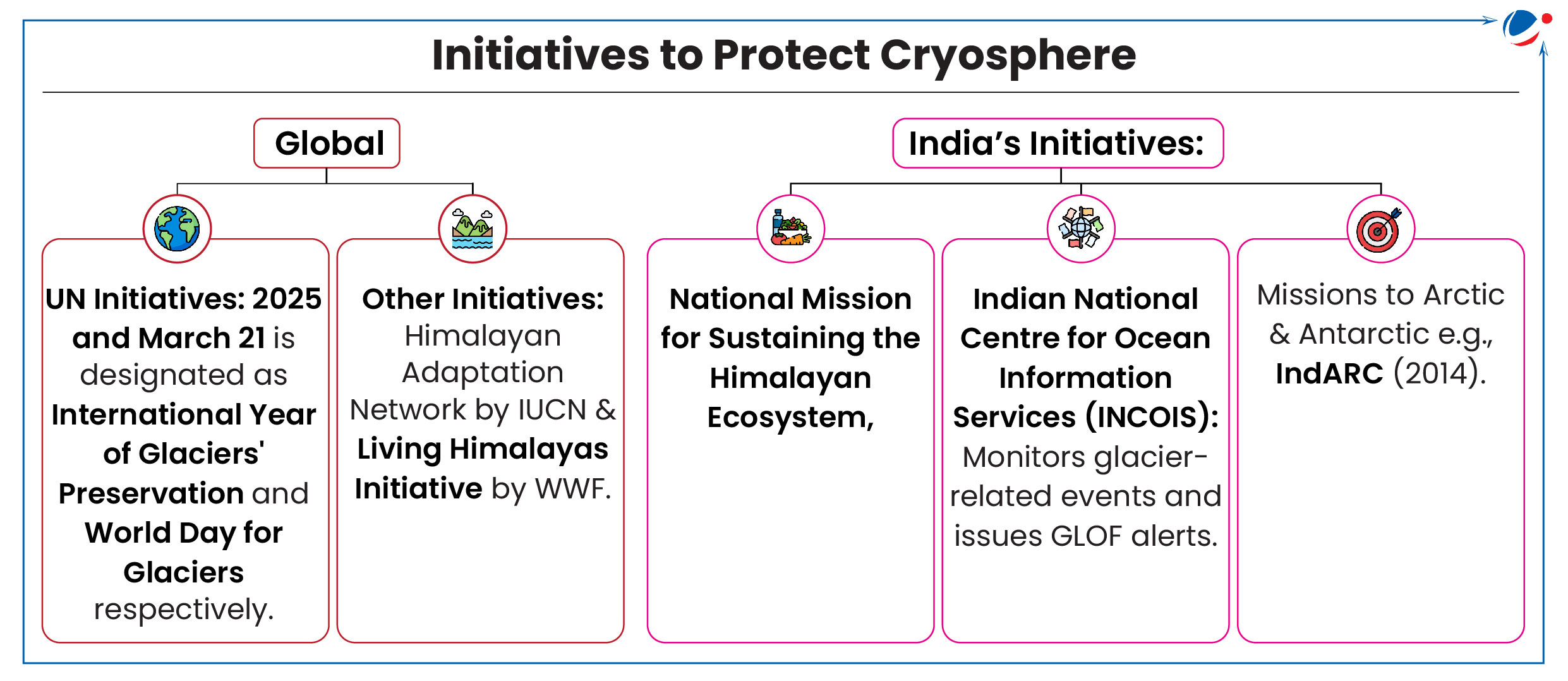
Recently, UN has declared 2025 as the International Year of Glaciers' Preservation.
- It was also announced that March 21 of each year will be celebrated as World Day for Glaciers, starting in 2025.
About International Year of Glaciers' Preservation
- Co-facilitated by: UNESCO and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Objective: To raise global awareness about the critical role of glaciers in the climate system and the hydrological cycle, and the economic, social and environmental impacts in the Earth’s cryosphere.
- Significance of Glaciers: There are more than 275 000 glaciers in the world, covering an area of around 700,000 sq. kms, which account for ~70% of the global freshwater.
The Yala glacier (Nepal) retreated by 680m and witnessed significant reduction in area (36%) between 1974 and 2021.
- It is the only glacier in entire Himalayas to be included in the Global Glacier Casualty List (GGCL) which highlights accelerating impact of climate change on Himalayan glaciers/cryospeher.
- The cryosphere is the frozen part of the Earth, including snow, ice, and frozen ground.
- The GGCL project was launched in 2024 by Rice University, University of Iceland, Iceland Glaciological Society, World Glacier Monitoring Service, & UNESCO.
About Glacier Retreat
- Glacier retreat is the process by which glaciers shrink in size & mass due to melting, evaporation, and other causes.
- Glaciers Already Lost: Pico Humboldt Glacier, Venezuela (2024), Sarenne Glacier, France (2023).
