Why in the News?
The Ministry of Ayush recently marked its 10th anniversary.
More on the News
- Founded in 2014, the Ministry of Ayush aims to revive ancient medical knowledge while supporting the UN's Sustainable Development Goals and Universal Health Coverage.
- The Ministry evolved from the Department of Indian System of Medicine & Homoeopathy, which was created in 1995 and renamed the Department of Ayush in 2003.
- "AYUSH" is an acronym for the traditional medical systems practiced in India: Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy.
Key Achievements of Ministry of Ayush in last decade
- Expanding Ayush Infrastructure: India has over 755,780 registered Ayush practitioners, supported by 886 undergraduate and 251 postgraduate colleges.
- Additionally, three advanced National Ayush Institutes have been established to enhance education and healthcare in the Ayush sector.
- Research and Innovation: The Ayush Research Portal hosts over 43,000 studies.
- Key developments like AYUSH-64 and Kabasur Kudineer were introduced for COVID-19 management.
- Economic Impact: The Ayush market has grown from USD 2.85 billion in 2014 to USD 43.4 billion in 2023, with exports increasing from USD 1.09 billion to USD 2.16 billion.
- Technology Integration: Digital platforms like Ayush Grid, e-Sanjeevani, and Ayush Telemedicine have improved healthcare access, especially in remote areas.
- International Day of Yoga (IDY): Achieved global recognition, with 24.53 crore participants in 2024.
- National Ayush Mission (NAM): launched the Centrally Sponsored Scheme in 2014.
About National AYUSH Mission (NAM)
|
Steps taken by India to promote Traditional Medicines
- International Cooperation: 24 MoUs with countries and 48 institute-level MoUs and the Ayush Visa and Heal in India portal for medical tourism.
- Quality Assurance and Certifications: introduced the Ayush Mark and Ayush Premium Mark certification programs for Ayush products.
- Provided WHO Good Manufacturing Practices-Certified Manufacturing Units for Certificate of Pharmaceutical Products (COPP) certifications to 31 Ayurvedic drug manufacturers to facilitate international trade.
- WHO Collaboration: India signed an agreement with WHO to establish the WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine (GCTM) in Jamnagar, Gujarat, with a US$ 85 million commitment.
- Capacity Building: The Champion Sector Services Scheme (CSSS) was launched to develop skilled human resources in the AYUSH sector and promote medical value travel services.
- Education Reforms: Under the NCISM Act, 2020, the government established the National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM) and National Commission for Homeopathy (NCH) to improve education and practice standards.
- AYURGYAN Scheme: To enhance and develop capacity in the Ayush healthcare sector.
- Policy Support: MoUs with various government departments to support infrastructure development, research, and the promotion of AYUSH practices.
- For ex- establishment of the Strategic Policy and Facilitation Bureau (SPFB) to facilitate investment in the AYUSH sector.
