The Supreme Court of India held that State investigative agencies (including State Anti-Corruption Bureaus and State police) are competent to register and investigate corruption cases under the Prevention of Corruption Act (PCA), 1988, even if the accused is a Central Government employee.
- The Court clarified that no prior permission of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is required before registering the case against the central government employee by the State police.
About PCA, 1988
- PCA 1988 act criminalises corrupt conduct like bribery, misappropriation, disproportionate assets etc.
- It aims to combat corruption in different government organisations and public sector entities.
Prime Minister recently inaugurated the Kaziranga Elevated Corridor Project designed to ensure safe wildlife movement across the Kaziranga National Park.
About Kaziranga National Park (KNP)
- Location: Between the Brahmaputra River and the Karbi (Mikir) Hills in Assam.
- Status: National Park, Tiger Reserve, Important Bird Area (IBA), and UNESCO World Heritage Site (1985).
- An important area for migratory birds as it is located at the junction of the Australasia and Indo-Asian flyway.
- Biodiversity found: Tigers, elephants, swamp deer, wild buffalo, etc.
- Largest population of Indian one-horned rhinoceros found here.
Indian Railways’ One Station One Product (OSOP) expanded to over 2,000 railway stations, empowering 1.32 Lakh artisans as of Jan 2026.
About OSOP
- Aim: Launched in 2022 to encourage indigenous and specialised products and crafts of India through providing display and sale outlets on railway stations across the country.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Railways.
- Products include: Artefacts made by indigenous tribes, handlooms by local weavers, handicrafts like wood carving, chikankari and zari-zardozi work and other processed/semi processed food items/products.
- Part of the broader “Vocal for Local” and Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecent policies of the present US President Donald Trump are referred to as The ‘Donroe doctrine’ as these largely reflect the 200 years old ‘Monroe Doctrine’.
About Monroe doctrine
- Proclaimed: In 1823 by U.S. President James Monroe (United States’ policy on the new political order).
- Objective:To establish U.S. dominance and security in its surrounding region.
- The three main concepts of the doctrine
- Non-colonization: European powers should not establish new colonies in the Americas.
- Non-intervention: Europe must not interfere in the affairs of independent American states.
- U.S. Non-interference: The U.S. would not meddle in European wars or colonies.
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Science and Technology recommended the use of steel slag–based technology for sustainable road construction, particularly in hilly terrains.
- Ministry’s Technology Development Board (TDB) also signed an agreement for commercial rollout of 'ECOFIX'.
- It is a pothole repair mix developed by CSIR–Central Road Research Institute (CRRI).
Steel slag
- Steel slag is a solid waste generated in the process of steel making and is mainly composed of oxides of calcium, iron, silicon, magnesium, and some other elements.
- Properties: Possesses strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Suitable for use as a construction material, concrete and cement applications, road construction etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has issued a notification declaring Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary as an Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ).
- ESZs are notified under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 by the central government as a "transition zone" from areas of high protection to areas involving lesser protection.
- It is generally declared around 10 Km area, but can vary for each site as per the notification.
About the Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary (1971)
- Location: It is a 610.5 sq km areasurrounding Kumbhalgarh Fort (a UNESCO World Heritage Site), in parts of Rajsamand, Udaipur, and Pali districts of Rajasthan.
- Covers four hill and mountain ranges of the Aravallis: Kumbhalgarh Range; Sadri Range; Desuri Range and the Bokhada Range.
- Wildlife: leopard, striped hyena, jungle cat, Indian pangolin, blue bull, chinkara etc.
- Vegetation: Predominantly dry deciduous, with forests of Dhok, Salar, Khair, and Churel trees.
India’s mustard crop is facing a serious threat in the form of Orobanche aegyptiaca.
- Orobanche aegyptiaca (Egyptian Broomrape) is a root-parasitic weed that lacks chlorophyll and depends entirely on host plants, especially mustard, extracting nutrients, carbon and water from them.
- By depriving the host crop of these, it causes wilting, yellowing and stunted growth of the plants and, thereby, lower mustard seed yields.
About Mustard
- Mustard is India’s biggest edible oil-yielding crop, which generally sown from mid- to late-October.
- Rajasthan is the largest mustard producing state.
- It is also susceptible to other pathogens including pests (especially aphids) and fungal diseases (white rust, leaf blight, stem rot and powdery mildew).
US President Trump has criticised the potential return of Diego Garcia by the UK to Mauritius which hosts a vital US military base.