- Dagu glacier in China is expected to disappear by 2030.
Impact of Melting Glaciers/Cryosphere
- Disruption of Ecosystem & livelihoods: Glaciers and ice sheets hold approximately 70% of the world’s freshwater, essential for ecosystems & human life.
- e.g., 240 million people in the Hindu Kush Himalaya rely on the cryosphere for survival.
- Increased Risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Rapid glacier melting creates unstable glacial lakes that can breach, causing catastrophic floods.
- Climate Feedback Loop: Melting glaciers reduce Earth's reflectivity (albedo), absorbing more heat & accelerating global warming.
BUR-4 updates the Third National Communication (TNC) and contains the National Greenhouse Gas (GHG) inventory for the year 2020.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change is India's nodal ministry for managing and coordinating climate change activities and reporting under Article 4.1 of UNFCCC.
Key Highlights of report
- GHG emissions: It has decreased by 7.93% in 2020 compared to 2019.
- Sector wise Emissions: Energy ( 75.66%)> Agriculture( 13.72%)>Industrial Process and Product Use (8.06%)>Waste (2.56%).
- Emission Intensity of GDP: It has reduced by 36% (Between 2005 to 2020)
- Share of non-fossil sources: It constitutes 46.52% of installed electricity generation capacity (October 2024)
- Generation of Carbon Sinks: An additional carbon sink of 2.29 billion tonnes of CO2 have been created through forest and tree cover (2005 to 2021)
- Forest and tree cover: It currently stands at 25.17% of the country's total geographical area and has consistently increased

Notification, amending the Environment Relief Fund (ERF) Scheme 2008, has been issued in exercise of powers conferred under Section 7A of Public Liability Insurance Act (PLIA), 1991.
- Section 7A of PLIA provides for establishment of Environment Relief Fund (ERF), which is utilized for providing immediate relief to victims of accidents involving hazardous substances.
Key Amendments
- Administration: It vests the Environment Relief Fund (ERF) in the Central Government.
- Fund Manager: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) replaces United India Insurance Company Limited as the fund manager for five years with effect from 1st January, 2025.
- Disbursement: Fund Manager, in consultation with Central Government, shall develop and maintain an online portal and shall disburse amount as per the order of District Collector or Central Government.
- Investment: ERF amount shall be invested appropriately in public financial institutions and in saving accounts to ensure timely availability of funds.
- Restoration of Environmental Damage: Fund Manager shall earmark the ERF funds for restoration of damage caused due to manufacture, processing, treatment, package, storage, transportation, use, collection, destruction, conversion, transfer etc., of hazardous substances.
- The accounts of the Relief Fund shall be audited by an independent auditor appointed by the Central Government from the panel approved by the Comptroller and Auditor-General.
Related NewsPublic Liability Insurance (Amendment) Rules, 2024 MoEF&CC notified Public Liability Insurance (Amendment) Rules, 2024, in exercise of powers conferred by PLIA 1991. Key Amendments
|
Article Sources
1 sourceChhattisgarh has introduced an innovative plan that connects ecosystem services of its forests with the Green GDP.
- The move highlight the direct link between significant environmental contributions of forests like clean air, water conservation, biodiversity and the state’s economic progress.
- Forest accounts for Chhattisgarh’s 44% of land cover playing crucial role in mitigating climate change.
- Also, forest products like tendu leaves, lac, honey, and medicinal plants contribute significantly to the rural economy.

About Green GDP
- Genesis: ‘Green GDP’ was coined in the late 1980s with aspiration to modify GDP better to reflect the impacts of economic activities on the environment.
- Definition: Green GDP refers to environmentally adjusted gross domestic product (GDP).
- Calculation:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product - (Cost of Depletion of Natural Resources + Cost of Degradation of Ecosystem)
- Need for Green GDP: GDP overlooks environmental depletion and degradation, often treating them as economic gains.
- For instance, cutting down a rainforest and selling the timber increases GDP but harms long-term wellbeing and growth.
Wall Street’s biggest banks including Goldman Sachs Group Inc., etc. have announced their exit from NZBA.
About Net-Zero Banking Alliance
- Bank-led and UN-convened, NZBA is a group of leading global banks committed to aligning their lending, investment, and capital markets activities with net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
- No Indian bank is a member of NZBA.
- It is the climate accelerator for UNEP Finance Initiative’s Principles for Responsible Banking (PRB).
Recently, the Union Minister of Commerce & Industry launched the Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform at the Bharat Climate Forum 2025.
About Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform
- It is designed to enhance India's cleantech value chains in the solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Provide an opportunity for the Indian firms to collaborate, to co-innovate and will help provide a platform for financing, to share ideas, technologies and resources.
- This will help India become an attractive business case and a global leader in the sustainability and cleantech sector.
The Report is also known as Assessment Report on the Underlying Causes of Biodiversity Loss and the Determinants of Transformative Change and Options for Achieving the 2050 Vision for Biodiversity.