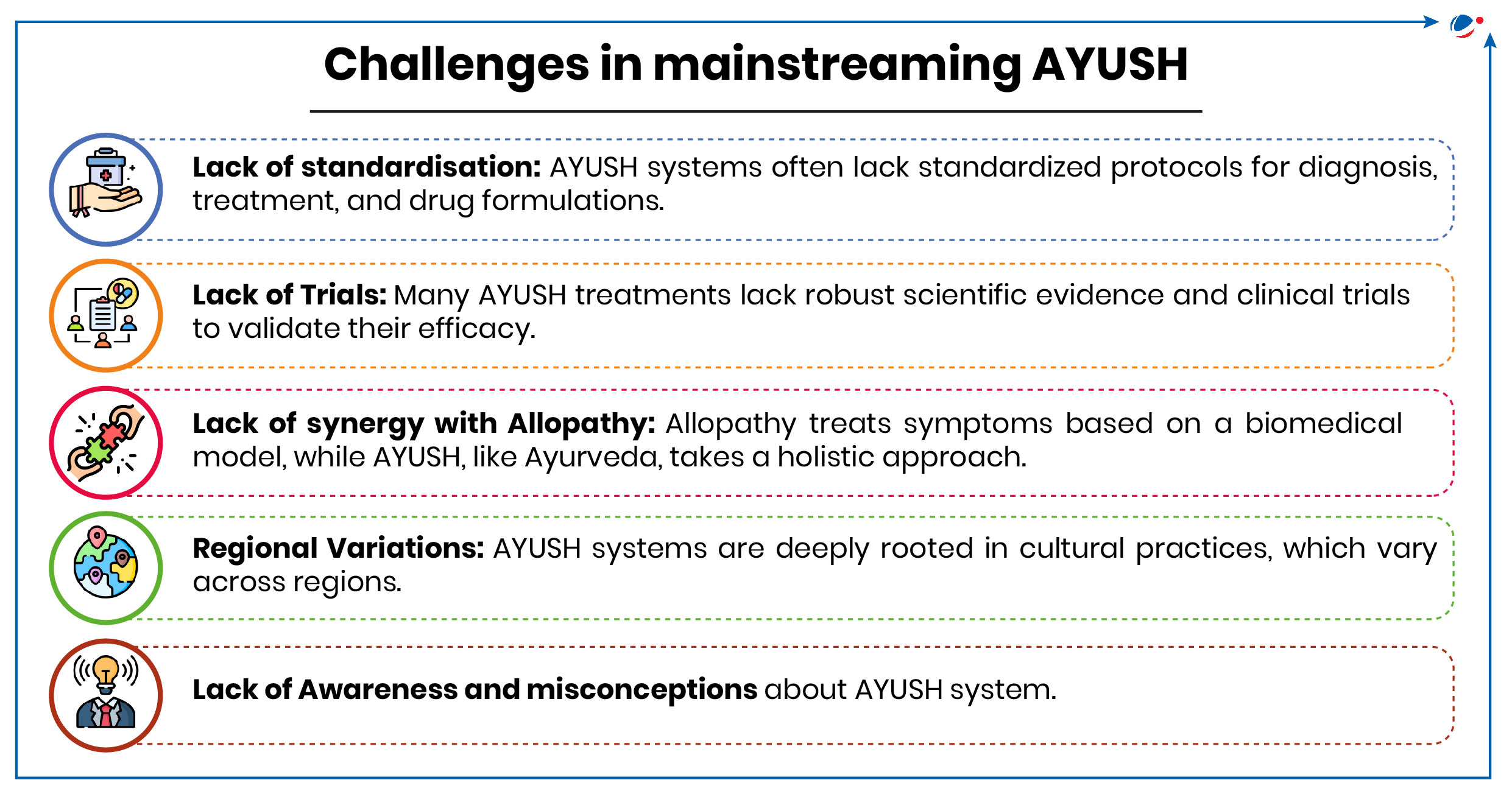
Way ahead
- Quality Control and Standardization:
- Invest in advanced labs and testing protocols.
- Develop systems for reporting adverse events with Ayush medicines.
- Conduct regular post-marketing surveillance for safety and efficacy.
- Align Ayush quality standards with global benchmarks like WHO.
- Research and Evidence-Based Practice
- Increase funding for clinical research on Ayush therapies, focusing on chronic diseases and prevention.
- Use local health data for large-scale epidemiological studies, with improved infrastructure and training.
- Bridging the Integration Gap
- Develop referral pathways and collaboration protocols between Ayush and allopathic systems.
- Integrate Ayush practitioners into primary healthcare teams and community health campaigns.
- Addressing Delays: By creating action plans for Ayush Health and Wellness Centres (AHWCs), providing training, financial incentives, and streamlining processes with technology.
- Consumer Confidence and Advocacy
- Promote responsible advertising and educate patients on the safe use of Ayush medicines.
- Encourage private insurance companies to cover Ayush treatments like Panchkarma where applicable.



