India has signed a 15-year contract to explore polymetallic sulphides (PMS) with ISA in Carlsberg Ridge in Indian Ocean.
- It is India’s third exploration contract with International Seabed Authority (ISA), and second for PMS.
- Previous exploration contracts are Polymetallic Nodules in the Central Indian Ocean Basin and PMS in the Indian Ocean Ridge.
- Polymetallic nodules, also called manganese nodules, are rock concretions formed of concentric layers of iron and manganese hydroxides around a core, such as a shark tooth or shell.
- This is the first licence granted globally for exploring polymetallic sulphur nodules in the Carlsberg Ridge.
- The Carlsberg Ridge is a 3,00,000 sq km area in the Indian Ocean, specifically in the Arabian Sea, northwest Indian Ocean.
- It forms the boundary between the Indian and Arabian tectonic plates, extending from near Rodrigues Island to the Owen fracture zone.
- Previously, India has also applied for the Afanasy-Nikitin Sea (ANS) mount which is yet to be approved.
- ANS is located in the Central Indian Ocean and the territory has been claimed by Sri Lanka for exploration rights.
About Polymetallic sulphides (PMS)
- These deposits are rich sources of metals such as copper, zinc, gold, and silver, found on the ocean floor.
- These deposits occur in regions where hot, mineral-rich fluids from the Earth's mantle mixed with cold Ocean waters, leading to the precipitation of metal sulphides.

Union Minister for Communication unveiled the UPI- (Universal Postal Union) UPU Integration project aimed at transforming cross-border remittances.
About the UPU
- Established in 1874.
- It became a specialized agency of the UN in 1948.
- Headquarters: Berne.
- It is the second oldest international organization after the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) (1865).
- Members: 192 member countries, India is member.
- Function: Primary forum for cooperation between postal sector players. It helps to ensure a truly universal network of up-to-date products and services.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Indian government has introduced voluntary Hallmarking Unique Identification (HUID)-based hallmarking for Silver jewellery under revised standard aligning with the gold hallmarking system and enhancing traceability.
Hallmarking
- Hallmarking is the accurate determination and official recording of the proportionate content of precious metal in precious metal articles.
- It ensures authenticity, consumer protection, quality and traceability of jewellery and articles.
- In India it is regulated by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) [HQ: New Delhi]
- National standards body under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs
- Established under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986, now operates under BIS Act 2016.
- Formulates standards, certifies products (ISI mark, Hallmarking) and operates testing labs.
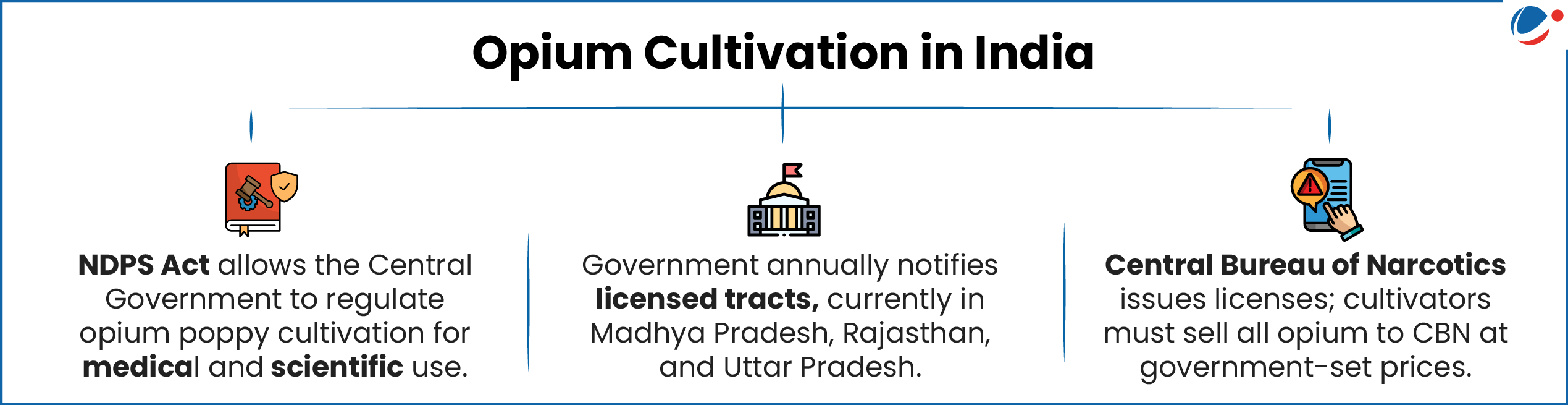
Union Government has announced Annual Licensing Policy for Opium Cultivation for 2025-26.
- The licensing policy is announced annually under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Rules, 1985, framed under the NDPS Act, 1985.
About Opium
- Opium poppy plant is the source of opium gum which contains several indispensable alkaloids (naturally occurring organic nitrogen-containing compounds) such as morphine, codeine and thebaine.
- Morphine is commonly used analgesic (pain relieving medicine) while codeine is used in manufacture of cough syrups.
- It is also grown as a source of edible seed and seed oil.
- India is the only country authorised by the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961) to produce gum opium.
- 11 other countries cultivate opium poppy, but do not extract gum.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe report was released by released by the Comptroller and Auditor General.
