According to the World Bank, India secured 14.3% of Global Remittances in 2024, highest share ever.
- Remittances are financial transfers made by individuals working abroad to support their families in their home country.
Trend in Remittances flow
- Top five recipients in 2024: India at $129 billion (Compared to $125 billion in 2023), Mexico, China, Philippines, and Pakistan, driven by recovery in job markets in high-income countries of OECD.
- Remittances to Low- and Middle-Income Countries are projected to surge to $685 billion in 2024, with 5.8% growth rate.
- China's share of global remittances dropped to 5.3% in 2024, its lowest share in two decades, due to reduced low-skilled emigration stemming from its rising economic prosperity and aging population.
Factors responsible for High Remittances in India
- Scale of Migration: India has one of the largest diaspora populations in world, with over 18 million Indians living abroad as of 2023 (UN World Migration Report 2024).
- Shift in Destination Trends: Increasingly, Indian migrants are moving to high-income economies like US, UK, and Australia.
- Skilled and Unskilled Labor: Indian migrants range from highly skilled professionals (IT, healthcare) to semi-skilled and unskilled labourers.
Significance of High Remittances
- For Recipient Households: used for essential expenses like food, healthcare, and education, directly improving living standards.
- For Macro-economy: Major source of foreign exchange, reduced reliance on foreign aid, funding current account deficits and fiscal shortfalls etc.
World Bank's latest Global Economic Prospects Report gives overview of Global Economy for the 1st quarter of 21st Century (refer to the infographic).
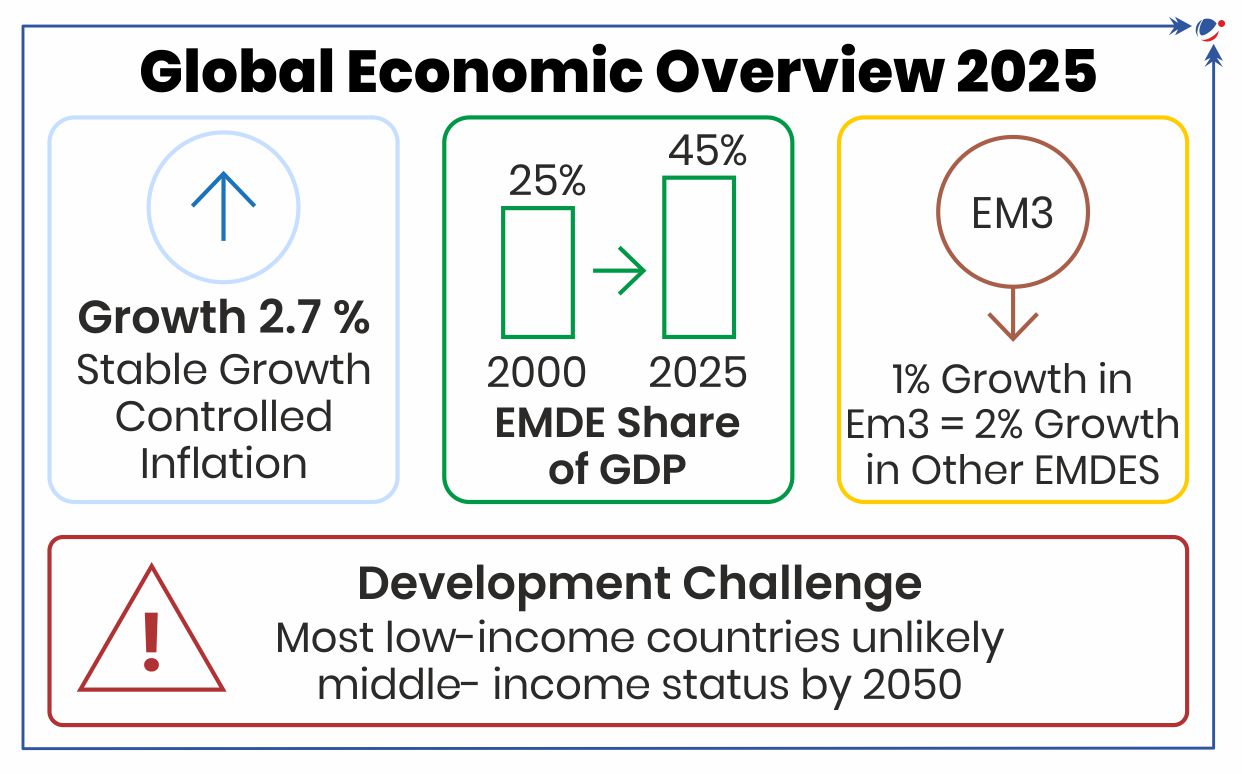
Key Highlights
- Rising influence of EMDEs: Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs), led by the EM3 nations (China, India, and Brazil), have significantly increased their share in the global economy from 2000 to 2025.