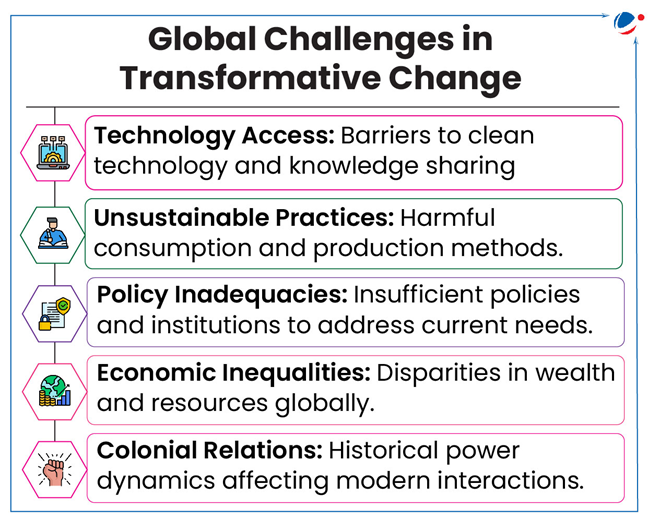
About Transformative Change
- Definition: Transformative Change is a fundamental system-wide shifts in views (ways of thinking), structures (ways of organizing & governing) and practices (ways of doing & behaving).
- Four principles to guide transformative change: equity and justice; pluralism and inclusion; respectful and reciprocal human-nature relationships; and adaptive learning and action.
Five Strategies for Transformative Change for Global Sustainability

- Conserve, restore and regenerate places of value. E.g., Community Forestry Programme in Nepal; Community-based Forest management in India.
- Drive systematic change in sectors responsible for nature’s decline. Sectors like: agriculture and livestock, fisheries, forestry & urban development.
- Transform economic systems for nature and equity. E.g., Biodiversity management needs over $900 billion yearly, but only $135 billion is spent.
- Over 50% of annual global GDP ($58 trillion) depends moderately to highly on nature.
- Transform governance systems to be inclusive & accountable. E.g., The Galapagos Marine Reserve exemplifies ecosystem-based governance.
- Shift views to recognize human-nature interconnectedness: Achieved through nature-based experiences, policy support, and integrating Indigenous knowledge to transform behaviors.
It is the first-ever multi-taxon global freshwater fauna assessment for The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species led by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Key-findings

- 24% of the world's Freshwater Species are at risk of extinction.
- Major Hotspots: Lake Victoria (Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda), Lake Titicaca (Bolivia and Peru), Sri Lanka’s Wet Zone, and the Western Ghats (India).
- Key threatened species: Crabs, crayfishes and shrimps are at the highest risk of extinction followed by freshwater fishes
- At least 4,294 species out of 23,496 freshwater animals are at high risk of extinction.
- Other: Areas with high water stress (where there is high demand and low supply) and areas with more eutrophication are not home to higher numbers of threatened species than areas with lower water stress and less eutrophication.
- Eutrophication refer to an excess of nutrients in the water leads to overgrowth of algae and plants
About Freshwater Landscapes
- Status: These are home to 10% of all known species on Earth.
- Significance: Provides safe drinking water, livelihoods, flood control and climate change mitigation.
- Threat Faced:
- Pollution: Mainly from agriculture and forestry.
- Degradation: E.g. land conversion for agricultural use, water extraction and the construction of dams.
- Other: Overfishing and the introduction of invasive alien species.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) published report on sustainable nitrogen management in Agrifood Systems.
- The report provides a comprehensive overview of nitrogen use, resulting challenges in agrifood systems, and offers recommendations for sustainable nitrogen use.
Key Highlights of Report
- Alteration in Nitrogen Cycle: Humans currently add approximately 150 teragrams (Tg) of reactive nitrogen to the Earth’s land surface each year through agriculture and industry.
- Climate change could raise this to 600 Tg per year by 2100, increasing nitrogen loss into the environment.
- Nitrogen Loss: It occurs through:
- Emissions of ammonia (NH3) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), which lead to air pollution,
- Nitrous oxide (N2O), a potent greenhouse gas (GHG), and
- Leaching of Nitrates (NO3–) in soil and water bodies, causing eutrophication and acidification, harming ecosystems.
- Role of Agrifood Systems: About one-third of anthropogenic nitrogen emissions are contributed by livestock sector.
- In it, synthetic fertilizers, land-use change, and manure emissions are main causes of nitrogen pollution.
- Dual impact of Nitrogen Usage:
- Judicious use in agriculture helps prevent soil degradation and nutrient depletion while increasing crop yields.
- Excessive use exacerbates global warming, degrades air and water quality, and depletes stratospheric ozone.
