Why in the News?
Recently concluded 2024 General Elections of Lok Sabha resulted in formation of a coalition government at the centre as no political party got a clear majority in the Lower House of the Parliament.
About Coalition Government
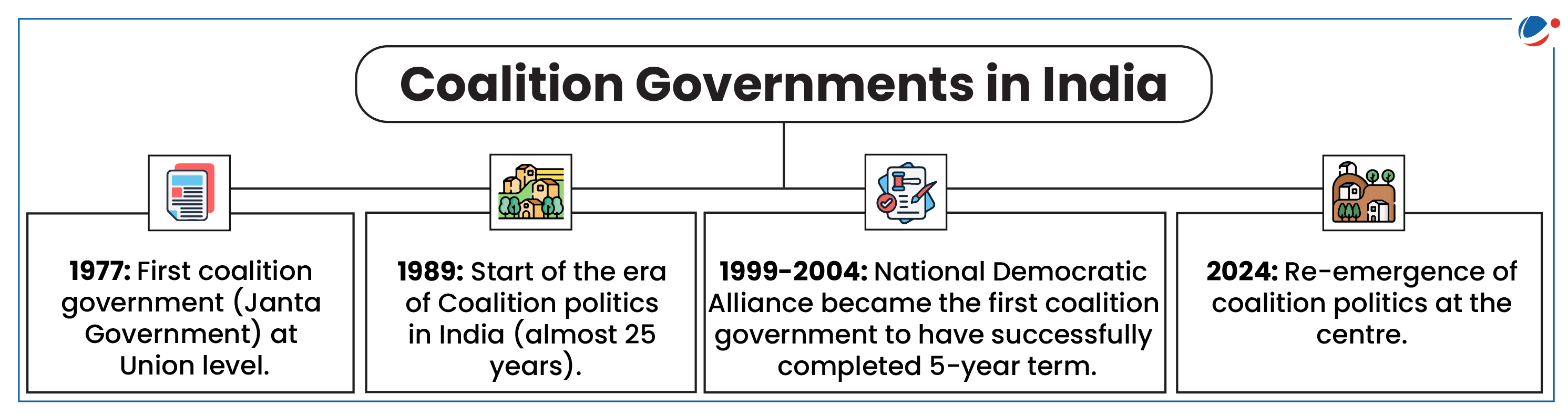 |
Significance of Coalition Government
- Broader representation: Coalitions often represent a wider range of interests and regions, potentially leading to more inclusive policies and programmes.
- Checks and balances: Coalition partners can act as a check on each other, potentially reducing the risk of authoritarianism and hasty policy decisions.
- Consensus building: Coalitions necessitate negotiation and compromise, potentially leading to more widely accepted policies.
- Role of Lok Sabha: Coalition governments result in more vibrant and substantive debates in the Lok Sabha, increased accountability of government.
- Cooperative federalism: Coalition governments have often included regional parties resulting in increased bargaining power of states and decentralized approach to governance.
Challenges due to Coalition Government
- Political instability: Divergent interests of coalition partners can lead to frequent disagreements and government instability. e.g., Fall of first NDA government in 1998 after just 13 months.
- Policy paralysis: Decision-making can be slow due to the need for consensus among coalition partners.
- e.g., Withdrawal of support by Left parties from the UPA-I government over Indo-US nuclear deal in 2008.
- Myopic decision-making: Frequent changes in coalition dynamics can result in hindering the implementation of long-term strategies.
- e.g., Frequent changes in the Human Resource Development Ministry during the 2004-2014 led to inconsistent policies in the education sector.
- Compromise on ideologies: Political parties may have to dilute their core ideologies to maintain the coalition.
- Regionalism: Regional parties in coalitions often leverage their position to push for state-specific benefits, allocation of resources to satisfy regional allies, etc.
- Foreign policy: Coalition dynamics can influence foreign policy decisions, particularly regarding regional issues.
- e.g., Stalled decision on Teesta Water Agreement in 2011.
Way Forward
- Political stability: Amend the Rules of Procedure of the Legislatures for adoption of a system of constructive vote of no confidence. (NCRWC)
- Constructive vote of no-confidence means motion of no-confidence should be accompanied by a proposal of alternative Leader to be voted simultaneously.
- If one or more parties in a coalition realign midstream with one or more parties outside coalition, then members of that party/ parties shall seek fresh mandate from electorate. (ARC-II)
- Election of Prime Ministers: Provide for a mechanism for election of the Leader of Lok Sabha, along with the election of Speaker, under the Rules of Procedure who may be appointed as the Prime Minister. (NCRWC)
- Transparency in functioning of coalition: Mandate regular public reporting on the progress of Common Minimum Program implementation and introduce 'coalition impact assessments' for major policy decisions.
- Long-term policy strategies: Use of constitutional bodies like Inter-State Council and non-partisan bodies like NITI Aayog in national policy formulation that transcends coalition politics.