- India's Growth Leadership: India remains the fastest-growing economy, with projected 6.7% annual growth through FY26–FY27, slightly below the 7% achieved in 2022.
Factors reflecting robustness of Indian Economy
- Strong Sectoral Performance:
- Services: The services sector is set for sustained expansion, with rising service exports boosting trade integration in South Asia since 2000.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing is strengthened to grow, driven by government initiatives to improve logistics and tax reforms.
- Solid Economic Foundation
- Fiscal Health: Shrinking fiscal deficits and increasing tax revenues.
- Investment Outlook: Investment growth overall is expected to be steady, with rising private investment, supported by healthy corporate balance sheets and easing financing conditions.
- Consumption outlook: Private consumption growth is expected to be boosted by a strengthening labor market, expanding credit, and declining inflation.
- However, government consumption growth is likely to remain contained.
The report identifies key challenges, including rising protectionism, geopolitical tensions, mounting debt burdens, and climate change-related costs. Success requires focused policies on boosting investment, productivity, and macroeconomic stability while effectively managing external pressures.
Article Sources
1 source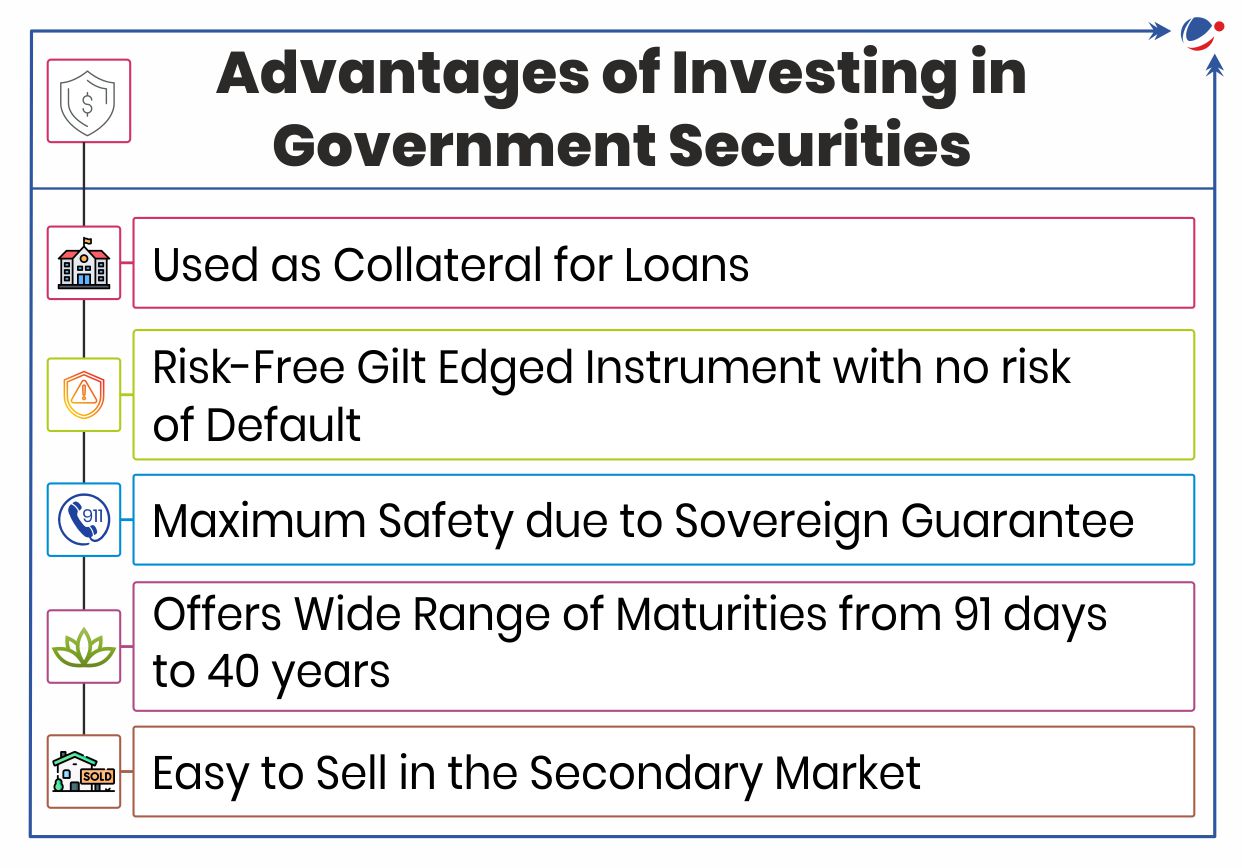
Recently, RBI notified the calendar for issuance of T-Bills, one of the types of Government Securities (G-Sec).
Government Securities Market in India
