Why in the News?
INTERPOL issued its first Silver Notice in a 52-country pilot, including India, and Ministry of Home Affairs also launched BHARATPOL portal to seamlessly connect with INTERPOL.
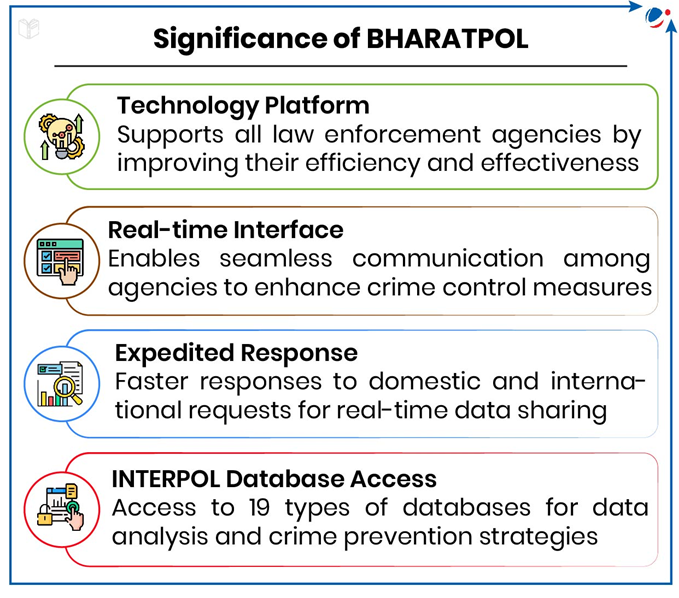
About Bharatpol
- Portal: BHARATPOL is an online portal for international police cooperation developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Through this, every agency and police force in India will be able to seamlessly connect with INTERPOL, thereby expediting investigations.
- Five Key Modules:
- Connect: Will enable all law enforcement agencies to essentially function as an extension of INTERPOL's National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi).
- INTERPOL Notices: System will ensure quick, secure, and structured transmission of requests for INTERPOL notices, enabling a scientific mechanism to swiftly locate criminals from India and across the globe, within India.
- References: INTERPOL references from 196 countries will make it much simpler to seek and provide international assistance for investigations abroad.
- Broadcast: Through this, requests for assistance from 195 countries will now be immediately available.
- Resources: It will facilitate the exchange and management of documents and capacity-building initiatives.
About INTERPOL
- Genesis: Established as International Criminal Police Commission (ICPC) during 2nd International Police Congress in Vienna in 1923.
- It was established as INTERPOL – The International Criminal Police Organization – after adoption of its Constitution in 1956 at its 25th General Assembly.
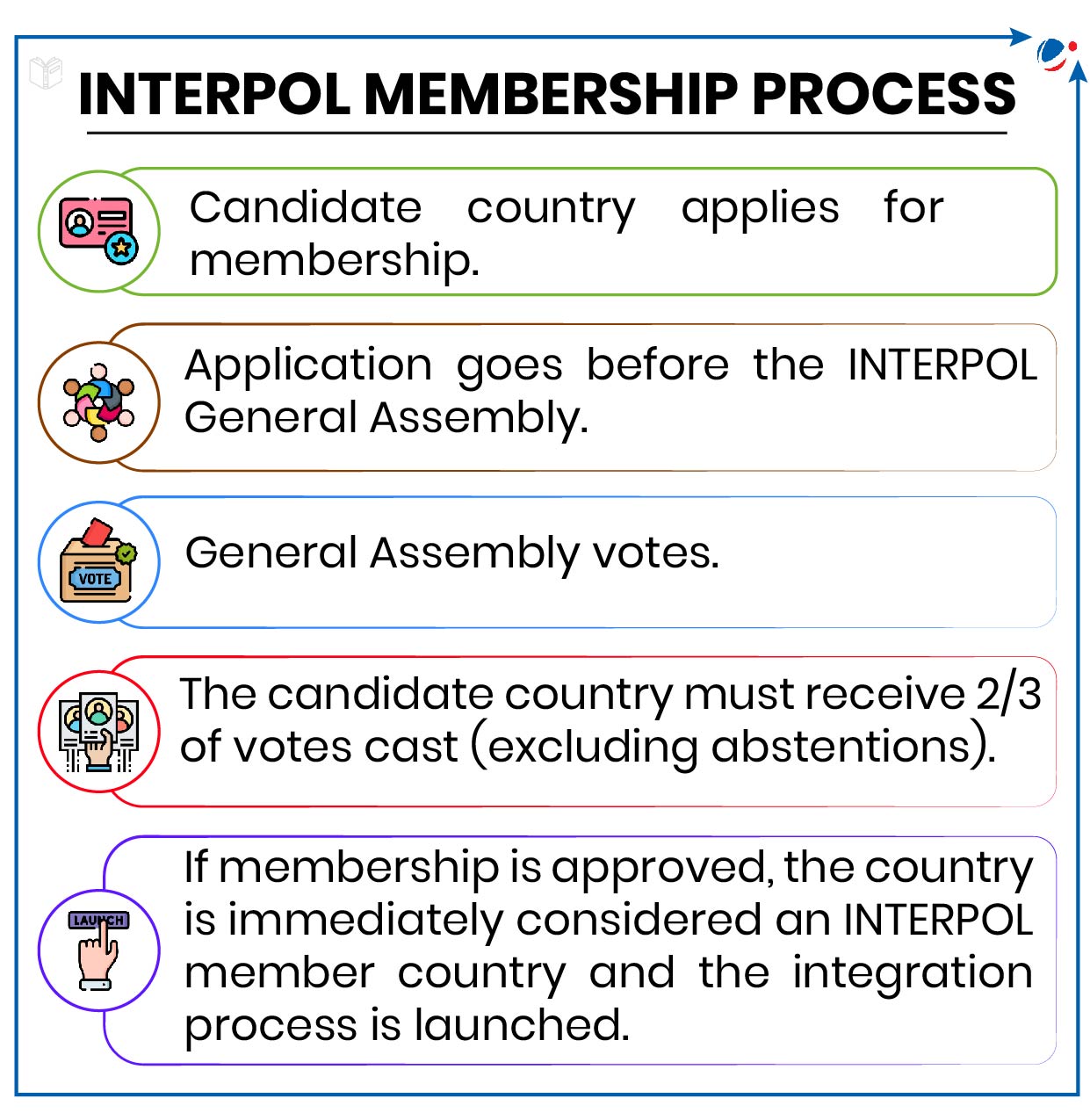
- Members: 196 countries including India as one of the founding members.
