Why in the news?
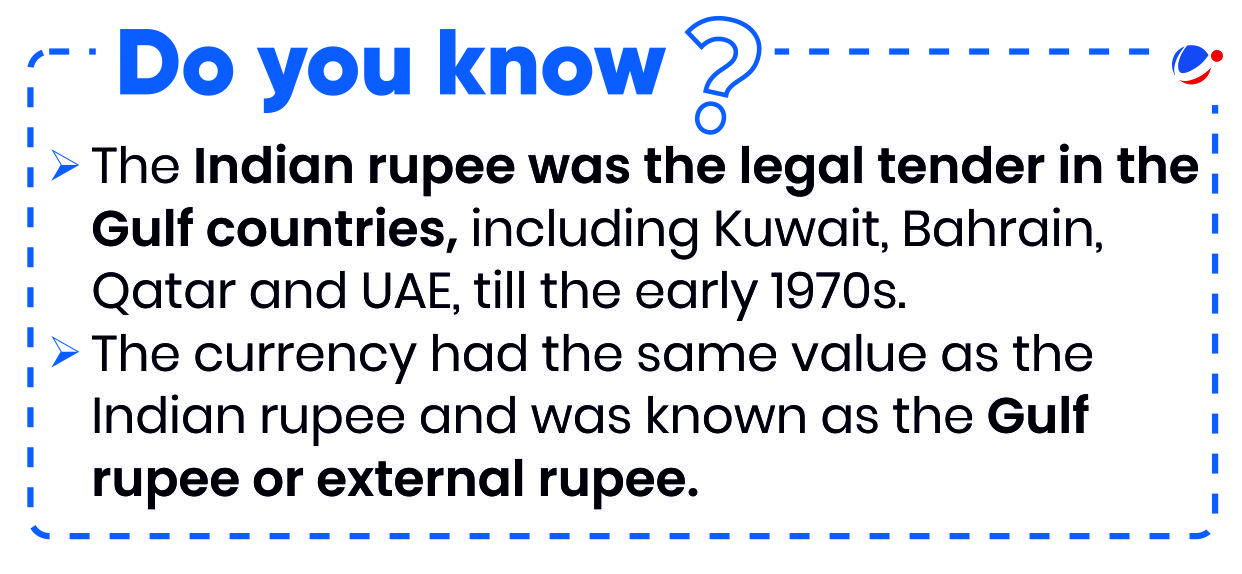
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) liberalized FEMA regulations, 1999 to encourage use of Indian Rupee (Internationalization of Rupee) for settlement of cross border transactions.
Recent Changes made in FEMA regulations by RBI:
- People residing outside of India will be able to -
- Open Indian Rupee (INR) accounts in overseas branches of Authorized Dealer banks for settling all permissible current and capital account transactions with a person resident in India.
- Settle transactions with other persons resident outside India using balances in their repatriable INR accounts such as Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account & Special Rupee Vostro Account (SVRAs).
- Any person resident outside India, having a business interest in India, can open SNRR account for purpose of putting through bona fide transactions in rupees.
- Use their balances held in repatriable INR accounts for foreign investment.
- Indian exporters will be able to open accounts in any foreign currency overseas for settlement of trade transactions, including receiving export proceeds and using these proceeds to pay for imports.
Difference between Vostro and Nostro Account
Vostro Account | Nostro Account |
|
|
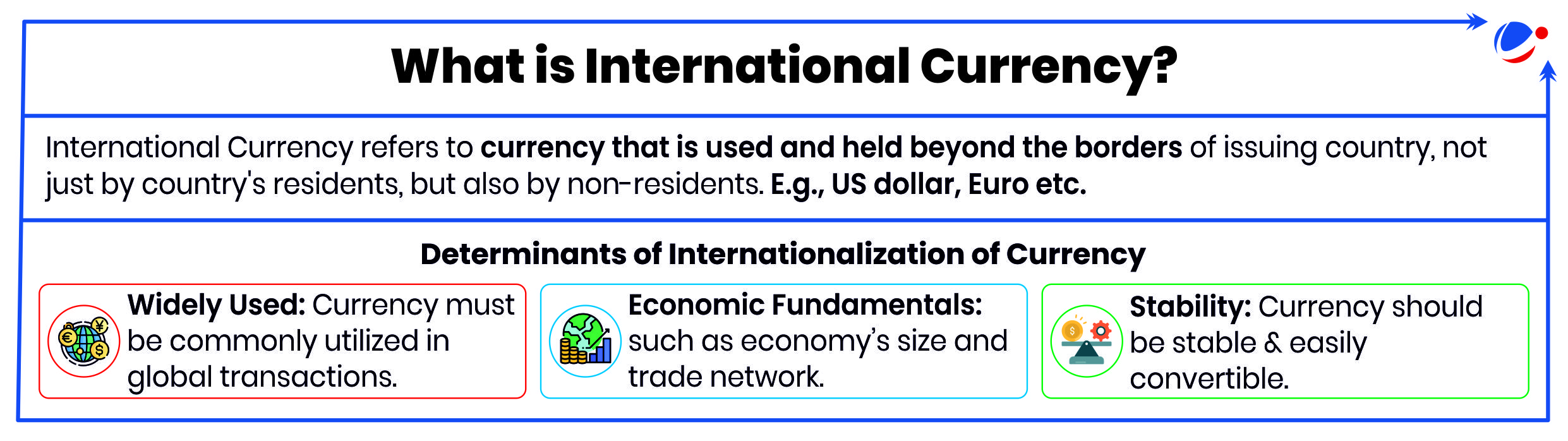
What is Internationalization of Rupee?