- About: It is a tradeable instrument issued by the Central or State Governments acknowledging the Government’s debt obligation.
- Issued by: RBI through an auction on its electronic, E-Kuber platform.
- RBI’s Public Debt Office (PDO) acts as its registry/ depository.
- Major Participants: Commercial banks, Primary Dealers, Insurance companies, co-operative banks, regional rural banks, mutual funds, retail investors (non-competitive bidding section), etc.
Types of G-Secs
- Short term with original maturities less than a year. E.g., T-Bills
- Treasury Bills (T-bills)
- Money market and short term debt instruments issued by the Government of India (GOI)
- Zero coupon securities and pay no interest.
- Issued at a discount and redeemed at the face value at maturity.
- Issued in 3 tenors, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day.
- Cash Management Bills (CMBs)
- Short-term (maturities less than 91 days) instrument introduced by the GOI in 2010 to meet the temporary mismatches in its cash flows.
- Treasury Bills (T-bills)
- Long Term, with original maturity of one or more year. E.g., Government Bonds or Dated Securities.
- Dated G-Sec: They carry a fixed or floating interest rate paid on the face value, on half-yearly basis, with maturities ranging from 5 to 40 years.
- SDLs: Dated securities issued by State Governments with half-yearly interest payments.
- NOTE: In India, the Central Government issues both T-Bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, called the State Development Loans (SDLs).
