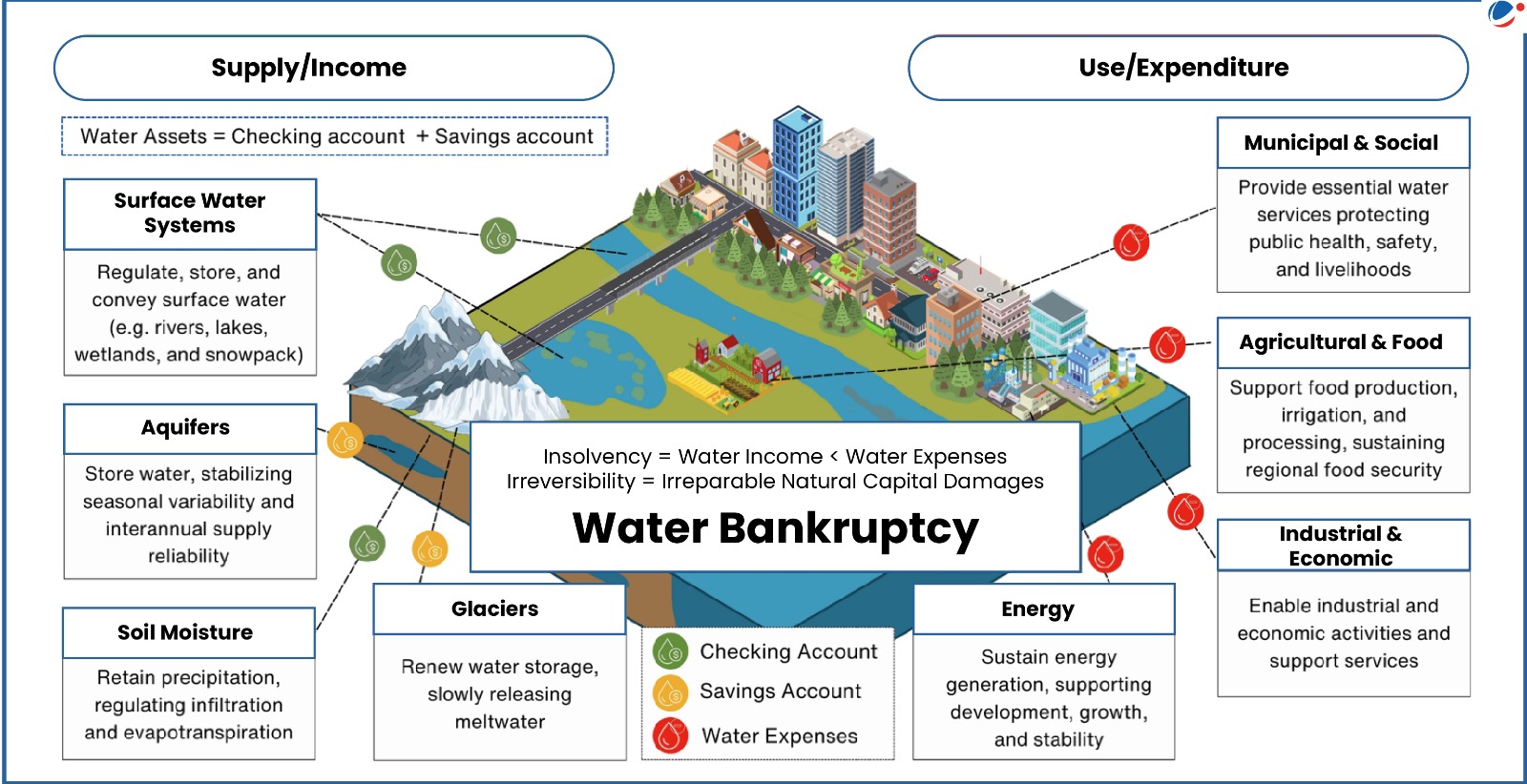
The report highlighted that the planet has entered the Global Water Bankruptcy era.
- Water Bankruptcy is a persistent post-crisis condition of human-water system in which long-term water use has exceeded renewable inflows and safe depletion limits, causing irreversible or effectively irreversible degradation.
- Report highlights that parts of the water and natural capital—rivers, lakes, aquifers, wetlands, soils, and glaciers—have been damaged beyond realistic prospects of full recovery.
- In contrast, water stress is a condition of high-water demand relative to supply but impacts are largely reversible and water crisis is where shock-driven disruptions temporarily push water systems beyond capacity but which can be restored through emergency and restoration measures.
Factors leading to Water Bankruptcy
- Slow-onset depletion: Chronic overuse of surface and groundwater slowly degrades storage and quality, with early warning signs ignored until irreversible thresholds are crossed.
- Infrastructure-driven overshoot: Large dams and transfers enable expansion beyond sustainable limits.
- Ecological liquidation: Wetlands, floodplains, forests, and soils are converted or degraded in ways that increase short-term productive capacity while eroding long-term water storage, filtration, and buffering.
- Climate-amplified overshoot: Climate change accelerates existing stress by reducing reliable supply and increasing variability in already overexploited systems.