Why in the News?
DRDO has conducted first successful flight test (named Mission Divyastra) of indigenously developed Agni-5 missile with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-Entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology.
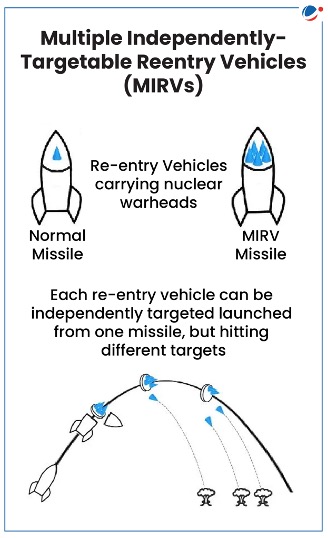
About MIRV technology
- Genesis: Originally developed in the early 1960s to allow a single missile to carry multiple nuclear warheads, each capable of striking different targets independently.
- Warheads can be released from the missile at different speeds and in different directions.
- First country: The United States of America was the first country to develop MIRV technology.
- Russia, United Kingdom, France, and China also have MIRV Technology.
- In 2017, Pakistan reportedly tested a MIRVed missile, the Ababeel.
- MIRVs can be launched from land or sea platforms (with submarine).
- The use of MIRVs on submarines is considered less destabilizing than on land-based missiles as nuclear submarines (carrying these missiles) is difficult to locate.
- Although MIRVs were not initially intended to defeat ballistic missile defences (BMD), they are much more difficult to defend against than traditional missiles and are considered effective BMD countermeasures.

Challenges in MIRV technology
- Vulnerable: Land-based MIRVs are particularly destabilizing because many warheads on fewer missiles are vulnerable to attack, incentivizing an adversary to strike first in a time of crisis.
- Arm-race: MIRVs held open the possibility of a damage-limiting first strike against an adversary’s strategic nuclear forces, thereby exacerbating both arms-race and crisis instability.
- Other Challenges: miniaturisation of warheads, development of advanced guidance systems, requirement of additional fissile material like plutonium etc.
Conclusion
While affirming its commitment to global disarmament, India must navigate the delicate balance between technological advancements, regional power dynamics, and international perceptions. As India stands at the forefront of MIRV-capable nations, the road ahead calls for strategic foresight, diplomatic acumen, and a steadfast commitment to maintaining a stable and secure global order.
Agni-5 Missile
|