Article Sources
1 source
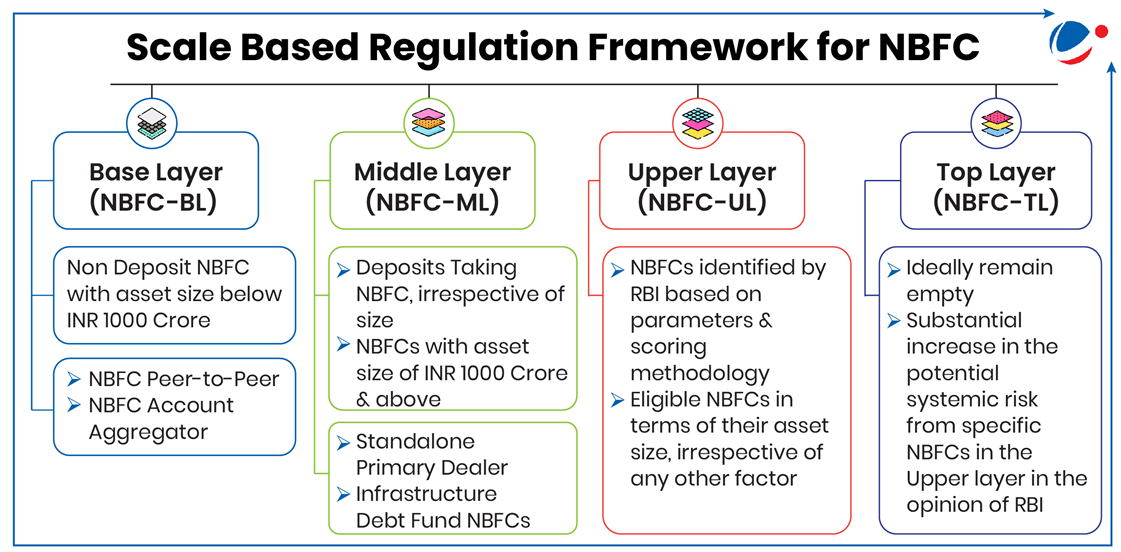
- The list includes LIC Housing Finance Limited, PNB Housing Finance Limited, Shriram Finance Limited etc and is in accordance with Scale Based Regulation (SBR) , a regulatory framework for NBFCs.
- Once an NBFC is classified as NBFC-UL, it is subjected to enhanced regulatory requirement, at least for a period of 5 years
- The framework has been introduced to mitigate contagion or systemic risks, apply the principle of proportionality in regulation and strengthen quality and improve risk management of NBFCs.
Scale Based Regulation Framework for Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFCs)
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Finance launched a revamped e-auction portal ‘BAANKNET’.
About BAANKNET
- It consolidates information on e-auction properties from all Public Sector Banks and offers a one-stop destination for buyers and investors to discover a wide range of assets.
- The listings include residential properties such as flats, independent houses, and open plots, as well as commercial properties, industrial land and buildings, shops, etc.
- The platform is expected to unlock the value of distressed assets and boosting investor confidence.
RBI has allowed Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) holders to make and receive Unified Payments Interface (UPI) payments through third-party mobile applications.
About PPI
- PPIs are instruments that facilitate the purchase of goods and services, conduct of financial services, enable remittance facilities, etc., against the value stored therein. E.g. Mobile wallets, digital wallets, gift cards
- PPIs can be issued by banks and non-banks.
- Classified under two types: small PPIs (issued after obtaining minimum details of the PPI holder) and Full KYC PPIs.
