Acknowledging the right to access to justice as the cornerstone of democracy, SC recently imposed a penalty on a petitioner for filing multiple frivolous litigations that burden the judicial system.
- A frivolous litigation is a lawsuit that lacks any arguable basis either in law or in fact and intends to harass, or delay the judicial process.
- The issue was also taken up by the apex court earlier in the Subrata Roy Sahara Vs Union of India (2014), Dalip Singh v. State of Uttar Pradesh and others (2010), and the K.C. Tharakan Vs State Bank of India & Ors (2023).
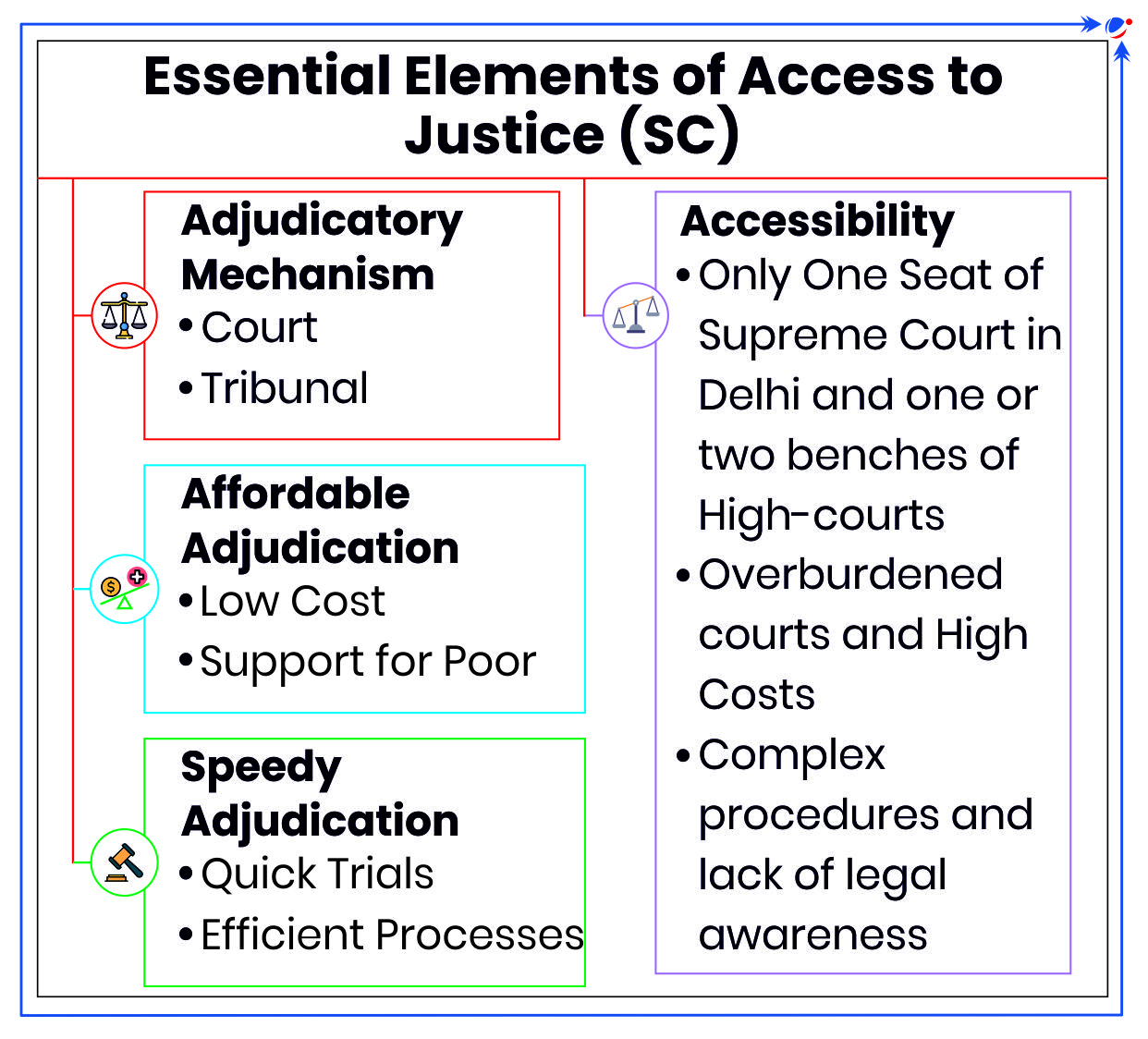
Right to Access to Justice
- Meaning: It is a basic principle of the rule of law and deals with the ability of people to seek and obtain a remedy through formal or informal institutions of justice for grievances.
- SC in Anita Kushwaha v. Pushap Sudan (2016) held Access to Justice is a Fundamental Right under Article 14 (Right to Equality) and Article 21 (Right to Life and Personal Liberty).
