Updated NBSAP was launched at the Conference of Parties (COP) 16 to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in Colombia.
- NBSAP provides a framework for biodiversity conservation, enables focus on sustainable use of biological resources, and ensures fair and equitable sharing of benefits derived from them.
Key highlights of NBSAP 2024-30
- Background: First NBSAP was created in 1999. National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP) was adopted in 2008, which was updated in 2014 to align with Aichi Biodiversity Targets.
- Aligns with KMGBF: Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets: They are focused on three themes
- reducing threats to biodiversity,
- ensuring sustainable use of resources, and
- enhancing tools for implementation
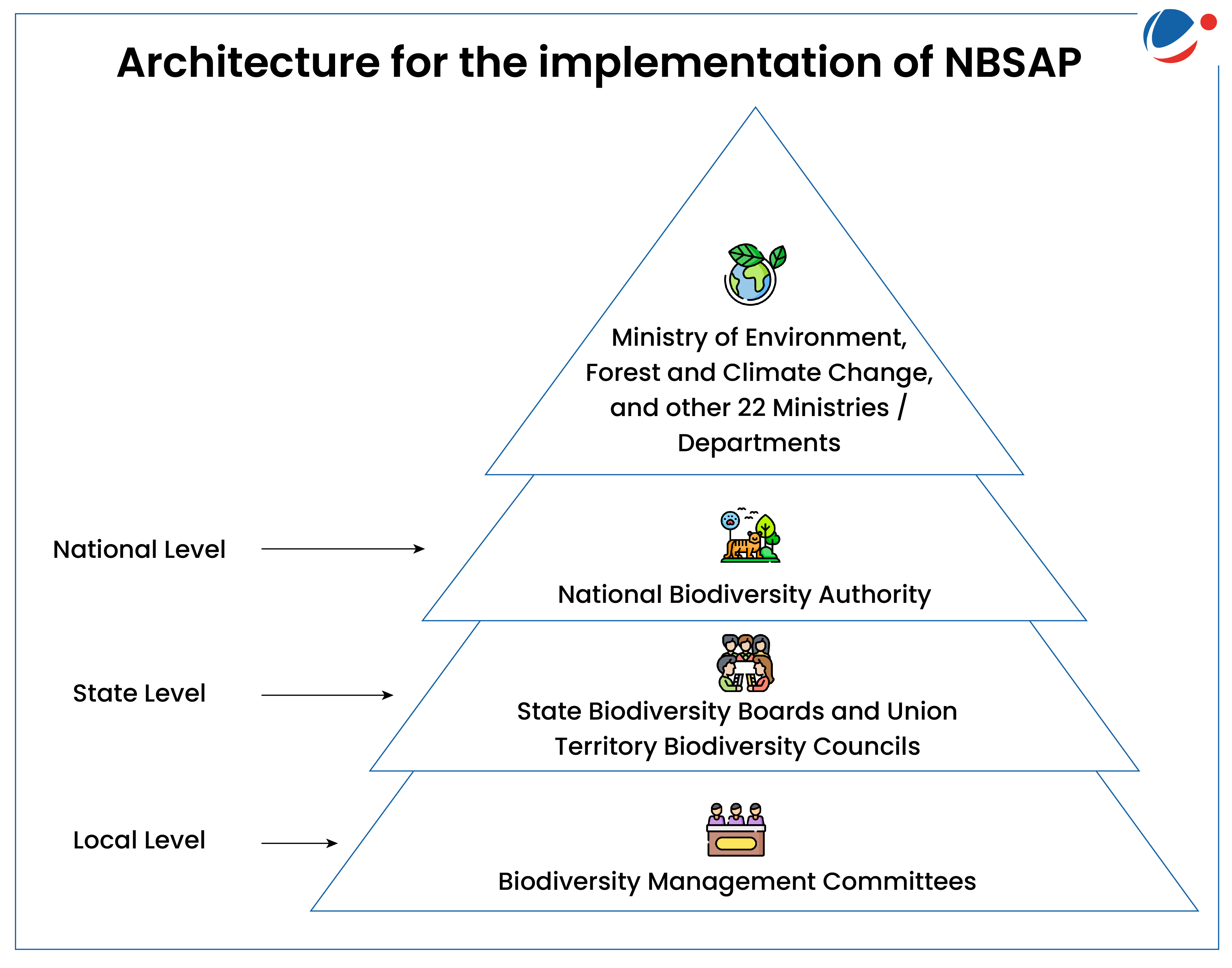
- Implementation: MoEFCC serves as the central agency (refer to the infographic)
- Capacity building: Efforts may include
- need and gap assessment;
- target group identification;
- identify experts/environment;
- Train for the acquisition of knowledge, skills
- Resource mobilization:
- Recognises India among the leading countries for implementation of Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN) at national level.
- BIOFIN is a global partnership launched by UNDP and the European Commission to support countries to enhance their financial management of biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Calls for encouraging private entrepreneurs, business houses, donors, and international agencies to support initiatives like, Greenbonds, Green Fund, Payment for Ecosystem Services, etc.
- Recognises India among the leading countries for implementation of Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN) at national level.