About Diego Garcia
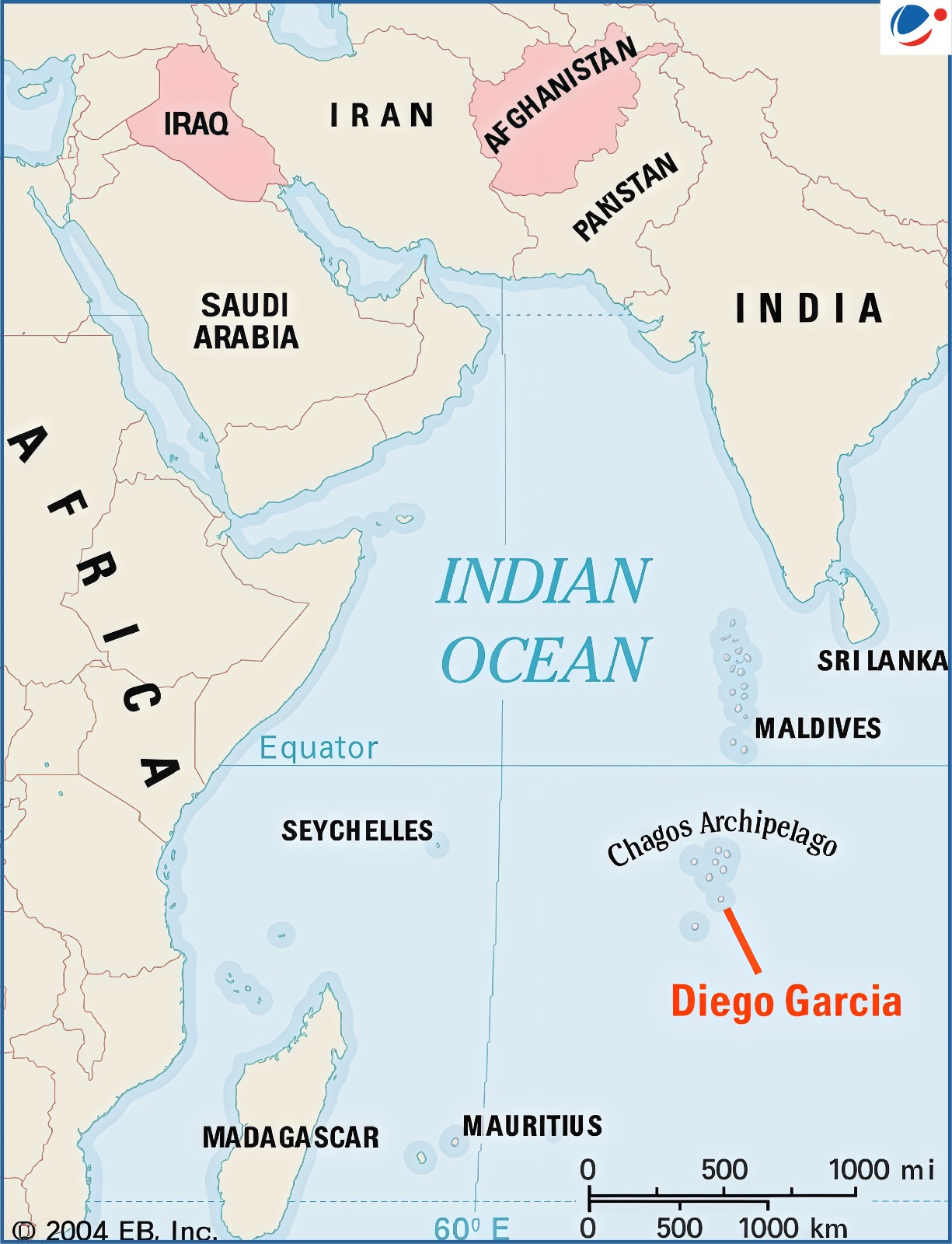
- Location: Diego Garcia is a coral atoll in the central Indian Ocean, part of the Chagos Archipelago.
- History: The Chagos Archipelago was administered by the United Kingdom as the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) from 1965.
- In May 2025, the United Kingdom and the Republic of Mauritius signed an agreement under which Mauritius is recognised as sovereign over the entire Chagos Archipelago, including Diego Garcia (with UK having a 99 years lease of Diego Garcia)
- Military use: Diego Garcia hosts a joint UK–US military facility.
Department of Atomic Energy is pushing for fabrication of an Indian Light Water Reactor (LWR) as a priority within the nuclear establishment.
About Light Water Reactors (LWRs)
- LWRs are nuclear reactors that use ordinary (light) water (H₂O) as both the coolant and the neutron moderator.
- LWRs currently account for over 85% of the civil nuclear reactor capacity in the world.
- Working principle: Fission of uranium fuel produces heat, which is transferred by light water to generate steam that drives turbines for electricity production.
- Fuel used: LWRs typically use low-enriched uranium (3–5% U-235).
- Indian context: India traditionally developed Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs), but has identified LWRs as a priority for rapid capacity addition.





