The Study has found that flash floods are mainly centred in the Himalayas, the west coast, and Central India: Key Findings:
- Extremely flash flood-prone sub-basins are located in the Brahmaputra, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Brahmani, and West Coast River basins.
- High flash flood susceptibility is also observed in parts of the Godavari, Ganga, Mahi, and Indus River basins.
What are Flash Floods?
- Definition: A flash flood is a flood of short duration with a relatively high peak discharge in which the time interval between the observable causative event and the flood is less than four to six hours (WMO, 2006).
- Flash Floods and India:
- Between 2020-2022, the number of flash flood events increased from 132 to 184 (Jal Shakti Ministry).
- Every year, more than 5,000 people die due to Flash Floods
Key Drivers of Flash Floods
- 25% Flash floods occur typically within six hours of heavy rainfall often triggered by cloudbursts. E.g., Himalayan regions.
- Steep Topography and Narrow River Channels in Mountainous Regions: Facilitating rapid water accumulation and downstream surge.
- Saturated Soil (due to concrete, roads): Water fails to percolate and results in sudden surface runoff.
- Sudden release of dams, embankments, or check dams due to pressure buildup from upstream rainwater.
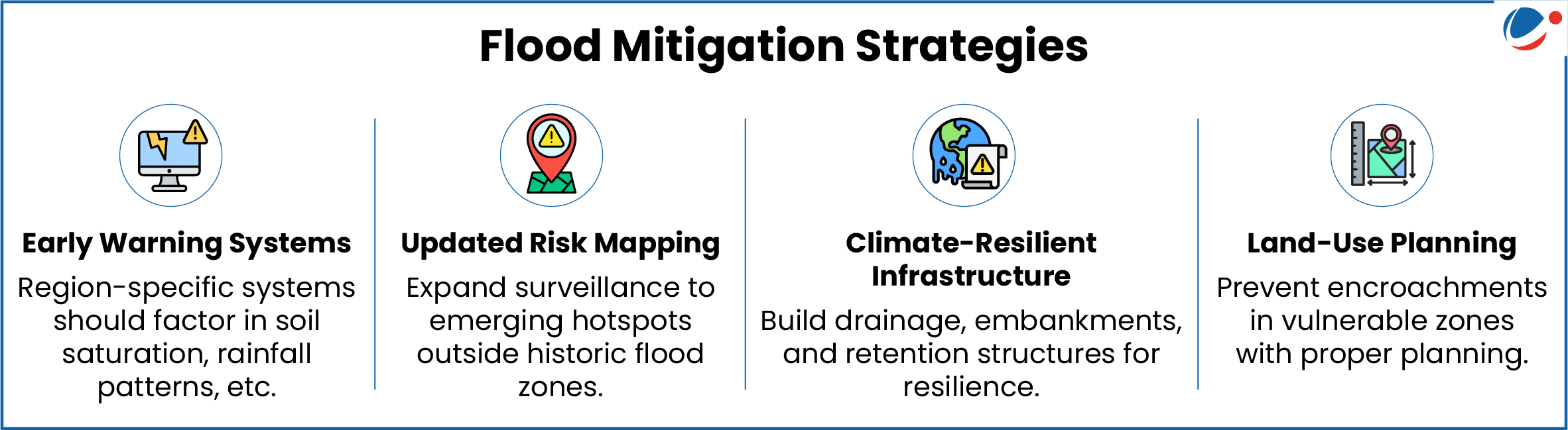
Flash Flood Guidance System (FFGS): A Tool for Early Warning and Risk Reduction
|