- Headquarters: Lyon, France.
- National Central Bureau (NCBs): Established by member countries as a point of access for INTERPOL affairs.
- NCBs connects with the General Secretariat via INTERPOL's secure global police communications network called I-24/7.
- CBI is India's NCB to the INTERPOL.
- Governing Bodies: The General Assembly and Executive Committee.
- General Assembly (GA) is INTERPOL's supreme governing body, comprising representatives from each of our member countries, which meets once a year.
- 13-member Executive Committee is the governing body in charge of supervising the execution of the GA's decisions and administration and work of General Secretariat.
- It has 13 members including President (elected for four years), which are elected by the GA and it meets thrice a year.
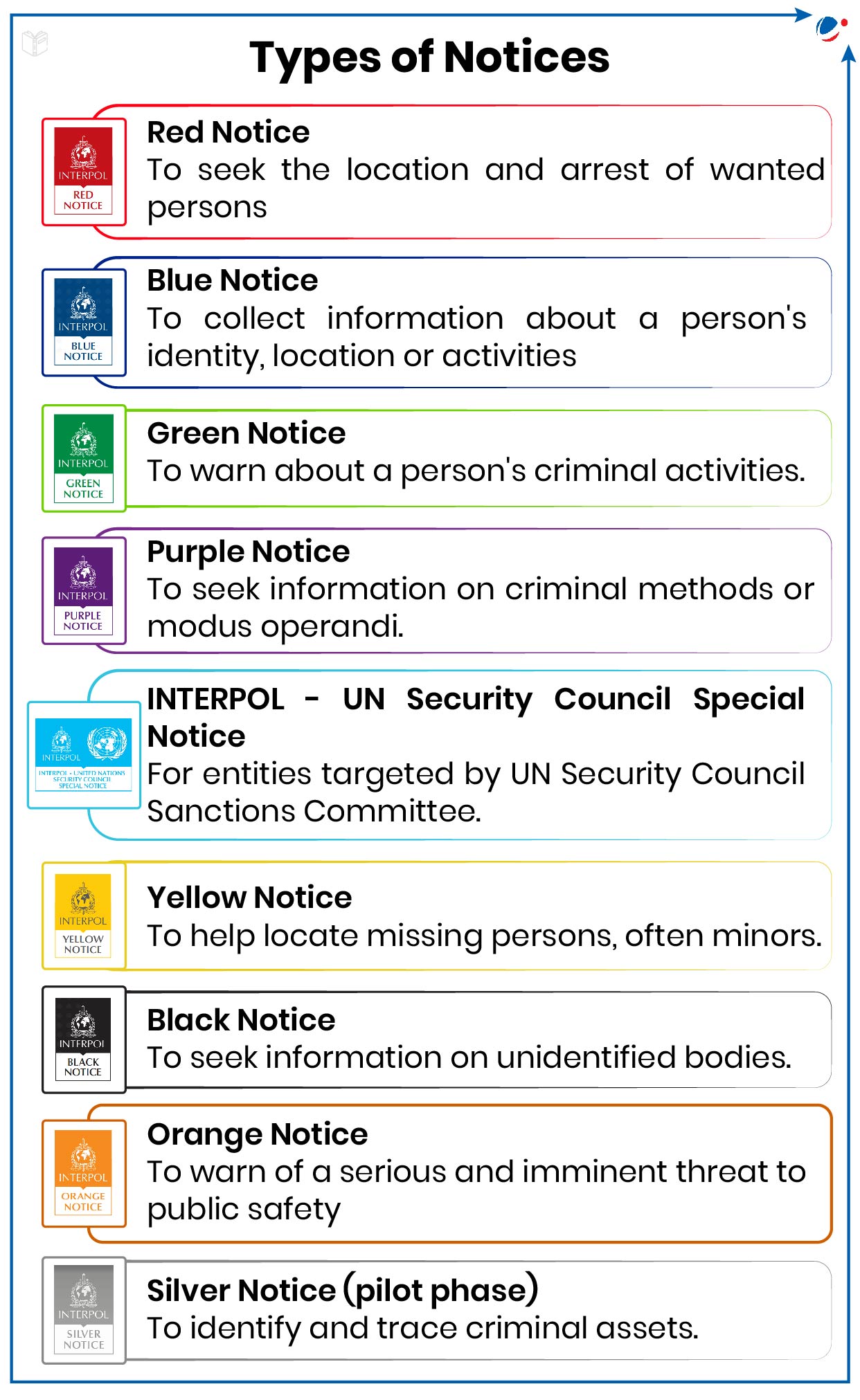
- Notices: INTERPOL's colour coded notices are international requests for cooperation or alerts allowing police in member countries to share critical crime-related information.
- Notices are published by the General Secretariat at the request of a NCB and are made available to all our member countries.
Role of India in INTERPOL
|
Need for International Police Cooperation
- Transnational nature of crimes: Crimes like money laundering, trafficking, and smuggling span borders.
- For instance, INTERPOL launched Operation HAECHI for strengthening transnational coordination against cyber-enabled financial crimes.
- New age criminal activities: Emerging threats like cybercrime, radicalization, and trafficking exploit global legal gaps.
- For instance, in November 2024, Operation Serengeti of INTERPOL led to arrests of more than 1,000 suspected cybercriminals responsible for 35,000 victims in 19 countries across Africa.
- Counter-terrorism efforts: Intelligence-sharing and coordinated law enforcement actions are key to countering sophisticated networks terrorist network for financing, recruitment, and execution of attacks worldwide.
- Strengthening legal assistance: INTERPOL's Operation FLASH-WEKA was coordinated with participation of 54 countries to dismantle organized crime networks behind human trafficking in Africa.
- Resource Optimization: Pooling of resources is required for intelligence sharing, mitigating transnational crimes and tracking new age criminal activities.
Obstacles in International Police Cooperation
- Legal and Procedural Disparities: Variations in legal systems, criminal laws and human rights standards create conflicts in investigative procedures, evidence collection and prosecutions.
- Cultural Barriers: Language barriers impede effective communication, cultural differences create conflicts and varying levels of corruption undermine trust.
- Resource limitations: Disparities in technological capabilities hinder seamless information sharing and restrict participation in joint operations.
- Political indifference: Political tensions and conflicting national interests hinder comprehensive cooperation.
Conclusion
While challenges like jurisdictional conflicts, legal differences, and data privacy concerns persist, continuous collaboration, technological advancements, and diplomatic efforts can strengthen global policing efforts. As crime continues to evolve in an increasingly interconnected world, international police cooperation remains indispensable in fostering a safer and more just global society.