- Internationalization of Rupee refers to a process that involves increasing the use of the rupee in cross-border transactions.
- It involves promoting the rupee for import and export trade and then other current account transactions, followed by its use in capital account transactions.
Benefits of Internationalization of Rupee
- Reduces Vulnerability: Reducing dependence on foreign currencies (particularly dollar), it will shield the economy from sudden exchange rate fluctuations, currency crises, and inflationary pressures.
- Limits Exchange Rate Risks: Protection from currency volatility not only reduces the cost of doing business, it also enables better growth of business, improving the chances for Indian businesses to grow globally.
- Reduces Requirement of Forex Reserves: It reduces the requirement to maintain and depend on large foreign exchange reserves in convertible currencies to manage external vulnerabilities.
- Deficit Financing: A globally accepted INR allows the Indian government to issue debt in its own currency to international investors, making it easier to manage fiscal deficits without exchange rate risks.
- Strengthening India's Financial Markets: Greater global demand for INR increases foreign participation in Indian financial markets, such as bonds and equity bringing in long-term investments.
Challenges in Internationalization of the Rupee
- Exchange Rate Volatility: It may result in a potential increase in volatility of its exchange rate in the initial stages.
- Monetary Policy Dilemma or Triffin Dilemma: Creates a monetary policy dilemma, including the Triffin Dilemma, where a country struggles to balance global currency demand with domestic monetary needs.
- Restricted Convertibility: INR is fully convertible in the current account but partially in the capital account limiting its global appeal.
- Risk to External Shock: Given the open channel of the flow of funds in and out of the country, it may increase the volatility of the financial system.
- Lack of global Usage: INR is not widely used in global trade compared to USD, EUR etc. further it lacks deep liquidity in international forex markets, restricting large-scale transactions.
Steps taken for Internationalization of Rupee
- Internationalization of Indian Payment Infrastructure: UPI is adopted in Singapore, France, UAE, Sri-Lanka, Bhutan, Mauritius, Nepal etc.
- Memorandum of Understanding (MoU): RBI has signed MoU with the central banks of the United Arab Emirates, Indonesia and Maldives to encourage cross-border transactions in local currencies, including Indian Rupee.
- RBI's Strategic Action Plan for 2024-25: In its Annual Report for 2023-24, the RBI unveiled a Strategic Action Plan for 2024-25 aimed at promoting the internationalization of INR. It includes-
- Permitting Opening of INR Accounts outside India; Extending INR-denominated loans to persons resident outside India (PROI).
- Implementation of the SPECTRA Project: SPECTRA (Software Platform for ECBs and Trade Credits Reporting and Approval) software platform of RBI aimed at streamlining the approval and reporting process for External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits.
- Special Vostro Rupee Accounts (SVRAs): RBI has enabled INR trade settlement with 22 countries by allowing banks to open SVRAs.
- Other: Bilateral Currency Swap agreements, INR as a Designated Foreign Currency in Sri Lanka, Issuance of rupee-denominated bonds i.e. Masala bonds.
Way Forward (Recommendations of Inter‐Departmental Group of RBI)
- Internationalisation of Indian Payment Systems: Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), UPI etc.
- Inclusion of INR in Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS): CLS is a global system for the settlement of foreign currency transactions on a Payment vs Payment (PvP) basis. It currently settles trades in 18 currencies.
- Currency Swaps & Local Currency Settlement (LCS): It stabilises local currency, protect businesses against currency risk exposure & reduces transaction costs.
- Efforts for Inclusion of INR to Special Drawing Rights (SDR) basket: SDR is an international reserve asset created by IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries' official reserves.
- Value of the SDR is calculated from a weighted basket of 5 major currencies - U.S. dollar, Euro, Japanese yen, Chinese Renminbi, & British pound.
- Strengthening Financial Markets:
- Harmonisation of KYC norms of RBI and SEBI to ease access of foreign investors to INR assets.
- Global 24x5 INR market: While customer transactions are facilitated round-the-clock in the offshore market, the inter- bank market operates only for a limited set of hours onshore.
- Inclusion of Indian Government Bonds in Global Bond Indices: It will enable widening of investor base, stable passive flows, appreciation of INR, and reduction of overall borrowing costs.
Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999
|