Sustainable Nitrogen Management (SNM)SNM seeks to minimize external nitrogen inputs and losses and increase recycling of nitrogen within the production system. Recommendations for SNM:
|
African Union (AU) Extraordinary Summit on the Post-Malabo Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) adopted the 10-year CAADP Strategy and Action Plan, and the Kampala CAADP Declaration on Building Resilient and Sustainable Agrifood Systems in Africa.
About Kampala Declaration
- Kampala declaration is the successor to the Malabo Declaration on Accelerated Agricultural Growth and Transformation for Shared Prosperity and Improved Livelihoods, adopted in 2014.
- Implementation period will be 2026-2035.
- It set forth six commitments that should transform and strengthen the agri-food system on the continent.
Recently, Rajasthan government introduced the M-Sand, 2024 policy for sustainable construction and infrastructure.
About M - Sand
- About: It is produced by crushing rocks or quarry stones, serving as a substitute for river sand in concrete construction.
- Advantages:
- Better Workability: It does not contain organic and soluble compounds that affect the setting time and properties of cement.
- Higher Strength: It does not have the presence of impurities such as clay, dust and silt coating.
- Eco-Friendly: Prevents dredging of river beds leading to environmental disaster like ground water depletion, water scarcity, etc.
Global Water Monitor Consortium released ‘Global Water Monitor 2024 Summary Report’.
- The report summarises the state of global water cycle, identify key trends and analyses major hydrological events.

Water Cycle
- Water cycle is the movement of water in all its phases — solid, liquid and gas — within the Earth and atmosphere.
- Liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates back to earth in the form of rain and snow.
Key Findings (State of Water Cycle)
- In 2024, Water-related Disasters caused over 8,700 deaths, displaced 40 million people, and inflicted more than US$550 billion in damages.
- Soil water showed strong regional contrasts, with extreme dryness in South America and Southern Africa and wet conditions in West Africa.
- Lake and reservoir water storage worldwide declined for the fifth year in a row.
Impact of climate change on water cycle
- Intensification: Climate change had intensified water cycle by up to 7.4%.
- Severe Storms: Warmer air can hold more water vapour (7% more moisture for every 1 degree Celsius temperature rise), increasing precipitation intensity, duration and frequency.
- Droughts: Temperature rise causes more evaporation, drying out soils, increasing drought risks.
- Extremely dry months have become increasingly common in recent decades.
- Sea-level rise: Thermal expansion and melting ice is contributing to sea level rise, resulting in oceanic acidification and affecting marine life.
New members including Angola, Bangladesh, Gabon, Guatemala, Kenya, Senegal & Tanzania joined GPAP.
About Global Plastic Action Partnership
- Launched: During Sustainable Development Impact Summit in 2018 of the World Economic Forum (WEF).
- It acts as a plastic pillar of the Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy and Friends of Ocean Action.
- Present members: 25 (including Maharashtra State from India)
- Objectives: accelerate global response to plastic pollution crisis (by bringing together governments, businesses, civil society), advance circular plastics economy to reduce emissions & protect land and ocean ecosystems.
- Key activities: Helps countries in developing National Action Roadmaps & Investment Mobilization for waste management
Challenges related to handling of Global Plastic Waste

- Scalability: Globally, plastic waste has more than doubled since 2000 (OECD’s Global Plastic Outlook Report, 2022).
- In 2024, India became the world’s largest plastic emitter country
- Limited Recycling: Only 9% of plastic waste was ultimately recycled, while 19% was incinerated and almost 50% went to sanitary landfills.
Impact of Plastic Waste
- On Environment: It affects all land, freshwater, and marine ecosystems. It leads to biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation and contributes to climate change.
- Plastic pollution is responsible for an estimated 1.8 billion tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions annually, especially Methane from landfills.
- On Health: Plastics in the form of microplastics damages animal and human health by entering the food chain.
- On Economy: leads to decline in income of sectors such as tourism, fisheries, agriculture, and water safety.
The GEAPP and the International Solar Alliance (ISA) signed an agreement to establish a $100 million fund to support high-impact solar energy projects.
- Additional Initiatives Announced:
- Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition (DUET)
- Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge (ENTICE 2.0)
About Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP)
- GEAPP is a global, public-private initiative focused on accelerating the clean energy transition in developing countries.
- Goals: 1 billion people with energy access, 150 million green jobs, 4 billion tons of emissions avoided.
- Focus Areas: Distributed renewable energy solutions, energy poverty alleviation, sustainable development.
Recently, the world’s largest CAES facility commenced full operation in China.
Compressed Air Energy Storage
- About: It is a technology used to store energy by compressing air into sealed locations often in underground mines or caverns created inside salt rocks.
- Stores electrical energy in the form of potential energy (compressed air).
- Energy is stored during off-peak hours and is released back to the grid when the demand is high.
Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC) notified Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025.
- Notified under Environmental Protection Act, 1986, the rules will come into force from 1st of April, 2025.
- End-of-Life Vehicles (EoLV) means all vehicles which are no longer validly registered or declared unfit through Automated Fitness Centres or their registrations have been cancelled.
