Why in the News?
Prime Minister met with President of France on the sidelines of the G7 Summit.
More on the News
- In the Meet, both the countries focused on the 'Horizon 2047' Roadmap and the Indo-Pacific Roadmap.
- The 'Horizon 2047' Roadmap constitutes 3 pillars.
- Partnership for security and sovereignty: Make Indo-Pacific an area of stability; Counter online radicalisation and combat terror through the No Money for Terror (NMFT), etc.
- Partnership for the planet: Through the Indo-Pacific Parks Partnership, International Solar Alliance and the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)
- Partnership for the people: The Partnership Agreement on Migration and Mobility (2021) will enhance the mobility of students, graduates.
- They also agreed to further intensify strategic defence cooperation with increased focus on 'Make in India'.
The growing convergence between India-France Relations
- Defense Cooperation: France (33%) is India's second largest arms supplier as per the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). Key projects e.g., Rafale aircraft purchases and the P-75 Scorpene Project.
- India and France have announced a "defence industrial roadmap": Aiming for co-design, co-development, and co-production to meet India's defense needs and export to friendly nations.
- Key project, e.g., Maintenance Repair and Overhaul (MRO) facilities for leading-edge aviation propulsion (LEAP) and Rafale engines.
- Military exercises: bilateral exercises e.g., VARUNA and FRINJEX-23, and multilateral exercises e.g., as La Perouse and ORION.
- India and France have announced a "defence industrial roadmap": Aiming for co-design, co-development, and co-production to meet India's defense needs and export to friendly nations.
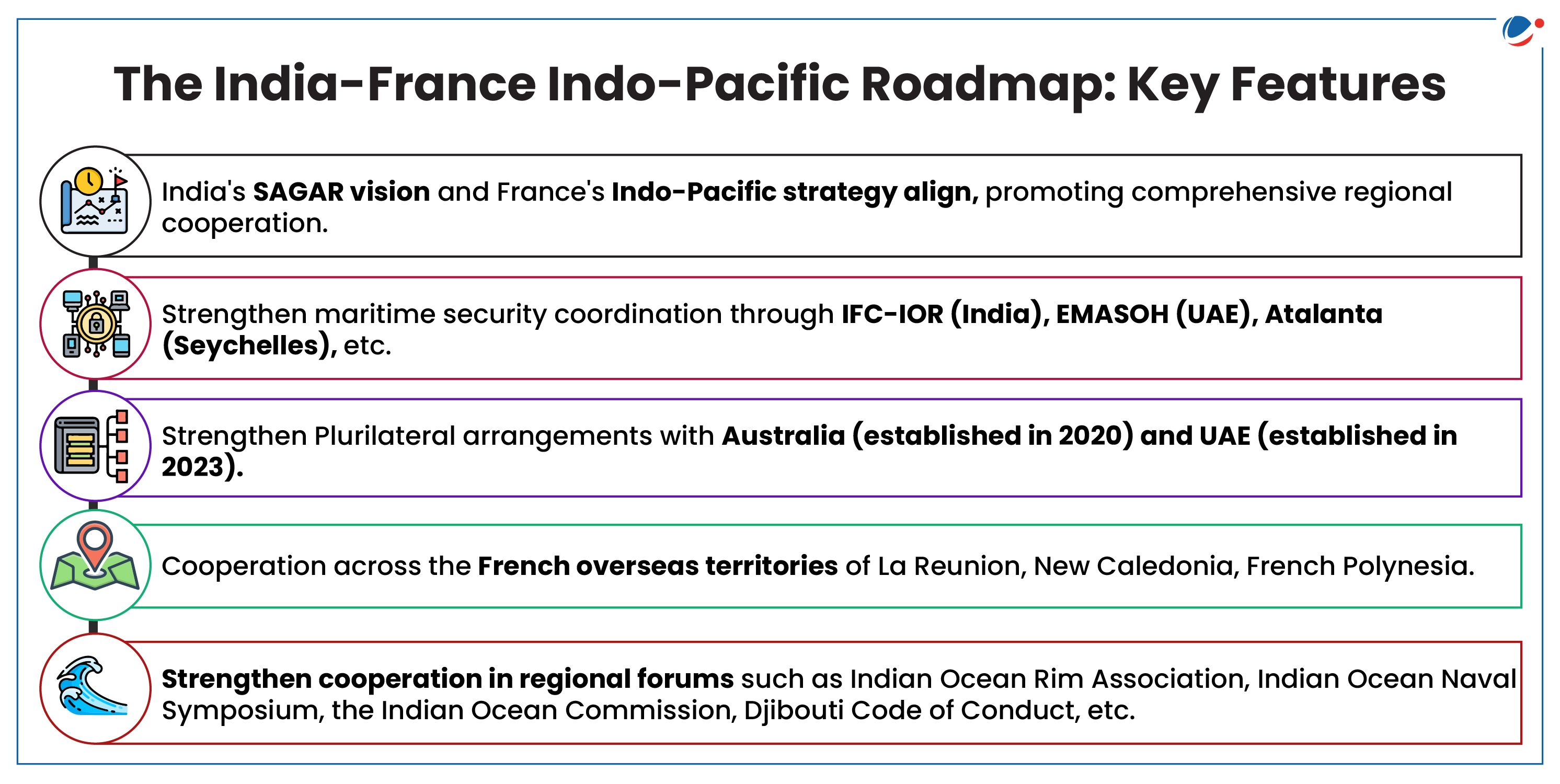
- Geo-Strategic: The India-France Indo-Pacific Roadmap, released in 2023 broadened the scope of bilateral cooperation from the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) to encompass the entire Indo-Pacific region.
- Space Cooperation: France remains a major supplier of components for the Indian space programme.
- Both agreed to collaborate on future launch vehicles and the TRISHNA Earth Observation mission.
- Economic Cooperation: France is one of the largest investors in India with FDI inflow of $659.77 million for FY 2022-23.
- India's Tata Group and France's Airbus have agreed to manufacture civilian helicopters.
- In the aviation sector, CFM International secured an agreement with India's Akasa Air for the purchase of over 300 LEAP-1B engines.
