Why in the news?
On January 1, 2025, National Institute for Transforming India (NITI) Aayog celebrated its 10th year of foundation.
About NITI Aayog
|
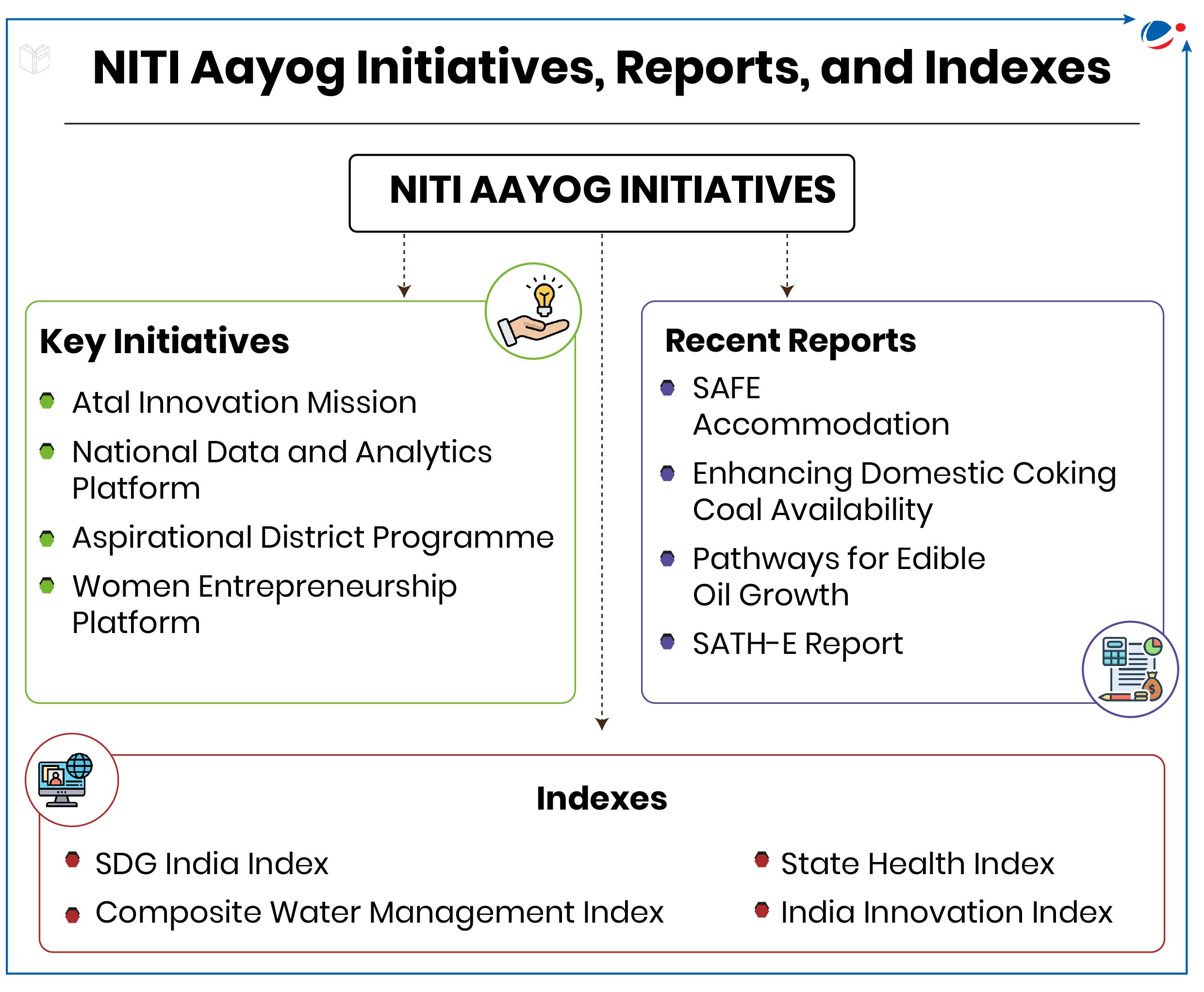
Achievements of NITI Aayog
- Enhanced cooperative federalism: Aayog served as a linking bridge between central and state governments, fostering collaboration to align regional priorities with national goals.
- E.g., NITI Aayog's 'Team India Hub' involves all states to work towards a national development agenda.
- Another example is the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) that aims to quickly and effectively transform 112 most under-developed districts across the country. NITI Aayog works closely with the respective line Ministries and various development partners to fast-track progress at the district level.
- Strengthened competitive federalism: Encouraged healthy competition among the states through data-driven and transparent indexes and ranking systems.
- E.g., Fiscal Health Index, Aspirational District Programme, Composite Water Management Index, State Energy and Climate Index etc.
- Governance and policy advice: As a think tank, Aayog advised on long-term strategic policies and shifted its focus from financial allocation (priority of erstwhile Planning Commission) to policy advisory, thus promoted decentralized governance approach.