Other Provisions/ Mechanism related to Right to Access to Justice
- Constitutional
- Preamble covers social, economic and political justice.
- Directive Principles of State Policy under Article 39A (Right to free legal aid).
- Article 32 (Right to Constitutional Remedies) Article 226 (Power of High Court to Issue Writs).
- Public Interest Litigation: Liberalised the rule of locus standi (where only the aggrieved person can file a case for the enforcement of right), to allow public spirited persons or organizations file a case for the enforcement of right.
- Alternative Dispute Redressal Mechanisms (ADR): Grievance Redressal with lesser formality at lower cost.
Hamara Samvidhan – Hamara Swabhiman Campaign organised to commemorate 75th anniversary of Indian Constitution and India’s establishment as a Republic under the DISHA Scheme.
About DISHA scheme
- Launch: Launched in 2021 by Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice for a period of 5 years (2021-2026).
- Aim: To secure “Justice” to the people of India as enunciated in the Preamble & under Articles 39A, 14 and 21 of the India Constitution.
- Other: It widens the outreach of Tele-Law, Pro Bono Legal Services (Nyaya Bandhu) & Legal Literacy and Legal Awareness programmes both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Home Affairs has amended Model Prison Manual, 2016 rules and Model Prisons and Correctional Services Act, 2023 to address caste-based discrimination within prisons across country.
- These amendments have been made in compliance with Supreme Court order on caste-based discrimination of prisoners in Sukanya Santha vs. UoI & Others Case.
- SC also directed that reference to habitual offenders in prison manuals should be in accordance with legislative definitions of respective State Laws.
- Habitual offenders are individuals convicted and sentenced multiple times within five years for separate offenses, with sentences not reversed on appeal or review.
- SC also directed that reference to habitual offenders in prison manuals should be in accordance with legislative definitions of respective State Laws.

Key Amendments
- Prison authorities strictly ensure that prisoners are not discriminated against, classified, or segregated based on their caste, including in allocation of duties or work within prison.
- Discrimination based on caste is prohibited under Article 14 (equality before law), Article 15 (prohibition of discrimination), Article 17 (abolition of untouchability), etc.
- Provisions of ‘Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013’ shall have a binding effect in Prisons and Correctional Institutions.
- Manual scavenging or hazardous cleaning of a sewer or septic tank inside a prison shall not be permitted.
Recently, Supreme Court (SC) highlighted the Doctrine of Merger.
About Doctrine of Merger
- It was explained in Kunhayammed v. State of Kerala, (2000).
- As per this doctrine, there cannot be more than one decree or operative order governing the same subject matter at a given point in time.
- Hence, once the superior court disposes of a case whether by setting aside, modifying, or confirming the lower court's decree, the superior court's order becomes the final, binding, and operative, merging the lower court's decision into it.
Supreme Court held that CBI does not require sanction of a state government to register a case under a Central legislation like the Prevention of Corruption Act against a Central government employee posted in state concerned.
- This overturned an Andhra Pradesh High Court decision that had dismissed cases against central employees due to lack of state consent.
About State Consent for CBI
- Law: Section 6 of Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946 requires CBI to get state consent for investigations a crime in a state.
- Two types of consent: General Consent, and Case-specific Consent.
Lok Sabha Speaker has inaugurated Panchayat Se Parliament 2.0.
About Panchayat Se Parliament 2.0
- Organised by National Commission for Women and Lok Sabha Secretariat in collaboration with Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- Aims to empower elected women representatives from Scheduled Tribes from Panchayati Raj institutions and enhance their knowledge of constitutional provisions, parliamentary procedures, and governance to foster effective leadership.
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions launched 'Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi' Initiative on Good Governance Day.
- Good Governance Day is celebrated on 25th December to commemorate the birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
About Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
- Aim: To enhance the capacity and competence of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) by equipping elected representatives and officials with the tools and knowledge required for effective governance and participatory planning.
- It is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign.
- The program promotes decentralized governance and grassroots-level decision-making.
The Union government approved the establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission.
About Pay Commission
- Constitution: by central government
- Since 1947, seven Pay Commissions have been constituted
- The 7th pay commission was implemented in 2016 and is set to complete its term in 2026.
- Chairman of 7th Pay Commission was: Justice Ashok Kumar Mathur.
- Importance: It plays a vital role in determining salary structures, allowances, and other benefits for government employees.
Recently, annual Edelman Trust Barometer was released before the start of the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting.
- Released by Edelman Trust, it is a survey of 28 countries that studies the influence of trust across society — government, media, business, and NGOs.
Key Findings
- India slipped to 3rd position, after China & Indonesia in terms of people's trust in the government, businesses, media etc. (in low-income population group).
- Within high income group, India was ranked 4th.
- India ranked 13th when it comes to trust of people in other countries, in companies with Indian headquarters.







