Why in the news?
The year 2024 marks 75 years since the creation of the modern Commonwealth, with the signing of the London Declaration.
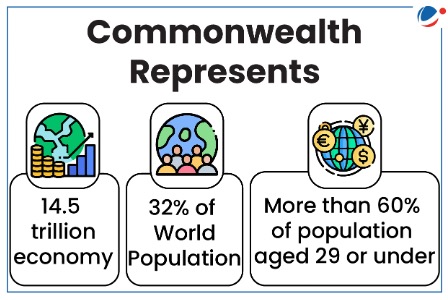
About Commonwealth

- About: It is a voluntary association of countries, most of which are formerly British colonies, collaborating on democracy, trade, and climate change.
- Genesis:
- The British Commonwealth of Nations: At the 1926 imperial conference, Britain and the Dominions (semi-independent countries) agreed as equal members of a community within the British Empire. They owed allegiance to the British monarch, but the UK didn't rule over them.
- India's Independence (1947): India desired to become a republic, but it also wanted to stay a member of the Commonwealth.
- Adoption of London Declaration (1949): Declared that republics and other countries could be part of the Commonwealth. Henceforth, the Modern Commonwealth of Nations was established.
- Initially it comprised eight members including India.
- Current Members: 56 members (including India)
- Working: Commonwealth Heads of Government (CHOGM) meet every two years (latest being in Rwanda in 2022) to discuss pertinent issues and release a summit communiqué.
- Organizational Structure:
Organisations | Objective | HQ |
|---|---|---|
The Commonwealth Secretariat(CS) | Supports members in achieving the organization's goals. | London |
The Commonwealth Foundation (CF) | Promotes people's participation in democracy and development. | London |
The Commonwealth of Learning(COL) | Advocates for open learning and distance education. | Burnaby, Canada |
- Other Key Information
- The Commonwealth has no charter, treaty or constitution.
- All members are considered equal, and decisions are made by consensus.
- Member countries choose the Head of the Commonwealth.
- Suspension of members can occur following breaches of human rights, as seen in cases such as Fiji, Pakistan, Zimbabwe, Nigeria, and the Maldives.
- Commonwealth Games are quadrennial international multisport event contested by athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations.
Major Initiatives of the Commonwealth
- Promoting democracy and human rights: Agreements such as the 1971 Declaration of Commonwealth Principles and the 1991 Harare Commonwealth Declaration underscore the Commonwealth's commitment to promoting these values.
- Commonwealth charter (2012): It sets out 16 core shared principles such as Rule of Law, etc. to which all member countries have committed.
- Role in Ending Apartheid: Commonwealth's advocacy and support played a significant role in ending apartheid in South Africa.
- Development Partnerships: Initiatives such as The Commonwealth Fund for Technical Co-operation (CFTC), Commonwealth Scholarships Commission, and Overseas Development Assistance to support development initiatives and economic growth in Commonwealth countries.
- Empowering Youths: It is the only intergovernmental organisation to have a dedicated youth programme, Commonwealth Youth Programme(CYP).
- Commonwealth Cyber Declaration (2018): To support the development of a cyberspace that promotes social and economic development and protects digital rights.
- Commonwealth Secretariat Countering Violent Extremism Unit: Established in 2017 to provide support to member countries in developing their national strategies to counter violent extremism.
- Commonwealth Climate Change initiatives: This includes Commonwealth Clean Ocean Alliance, the commonwealth Blue charter project, Commonwealth Climate Finance Access Hub etc.
India's relations with the Commonwealth
- India is the largest member state of the Commonwealth, with nearly 60% of the total population of the association.
- It is the fourth largest contributor to the Commonwealth. It additionally contributes to CFTC, CF, CYP and COL.
- India hosted the Commonwealth Summit (CHOGM) and Commonwealth Games (CWG) in 1983 and 2010 respectively in New Delhi.
- Commonwealth Sub Window (US$ 50 Million over 5 years) under the India-UN Development Fund was established in 2018 to provide grant-in-aid assistance to Commonwealth members for projects related to SDG implementation and Climate Action.
Is the Commonwealth relevant in the present times?
- Arguments in favour:
- Election Observation Missions: Since 1967, the Commonwealth has sent 140 missions to monitor elections in around 40 countries, promoting transparency and fair electoral processes and thereby upholding commitment to democracy.
- Evolving Membership: Newer members, including non-former British colonies such as Togo and Gabon indicate the Commonwealth's attractiveness as a forum for cooperation and dialogue.
- Advocacy for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Commonwealth committed to the implementation of SDGs, particularly Goal 16 focusing on peace and development.
- Trade: Bilateral costs for trading partners in Commonwealth countries are on average 21% less than between those in non-member countries.
- Unity through Shared Experiences: Common bonds, language (English), history and strong people to people connect foster unity and collaboration among Commonwealth nations.
- Arguments against:
- Critics points out that its very existence is legitimizing colonization. Members, as a sovereign nation, should focus on our international relationships in other platforms such as the UN, ASEAN and other bodies.
- Less relevant in addressing contemporary global issues: For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there were concerns about the organization's effectiveness in coordinating responses and providing support to member states.
- Host Country Controversy: The choice of Rwanda as the CHOGM host raises questions due to concerns over its human rights record.
- Lack of cohesion among members: Nine Commonwealth countries abstained from UN voting condemning Russia in the on-going Russia-Ukraine war.
- Funding Constraints: Limited funding to the Commonwealth's international bureaucracy hampers its effectiveness, with British investment primarily bilateral rather than directed to the Secretariat's programs.
Conclusion
Leveraging the Commonwealth network for mitigating climate Change, enhanced business, trade, and people-to-people connections and is essential for long-term growth and prosperity.




