Why in the news?
McKinsey Global Institute, in its report "Dependency and depopulation? Confronting the consequences of a new demographic reality", said that India has 33 years to reap the benefits of its demographic dividend.
Key Findings of the Report
Declining Fertility and Population Collapse |
|
Aging Populations and Economic Dependency |
|
Economic Consequences of Aging |
|
India Specific findings |
|
About Demographic Dividend
- When the share of the working age population exceeds that of the very young and old (dependent population), it lands a country in what is known as the demographic dividend zone.
- With fewer people to support, a country has a window of opportunity for rapid economic growth if the right social and economic policies are developed and investments made.

- With one of the youngest populations globally, sixty-five percent of India's fast-growing population is under 35.
- The Economic Survey 2018-19 says that the demographic dividend would peak around 2041, when the working age group will be 59% of India's total population.
Potential benefits of Demographic Dividend
- Economic growth: According to IMF, demographic dividend could add about 2 percentage points per annum to India's per capita GDP growth over the next two decades (2011).
- China is a prime example of a country that has experienced significant economic growth fueled by its demographic dividend.
- Increased Savings and Investments: With fewer dependents, individuals tend to save more, leading to increased capital accumulation and investment.
- Labor supply: More workers are added to the labor force, including more women.
- Consumption led growth: According to Mckinsey, India is projected to account for 16 per cent of global consumption at purchasing power parity (PPP) by 2050.
- Fiscal space: With a smaller dependent population, governments can allocate more resources to investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, further boosting economic development.
Challenges faced by India in reaping demographic dividend
- Unemployment and Underemployment: The current rate of job creation is not sufficient to absorb the millions of young people entering the labor market each year.
- In 2022, India's youth accounted for 83% of the country's total unemployed population, according to the India Employment Report 2024.
- Skill mismatch: Global Skills Gaps Measurement and Monitoring Report of ILO 2023 indicate that 47% of Indian workers, especially 62% of females are underqualified for their jobs.
- Health and Nutrition: India still faces challenges related to child malnutrition, maternal health, and access to quality healthcare, which can impact the overall health and well-being of its workforce.
- Gender Disparity: Female labor force participation in India is relatively low compared to other countries.
- Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2021-22 highlights that the FLFP 32.8% in India (47% global average)
- Regional Disparities: India's demographic dividend is not uniform across all regions. Some states have already achieved low fertility rates and are facing an aging population.
- Informal Economy: A large share of India's workforce is employed in the informal sector, where workers often face low wages, job insecurity, and lack of social protection.
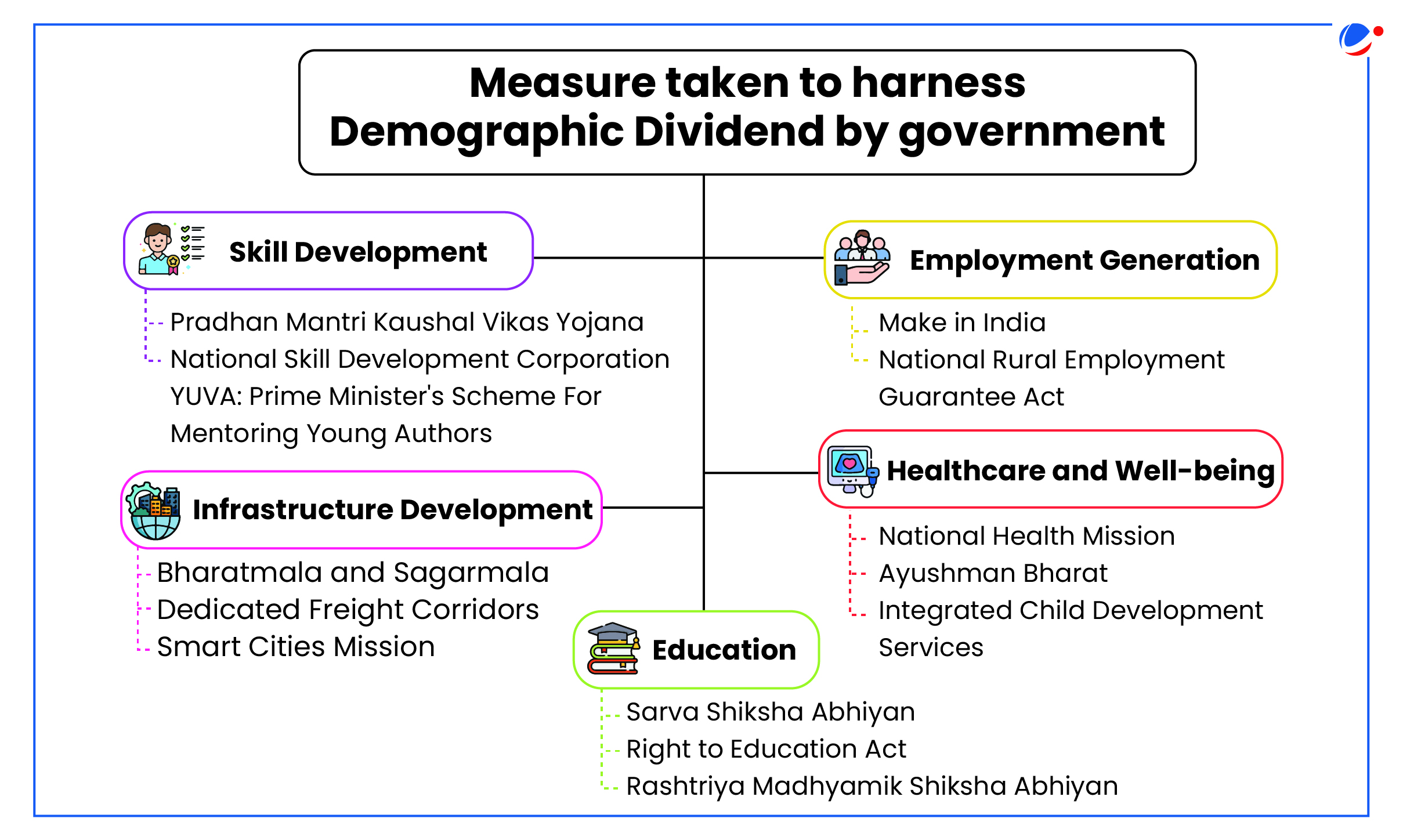
Way Forward
- Investing in Human Capital: Strengthen education and skills training, align curricula with job market needs, and invest in healthcare and nutrition for long-term productivity.
- Creating Employment Opportunities: Support job creation through entrepreneurship, business-friendly policies, and labor market reforms while promoting women's workforce participation.
- Managing Aging Populations: This may involve raising retirement ages gradually, incentivizing older workers to remain in the workforce longer, and reforming pension systems to ensure their sustainability.
- International Cooperation: Share best practices, provide technical assistance, and collaborate for well-managed migration strategies.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Improve demographic and labor market data collection to enable informed policymaking and effective economic planning.