Key Highlights
- Applicability: Apply to producer, registered owner of vehicles, Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF), automated testing stations etc. involved in testing of vehicles, handling, processing and scrapping of EoLV.
- Exception: Not apply to
- Waste batteries covered under Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022.
- Plastic packaging covered under Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Waste tyres and used oil covered under Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016.
- E-waste covered under E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022.
- Responsibilities of Producer: Fulfil Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) either through purchase of EPR certificate generated by its own RVSF or by any entity having RVSF.
- EPR certificate: Issued by Central Pollution Control Board through centralised online portal in favour of RVSF.
- Responsibilities of registered owner and bulk consumer: They must deposit EoLV at any of the producer’s designated sales outlet or designated Collection Centre or RVSF within 180 days.
- Implementation Committee: Constituted by Central Government and chaired by CPCB Chairman for effective implementation of rules.
Article Sources
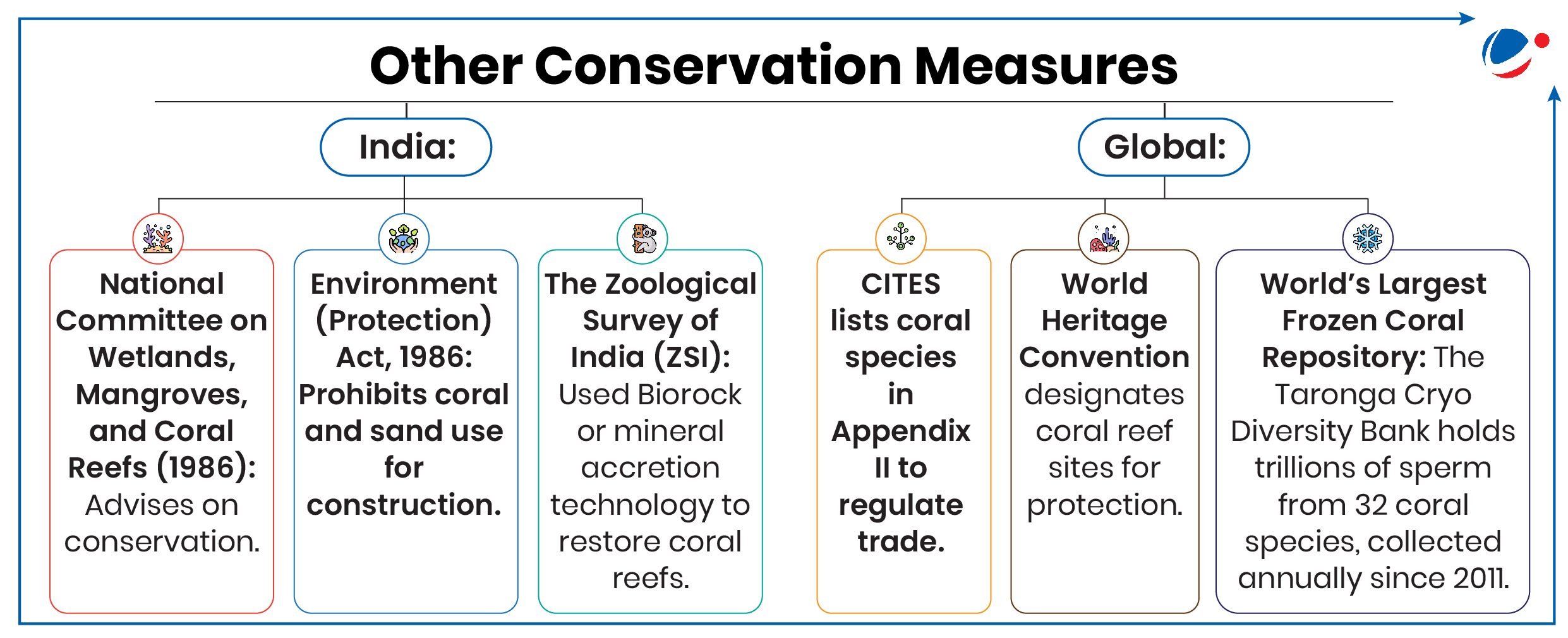
1 sourceWorld’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
- This groundbreaking advancement in coral conservation and restoration is a collaborative effort led by Australian researchers.

About Cryo-born coral
- Cryo-born corals: They are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- Cryopreservation Process:
- Coral cells and tissues contain water, which forms damaging ice crystals when frozen.
- Cryopreservation uses cryoprotectants to remove water from cells during freezing & Support cell structures when thawed.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The project aims to deploy millions of heat-tolerant corals onto the reef annually to combat the effects of climate change.
- Selective Breeding:
- Cryopreservation allows researchers to bypass the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year.
- It enables selective breeding and the use of colonies for reproduction multiple times.