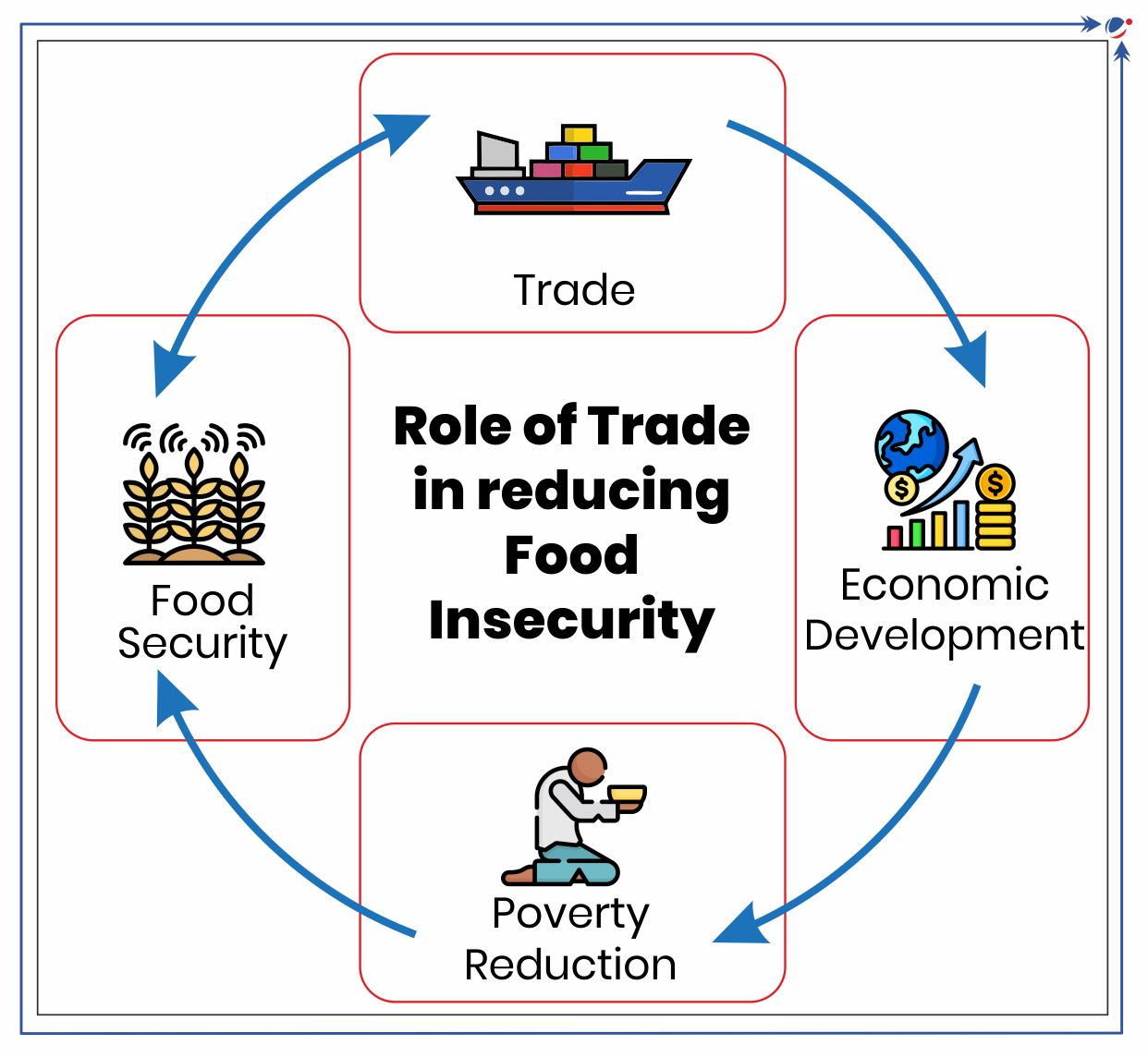
The report analyses various drivers of food insecurity and how can trade play a mitigating role in addressing these challenges.
Role of Trade
- Sustainable supplies can ensure food availability: E.g. 30% of Africa’s cereal needs are met through imports
- Stabilizing prices and markets: E.g. Black Sea Initiative (brokered by UN and Türkiye) during Russia-Ukraine war facilitated food and fertilizer exports
Challenges
- Higher costs: E.g. non-tariff measures, such as sanitary standards, can increase food import costs by 20%.
- High Import dependency: It exposes countries to global price hikes and supply chain disruptions.
- Rising transportation costs: It affects developing and least developed countries disproportionately.
Recommendations
- Reach a “Short Term Export Facilitation Mechanism to Combat Severe Food Insecurity” at international forum, such as WTO
- Reduce trade barriers & boost export capacities of food insecure countries.
- Invest in trade infrastructure such as ports, transport networks and storage facilities to shorten supply chains and reduce vulnerabilities to global disruptions especially for low-income countries.
- Support climate-smart and sustainable farming in developing countries
 Factsheet
Drivers of global hunger
|
The revised policy announced by Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution aims to enhance food security & bolstering ethanol production.
- It set Rice Reserve Price (₹2,250 per quintal) for sale to State Governments, Corporations, & Community Kitchens, without e-auctions.
- The policy set reserve prices at ₹2,250 per quintal (slashed by ₹550) of rice to ethanol distilleries to aid ethanol production.
What is Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic)?
