholders to address challenges such as duplication of efforts and “products-focused” digital health transformation.
- GIDH Secretariat will be hosted in WHO Headquarters (Geneva).
- Objective:
- Align efforts to support of the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025
- Support quality technical assistance to develop and strengthen standards
- Facilitate the use of digital transformation tools.
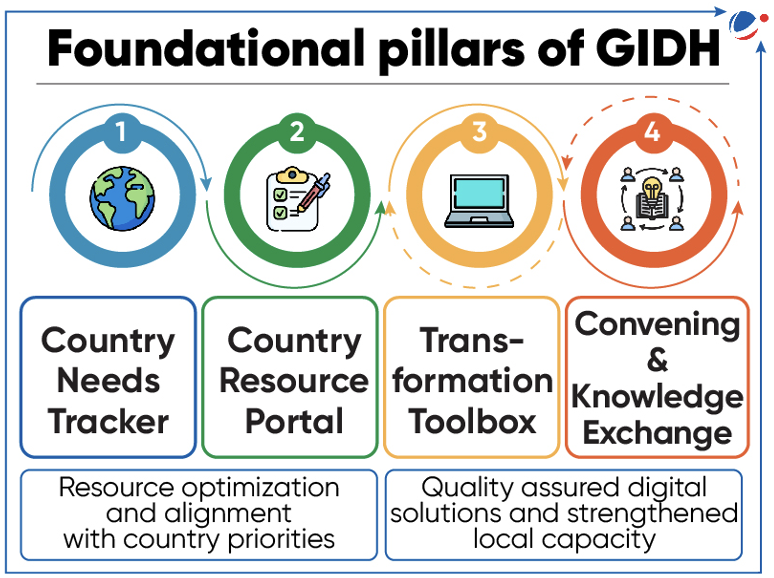
- Foundational Pillars of GIDH
- Country Needs Tracker to facilitate digital health investments
- Country Resource Portal to identify traditional as well as innovative resource opportunities
- Transformation Toolbox for quality-assured tools to strengthen country capacity to manage the national digital health transformation.
- Convening and Knowledge Exchange to promote strengthened collaboration and knowledge exchange
- Digital Health initiatives of India
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, launched in 2021
- It aims to establish a National Digital Health Ecosystem by creating an online platform enabling interoperability of health data within the health ecosystem
- Through components like Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) Number, Health Facility Registry, Healthcare Professionals Registry etc.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, launched in 2021
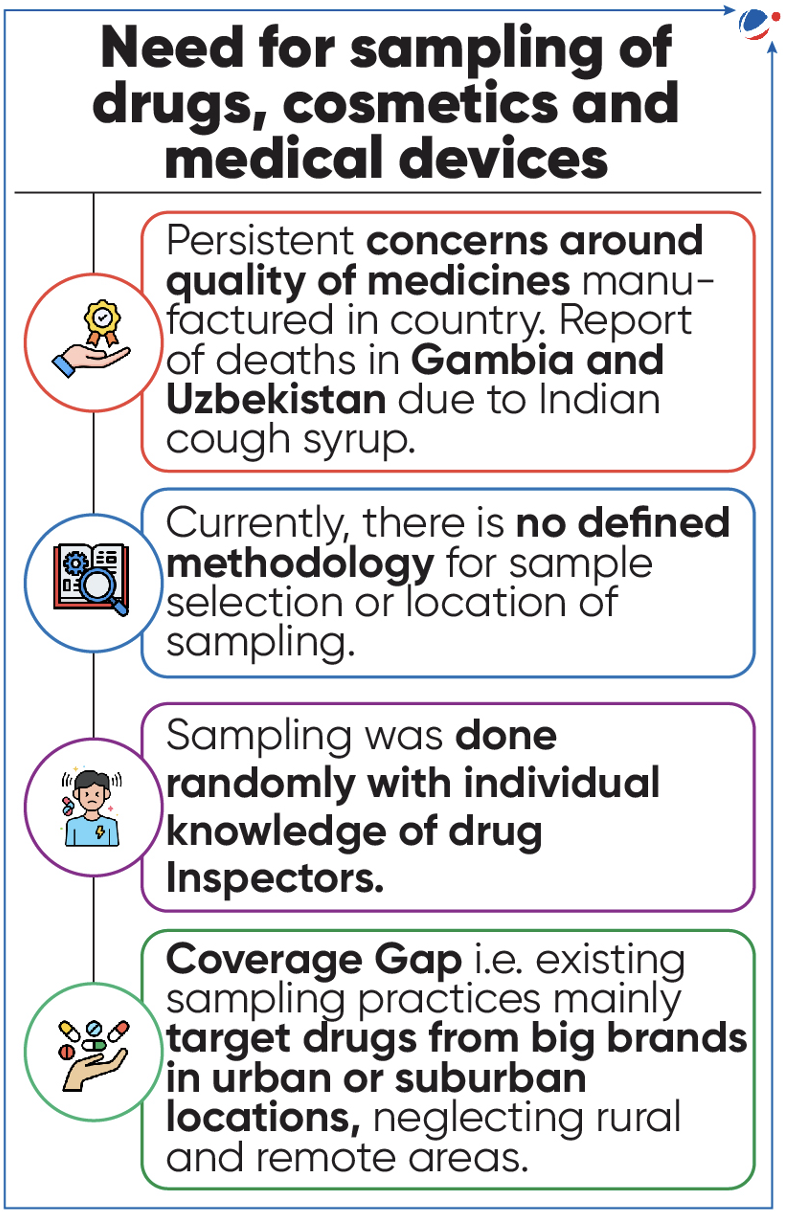
- Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) notified Regulatory guidelines for sampling of drugs, cosmetics & medical devices.