About Coral Reefs
- Corals are invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- They form reefs through colonies of polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Distribution: Mainly found in shallow, sunlit waters between 30°N and 30°S latitude, with a preferred temperature range of 16-32°C.
- Depth: They typically grow at depths less than 50 meters, where light levels are high.
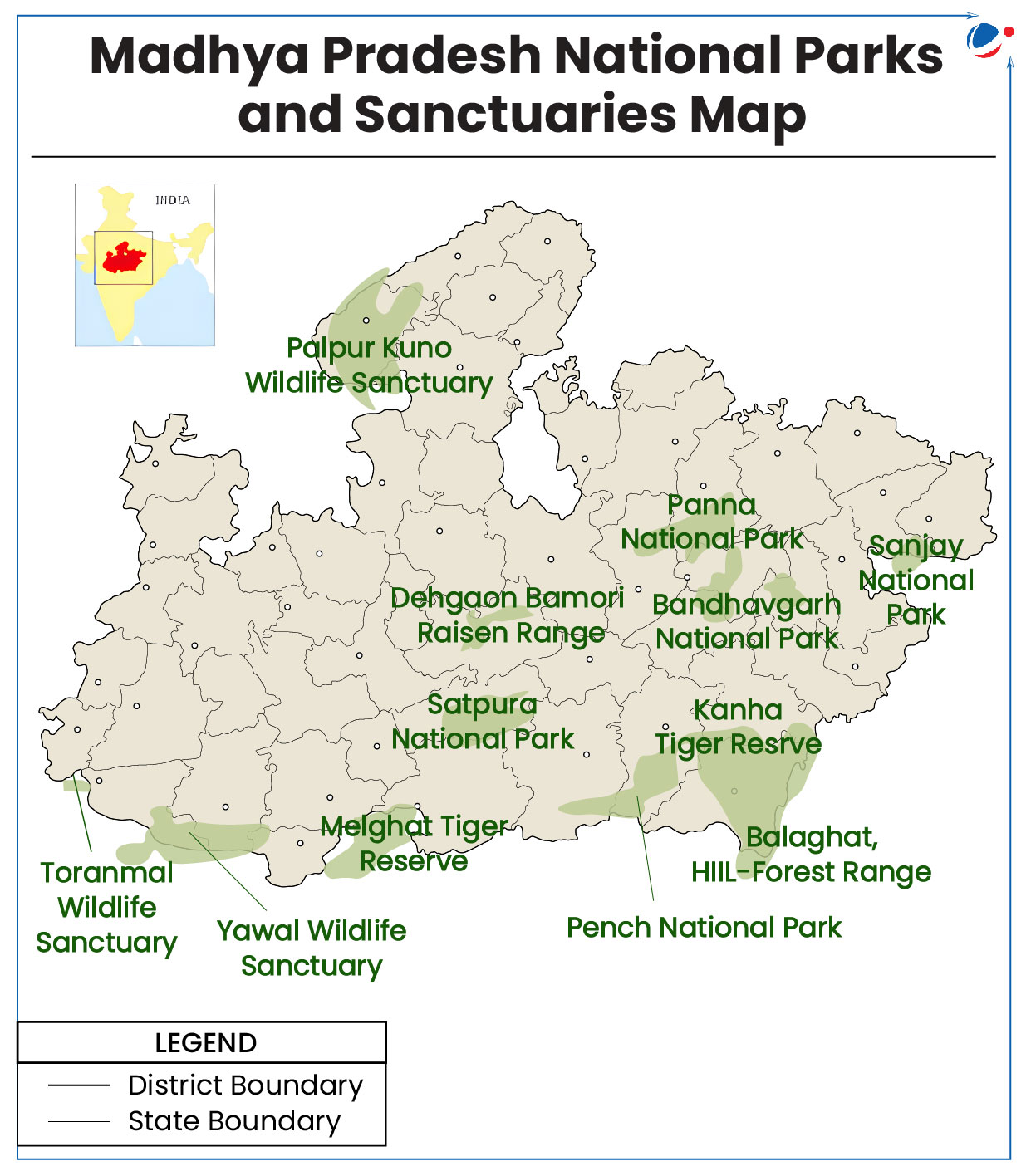
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh
- The tigers will be translocated from Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench tiger reserves.
- Translocation would be done under the animal exchange programme.
- It would be the biggest relocation of big cats from any state.
- Madhya Pradesh is facilitating this project because it has the largest tiger population (785) in the country.
About Inter-state Tiger Translocation Projects
- Objective:
- Re-introduction of a tiger population in an area once part of its historical range, but from which it has been extirpated or become extinct.
- Reinforcement/Supplementation of tigers to an existing population to enhance its long-term viability.
- The first tiger relocation project was initiated in 2018 wherein two big cats, from Kanha Tiger Reserve and Bandhavgarh, were relocated to Satkosia Tiger Reserve (Odisha).
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is key in facilitating such projects.