- Digital Cooperation: Launched Unified Payments Interface (UPI) from Eiffel Tower offering secure and convenient transactions for Indian visitors and NRIs.
- French company has developed 14 supercomputers including the fastest supercomputer Param Siddhi at 4.6 petaflops/second.
- Multilateral Cooperation: France has been a consistent supporter of a permanent seat for India on the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- It has also actively supported India's stances on Kashmir and terrorism at the United Nations (UN) as well as bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- Helped India's accession to the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), Wassenaar Arrangement (WA) and Australia Group (AG).
Challenges in India and France Relations
- Bilateral Trade Figures: In 2022, bilateral trade between India and France stood at US$15.8 billion, which is consistently increasing but still below its potential when compared to other partnerships.
- Visa restrictions: Correspondents based in India issued a letter of protest over the case, saying that they were all "grappling with increased visa restrictions in recent years".
- Inordinate delay in Nuclear Agreement: There are technical, financial, and civil nuclear liability issues that both sides have to resolve on Jaitapur nuclear power reactors.
- Differing approach in Strategic Autonomy: India's foreign policy prioritizes non-alignment and sovereignty, while France engages in pragmatic alliances to balance major powers' influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This difference in approach poses a substantial challenge to aligning their goals effectively, particularly in the face of China's growing assertiveness.
Way Forward
- Balance diverging 'strategic autonomy': Which means, more flexibility in accommodating each other's strategic imperatives while pursuing one's stated objectives.
- Leverage existing cooperation mechanisms: E.g., the India-France Joint Working Group on counterterrorism, can facilitate greater convergence in addressing shared security concerns in the Indo-Pacific.
- Effective coordination: Regular dialogue at diplomatic, security, military, level to align strategic objectives.
- Expand defense cooperation: E.g., through joint military exercises and knowledge-sharing through joint patrols.
- Active engagement in multilateral forums. E.g., the Quad and I2U2, etc., and foster cultural exchanges.
France's Ambassador quoting the 19th-century French historian Jules Michelet who described India as "the matrix of the world" said that the India-France partnership is "universal" as it goes from the "sea to the space" and beyond.