- CDSCO has issued new guidelines to ensure quality and efficacy of drugs and cosmetics by adopting uniform drug sampling methodology for drugs inspectors under drug regulatory authorities of state and central.
- Section 22 & 23 of Drugs & Cosmetics Act 1940 prescribes detail procedure for samples to be taken by Drugs Inspectors for routine drugs quality surveillance.
- Key highlights
- Establish a centralized database of outlets selling 'not of standard quality' or spurious drugs.
- Each drugs inspector with consultation of controlling authority shall prepare a sampling plan on monthly basis & annual basis for finalizing sampling locations to cover entire jurisdiction/ area under their office.
Drug regulation in India
|
- According to World Health Organization, world is near to eradicate GWD.
- About GWD (Dracunculiasis)
- It is an infection caused by parasite Dracunculus medinensis.
- Spread by drinking water containing Guinea worm larvae. Larvae are immature forms of worm.
- Affects people in rural, deprived, and isolated communities who depend mainly on open stagnant surface water sources like ponds.
- Also infections in animals, particularly in dogs, have been reported.
- It is one of the Neglected Tropical Diseases.
- There is no vaccine and drug to prevent the disease and treat patients.
- India successfully eradicated GWD in 2000.
- Sale of cotton candy has been banned in Tamil Nadu after samples reveal use of toxic industrial dye (Rhodamine-B) as artificial colouring agent.
- It is prohibited in the food industry by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- Rhodamine-B:
- Rhodamine-B is an organic chloride salt used as a colouring agent for dyeing in textile, paper, leather, and paint industry.
- Impact on human health:
- Immediate effect: Stomach fullness, itching, and breathing problems.
- Potential Chronic Health Effects: Liver dysfunction, Intestine cancers, neurotoxicity, and Kidney failure.
- India hit target towards eliminating Kala Azar for the first time in 2023 by reporting less than one case per 10,000 population across all blocks.
- About Kala Azar
- It is also known as Visceral Leishmaniasis and is a protozoan parasitic disease.
- Causing agent: Infected female phlebotomine sandfly.
- Symptoms: Irregular fever, weight loss, enlargement of the spleen and liver, and anaemia.
- The disease is endemic in Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
- Areas infected: Brazil, East Africa, and India.
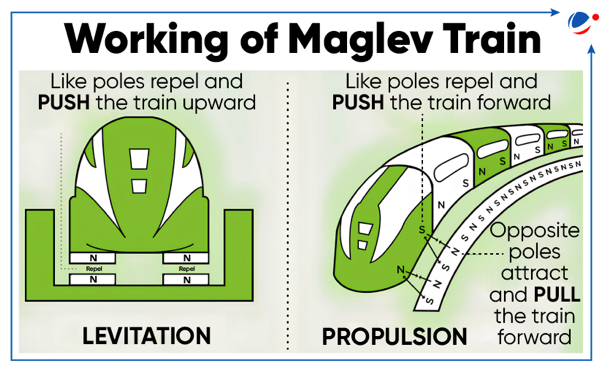
- In a significant breakthrough, China’s maglev train surpassed its previous record of 623 km/h.
- Maglev is a system in which the vehicle runs levitated from the guideway (corresponding to the rail tracks of conventional railways).
- In Maglev, superconducting magnets suspend the train above a U-shaped concrete guideway.
- Like ordinary magnets, these magnets repel one another when matching poles face each other.
- Advantages
- Produce no emissions as they lack engine.
- No friction between wheels and rail enables higher speeds
- Any two trains travelling the same route cannot catch up and crash into one another.
- Goa-based National Institute of Oceanography has launched an autonomous underwater vehicle called C-bot.
- C- bot is a robot with advanced features for increased surveillance over coral reefs.
- It can travel to a depth of 200 metres underwater.
- It will help Indian Navy perform bathymetry studies (mapping of sea floor) to help plot navigation channels.
- It will help in finding the active hydrothermal vents where geothermally heated water seeps up from deep below the ocean floor.
In January 2024 Monthly Magazine in Article 7.11.1 Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO) Project, there was misplaced box on “Steps taken in India” in the article. Kindly ignore this box for the article.