Benefits of Translocation
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces human-tiger conflicts in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns associated with Translocation
- Protests from local communities: Villagers living near tiger reserves fear that the tiger will endanger their lives, etc.
- Territorial disputes with existing Tigers: This pushes new tigers into human-dominated areas.
- Other: Poor forest management such as prey augmentation, etc.
Recently, the standing committee of National Board for Wildlife approved a proposal to carry out oil and gas exploration in the eco-sensitive zone of the Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary.
Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Located at Jorhat district of Assam.
- Officially extends to the Dissoi Valley Reserve Forest, Dissoi Reserve Forest, and Tiru Hill Reserve Forest.
- Establishment: 1997.
- Significance: Contains India's only gibbons - the hoolock gibbons and Northeastern India's only nocturnal primate - the Bengal slow loris.
- Other non-human primates found here are Capped Langur, Rhesus Macaque, Assamese Macaque, Pigtailed Macaque & Stump tailed Macaque.
Government of India has designated areas around Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary as Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs).
About Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Middle altitudinal range of the Himalayas in Mandi District, Himachal Pradesh.
- Named after the goddess Shikari Devi, to whom a temple is dedicated in the sanctuary.
- Streams: Juni Khud, a tributary of Beas River.
- It is recognised as an Important Bird Area by Birdlife International.
- Vegetation: Alpine pastures and Temperate Deciduous Forest.
- Fauna: Asiatic Black Bear, Leopard, Barking Deer, Giant Flying Squirrel etc.
Kerala has launched the Kerala Warnings, Crisis, and Hazard Management System (KaWaCHaM) for real-time disaster alerts.
About KaWaCHaM
- It is developed by the Kerala State Disaster Management Authority (KSDMA) with support from the National Disaster Management Authority and the World Bank.
- It is supported under the National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP).
- It offers hazard assessment, alert issuance, and threat-based action planning.
- Provides updates for extreme weather events such as heavy rain etc.
The Inter-Ministerial Central Team (IMCT) has declared Wayanad landslides as a ‘calamity of severe nature’.
Calamity of Severe Nature
- Legal provision: No specific criterion is given in the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) or National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) guidelines for declaring a natural calamity as a calamity of severe nature.
- However, based on the intensity and magnitude of losses to life and property, the Central government treats it as a calamity of severe nature, mostly based on the recommendations of the IMCT.
- Funding Support: For a "calamity of severe nature," additional funding comes from the NDRF in excess of the balances available in the state's own SDRF.
Karnataka launched the ‘Garudakshi’ online FIR system to curb wildlife crimes.
About Garudakshi
- It is software to enable an online FIR system similar to that of the Police Department.
- It will allow the public to register complaints on forest offences using mobile phones or email addresses
- Developed in collaboration with the Wildlife Trust of India.
India's coastline has been recalculated from 7,516 km in 1970 to 11,098 km in 2023-24, reflecting a 48% increase over the past 53 years.
- Upward revision is attributed to a new methodology to measure India's maritime established by National Maritime Security Coordinator.
- It measures complex coastal formations like bays, estuaries, and inlets, unlike older methods that used straight-line distances.
Key Findings
- West Bengal recorded highest percentage increase (357%) while Kerala (5%) reported the smallest increase.
- Puducherry's coastline contracted by 4.9 km.
- Gujarat retains its position as the state with the longest coastline followed by Tamil Nadu which overtaken Andhra Pradesh (now 3rd).
Experts attribute the severity of the wildfires in USA to hydroclimate whiplash, a phenomenon intensified by climate change.
About Hydroclimate whiplash
- It is a rare meteorological Hydro climatic volatility condition wherein an extremely wet season is succeeded by an extremely dry season.
- Impact
- Amplification of hazards like flash floods, wildfires, landslides, disease outbreaks etc.
- Affect water quality via harmful algal blooms or the influx of excess organic and/or mineral content.
- Affect food security through decreased plant productivity, crop failures, livestock mortality etc.
The ongoing extreme cold spell in USA & Canada is attributed to arctic blast due to southward expansion of the polar vortex.
What is Polar Vortex?