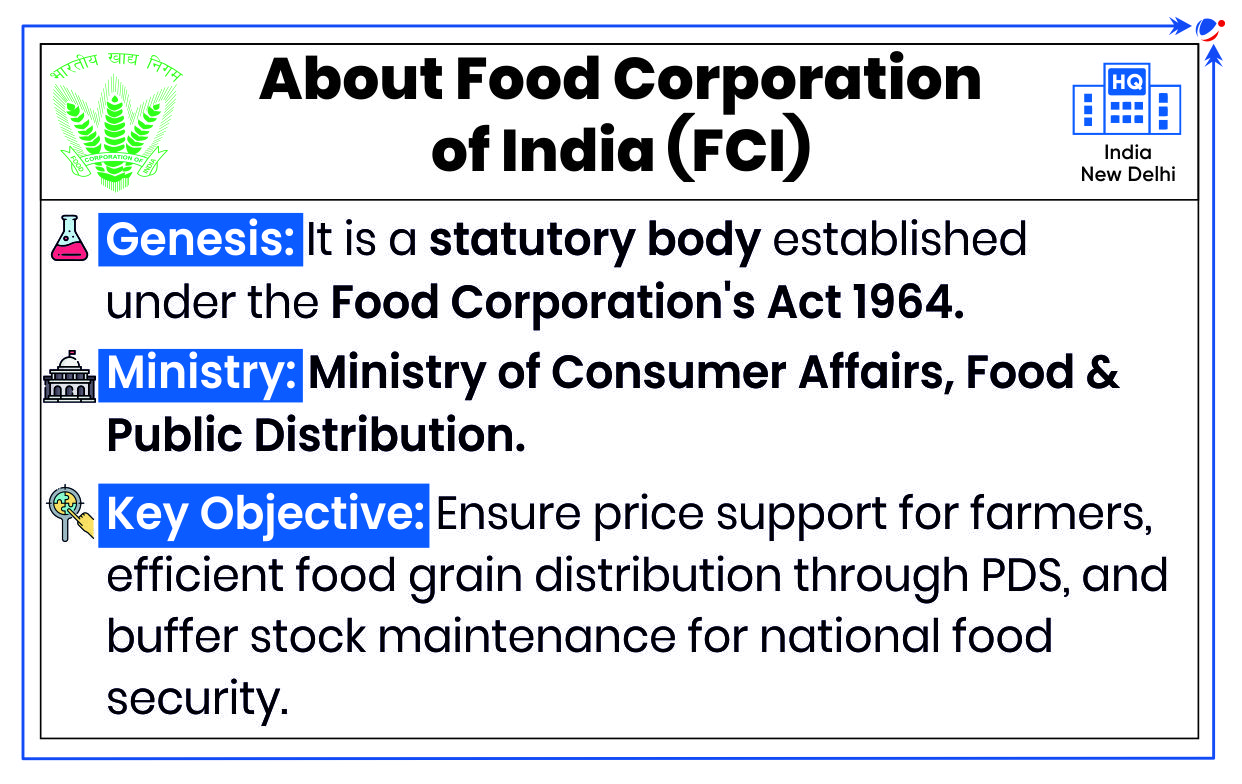
- About: Under this scheme, Food Corporation of India (FCI) sells surplus food grains (wheat & rice) from the central pool in open market via e-auction at pre-determined prices.
- Aim: To control market prices and curbs inflation.
- Eligibility: Processors / Atta Chakki / Flour Millers of Wheat Products. (Traders / Bulk Buyers are not allowed through e-auction.
- Usually, states are also allowed to procure food grains without participating in auctions.
Article Sources
1 sourceIIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources)
About VISTAAR
- It is a "Network" of Networks (Al-augmented) and every State can build their own Agri-Advisory network.
- It is a comprehensive network that connects decentralized databases to provide seamless access to vital agricultural resources.
- Objective: Enhance decision-making and resource utilization
- Significance
- Expand access to high-quality advisory services on crop production, marketing, value addition, and supply chain management.
- Provide farmers with information on relevant government schemes.