- E.g., It assisted several states in setting up of State Institutions of Transformation (SITs) for better governance and policy implementation.
- Inculcated innovation, entrepreneurship and digital transformation: Through initiatives like Atal Innovation Mission (Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centre etc.), Knowledge and Innovation Hub, National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP), roadmap for digital payments etc.
- Regional and inter-sectoral social interventions: E.g., NITI Forum for North East, SATH-E initiative, Poshan Abhiyan, State Health Index, School Education Quality Index etc.
- Sustainable Developments Goals (SDGs) monitoring: Tasked with monitoring and adoption of SDGs in India, Aayog played a crucial role in synchronizing nation's developmental programs in line with the targets. E.g., SDG India Index.
Conclusion
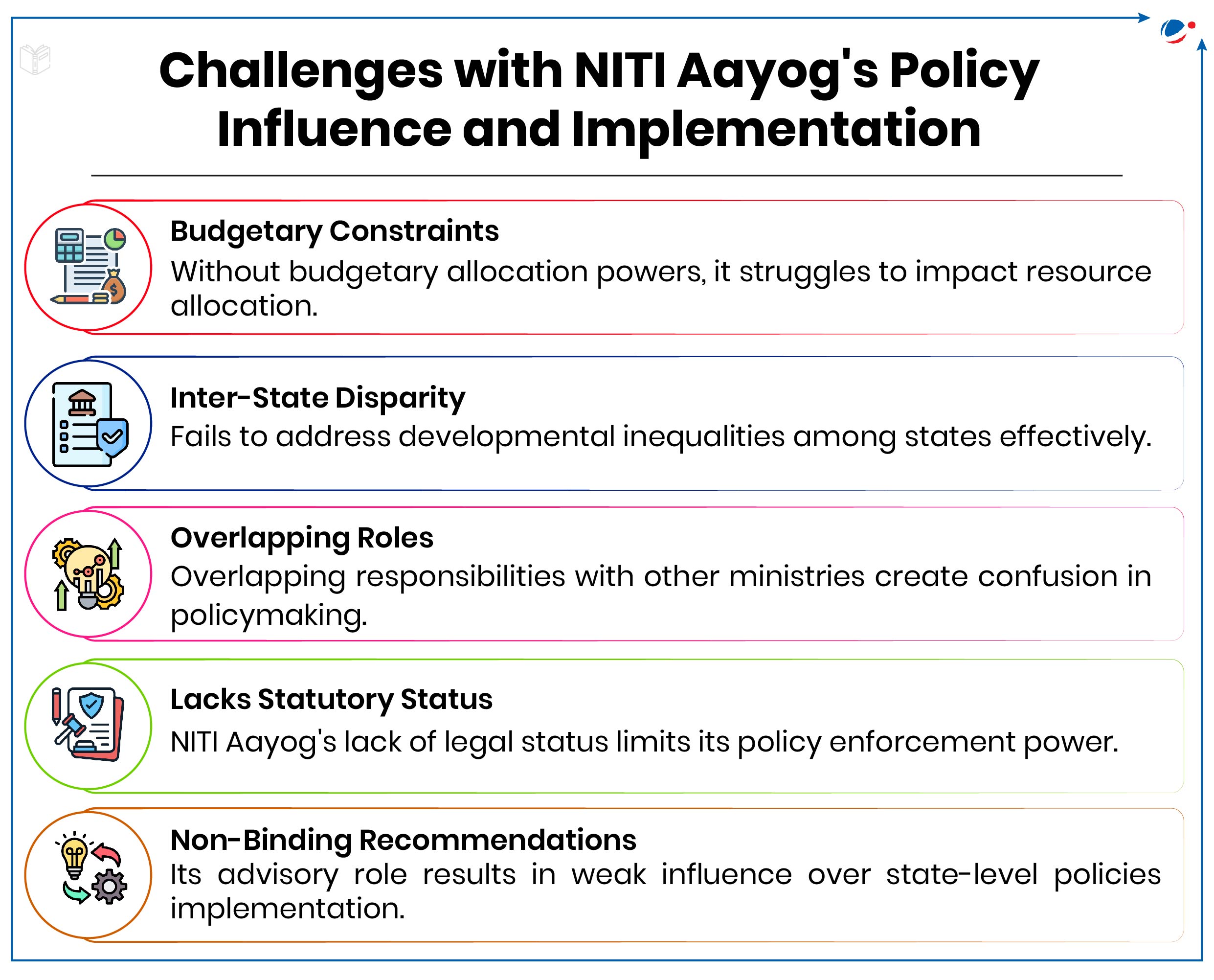
NITI Aayog has played a crucial role in shaping India's policy landscape through cooperative federalism, strategic planning, and fostering innovation. However, its effectiveness is constrained by several limitations. To enhance its impact, NITI Aayog must evolve into a more empowered institution with greater financial autonomy, resource allocation and stronger policy enforcement mechanisms, ensuring better coordination between the states and with states and the center.