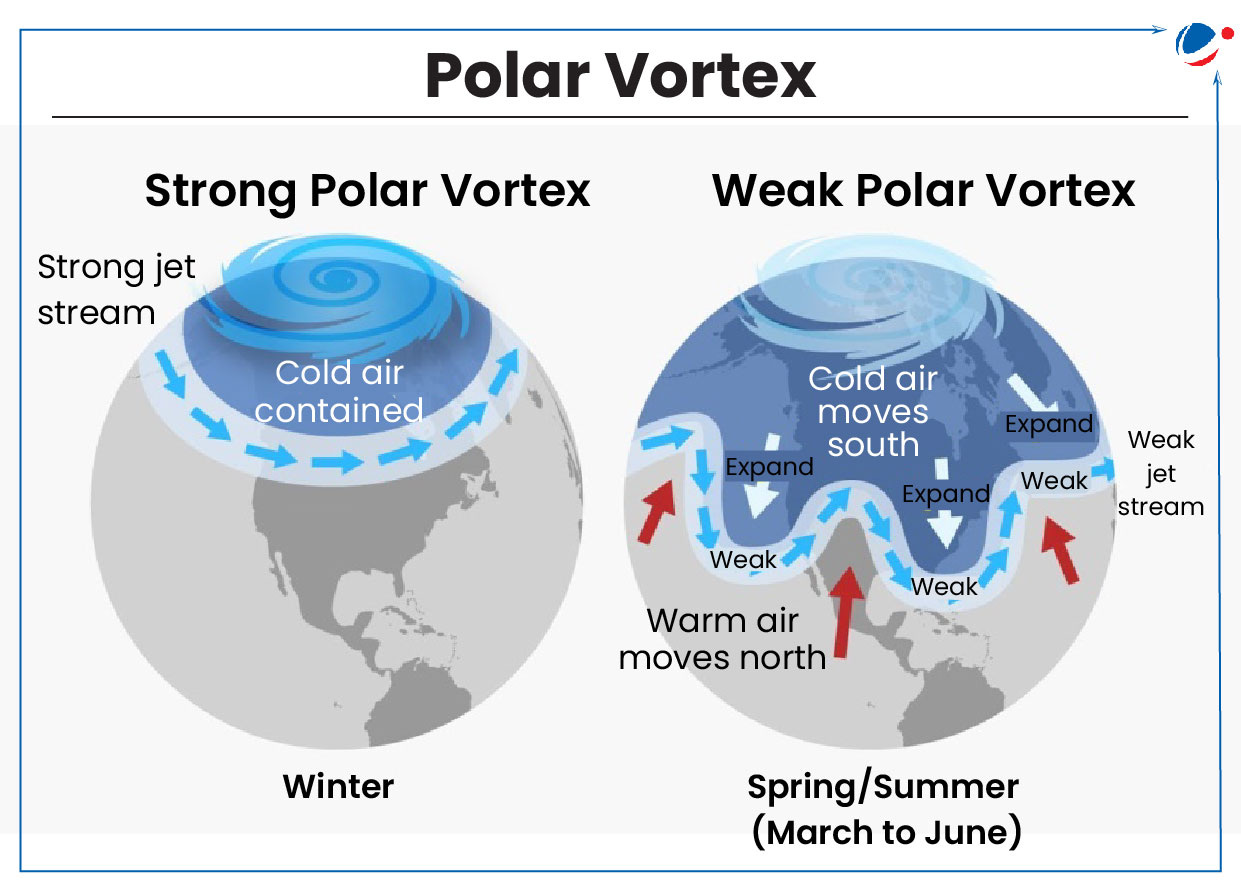
- Definition: It is a large area of low-pressure and cold air that swirls like a wheel (counter-clockwise) around both of the Earth’s poles.
- Types:
- Tropospheric Polar Vortex: It forms in the lowest atmospheric layer,
- 10-15 km.
- Stratospheric Polar Vortex: It forms at around 15 km to 50 km high.
- Unlike tropospheric polar vortex, the stratospheric polar vortex disappears during summer & is strongest during the autumn.
Impacts of Polar Vortex
- Arctic Blast: It is sudden and intense surge of cold air in US due to disruptions in the polar vortex, which usually keeps cold air confined to the Arctic region.
- Extreme Weather Events: A weakened vortex can cause the jet stream to dip southward, bringing cold Arctic air to lower latitudes & triggering extreme weather events.
- Ozone Depletion: The trapped cold air in the vortex accelerates ozone depletion, particularly over Antarctica, leading to the ozone hole.
- Impact on India: A weakened polar vortex results in more western disturbances, bringing heavy snowfall to the western Himalayas and colder temperatures to northern India.
Musi River historic buildings have been kept on World Monuments Watch 2025.
- World Monuments Watch is a biennial program which aims to raise awareness and mobilize action for the preservation of cultural heritage worldwide.
About Musi River
- Origin: Ananthagiri hills, Rangareddy district (Telangana).
- It is one of the major tributaries of Krishna river and flows into the Osmansagar and Himayatsagar reservoirs.
- It consists of 2 rivulets Esi (8 kms) and Musa (13 kms) which then converge into Musi River.
- Importance: major water sources for Hyderabad.
Indonesia’s Mount Ibu, on the remote island of Halmahera, erupted 1,000 times this month.
About Mount Ibu:
- As an active volcano, Mount Ibu is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region known for frequent volcanic activity and earthquakes.
- The Ring of Fire, also called the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by numerous active volcanoes and seismic activity.
- Indonesia has numerous volcanoes due to its location on converging tectonic plates, particularly the Pacific, Eurasian, and Australian plates.
- Other Recent Eruptions in Indonesia: Mount Sinabung and Mount Merapi.