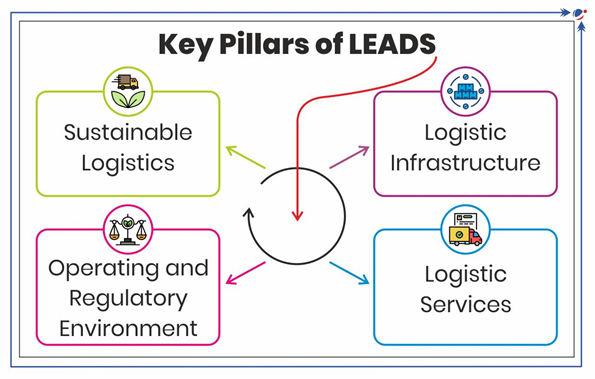
LEADS 2024 is has been released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
About LEADS
- Objective: Provides insights into improvement of logistics performance at State/UT level.
- LEADS was conceived on the lines of Logistics Performance Index (LPI) of World Bank in 2018.
- While the LPI relies entirely on perception-based surveys, LEADS incorporates both perception as well as objectivity.
- LEADS was conceived on the lines of Logistics Performance Index (LPI) of World Bank in 2018.
- Parameters: Evaluates logistics performance across four key pillars (refer to infographic).
- Categories of State/UTs: They are categorised into four groups Coastal, Landlocked, Northeast and Union Territories.
- And further they are given tags of Achievers, Fast movers, and Aspirers on the basis of their performance.
- Performance Highlights of 2024
- Achievers: Gujarat, Haryana, Assam, Chandigarh, etc.
- Fast movers: Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh etc.
- Aspirers: Kerala, West Bengal, Manipur, Chhattisgarh, etc.
LEAD frameworkMinistry also urged logistics sector to adopt LEAD framework – Longevity, Efficiency and Effectiveness, Accessibility and Accountability and Digitalisation of processes to transform the logistics sector.
|
The National eGovernance Division, under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, has developed Entity Locker.
About Entity Locker
- It is a secure, cloud-based solution that simplifies storage, sharing, and verification of documents for large organisations, corporations, micro, small, and medium Enterprises,etc.
- It is a critical component of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure.
- Entity Locker offer:
- Real-time access and verification of documents through integration with government databases
- Consent-based mechanisms for secure sharing of sensitive information
- Aadhaar-authenticated role-based access management to ensure accountability.
- 10 GB of encrypted cloud storage and Legally valid digital signatures for authenticating documents.
Prime Minister has inaugurated Z-Morh tunnel in Ganderbal’s Sonamarg area in J&K.
About Z Morh Tunnel
- Initially started by BRO in 2015 and evolved with National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited.
- APCO Infratech firm has been instrumental in executing the project.
- Situated at an altitude of 8,650 feet, it is a two-lane road tunnel equipped with parallel 7.5-metre-wide escape passage.
- Spanning 12 km that includes main 6.4 km main tunnel, an egress tunnel, and approach roads.
- Significance:
- Enhance all-weather connectivity between Srinagar and Sonamarg enroute to Leh.
- Ensure safe and uninterrupted access to Ladakh region.
- Promote tourism by transforming Sonamarg, boosting winter tourism, adventure sports, and local livelihoods.
The Banihal bypass has been completed.
About Banihal Pass
- The pass is 2.35 km road section of NH-44 in Jammu and Kashmir,
- NH44, also known as the Old NH 7, is the longest national highway in India.
- It stretches 3,745 kilometers, connecting Srinagar in the northern tip of Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari at the southernmost point of India.
- The bypass is particularly important for security forces, enabling rapid movement, and will also reduce the travel time between Kharpora, Banihal, and the Navyuga Tunnel to just seven minutes.
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Anji Khad Bridge: Key Details
- Location: Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir, part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) Project.
- Dimensions:
- Length: 725.5 meters
- Height: 331 meters above the Anji River (a tributary of the Chenab).
- Significance:
- Enhances connectivity between Katra and the Kashmir Valley.
- Expected to boost tourism and foster economic growth in Jammu and Kashmir.