The report is first of its kind, providing comprehensive data, analysis, and trends on fiscal parameters for all 28 states over a 10-year period (2013-14 to 2022-23).
Key Findings
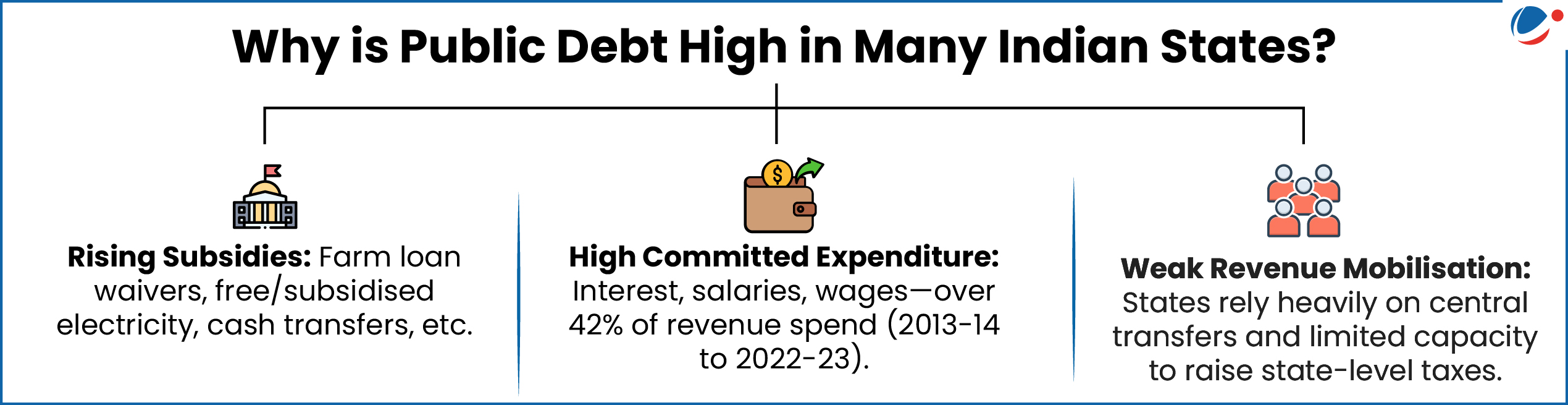
- States’ total debt in 2022-23 was 22.17 % of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM)Act (2003) benchmark: State Government Debt shall be 20% of GDP by 2024-25
- Debt-to-GSDP Ratio: Highest ratio of 40.35 per cent was recorded in Punjab, followed by Nagaland (37.15 per cent) and West Bengal (33.70 per cent)
- Fiscal Deficit: All 28 States in deficit; ranged from Gujarat (0.76% of GSDP) to Himachal Pradesh (6.46%).
- FRBM benchmark: States needed to achieve a fiscal deficit of 3.5 % of GSDP in FY 2022-23.
- Wide gaps in revenue capacity: States’ Own Tax Revenue (SOTR) share 70% in Haryana and as low as 9% in Arunachal Pradesh.
It is released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- It aims to provide meaningful insights into changes in the composition, growth, and structure of manufacturing industries, including output, value added, employment, and capital formation.
- The ASI is conducted annually under the Collection of Statistics (Amendment) Act, 2017.
- ASI covers factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948, Bidi and cigar units under the Bidi and Cigar Workers (Conditions of Employment) Act, 1966, and electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority (CEA).
- Defence establishments, oil storage and distribution depots, departmental units such as railway workshops, gas storage, etc., are not covered under ASI.
- The results are prepared at the state and major industry level.
Key highlights o’f the survey
- The top 5 industries in terms of Gross Value Added (GVA) are Basic metal, Motor vehicles, Chemical and Chemical products, Food Products, and Pharmaceutical products.
- The top 5 States in respect of employment are Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Gross Value Added (GVA) grew by 11.89% over the previous year.
- Industrial output increased by more than 5.80% over the previous year.
- Average emoluments per person engaged grew by 5.6% compared to 2022-23.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry launched the Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) 3.0.
- IPRS was introduced on a pilot phase in 2018 and IPRS 2.0 in 2021.
- IPRS 3.0 introduced an expanded framework with new parameters, including sustainability, green infrastructure, logistics connectivity, digitalization, skill linkages, and enhanced tenant feedback.
About Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) 3.0
- Objective: Strengthen India’s industrial ecosystem and enhance the competitiveness of industrial infrastructure.
- Developed by: the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) with support from the Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- Categorisation of Industrial park: Leaders, Challengers, and Aspirers based on their performance across key indicators.
- IPRS is an integral part of the India Industrial Land Bank (erstwhile Industrial Information System).
- India Industrial Land Bank serves as a one-stop Platform for all the industrial information by mapping the entire industrial infrastructure across the nation on the GIS platform.
About Industrial Parks
- Industrial parks are economic zones that are expressly developed to accommodate a cluster of industrial activity. E.g. Narela Industrial Area
- IP are also referred to by names such as Special Economic Zones (SEZs), enterprise zones, etc.
- There are more than 4000 operational industrial parks in India.
- Government is actively developing 20 plug-and-play industrial parks and smart cities under National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP).
Article Sources
1 source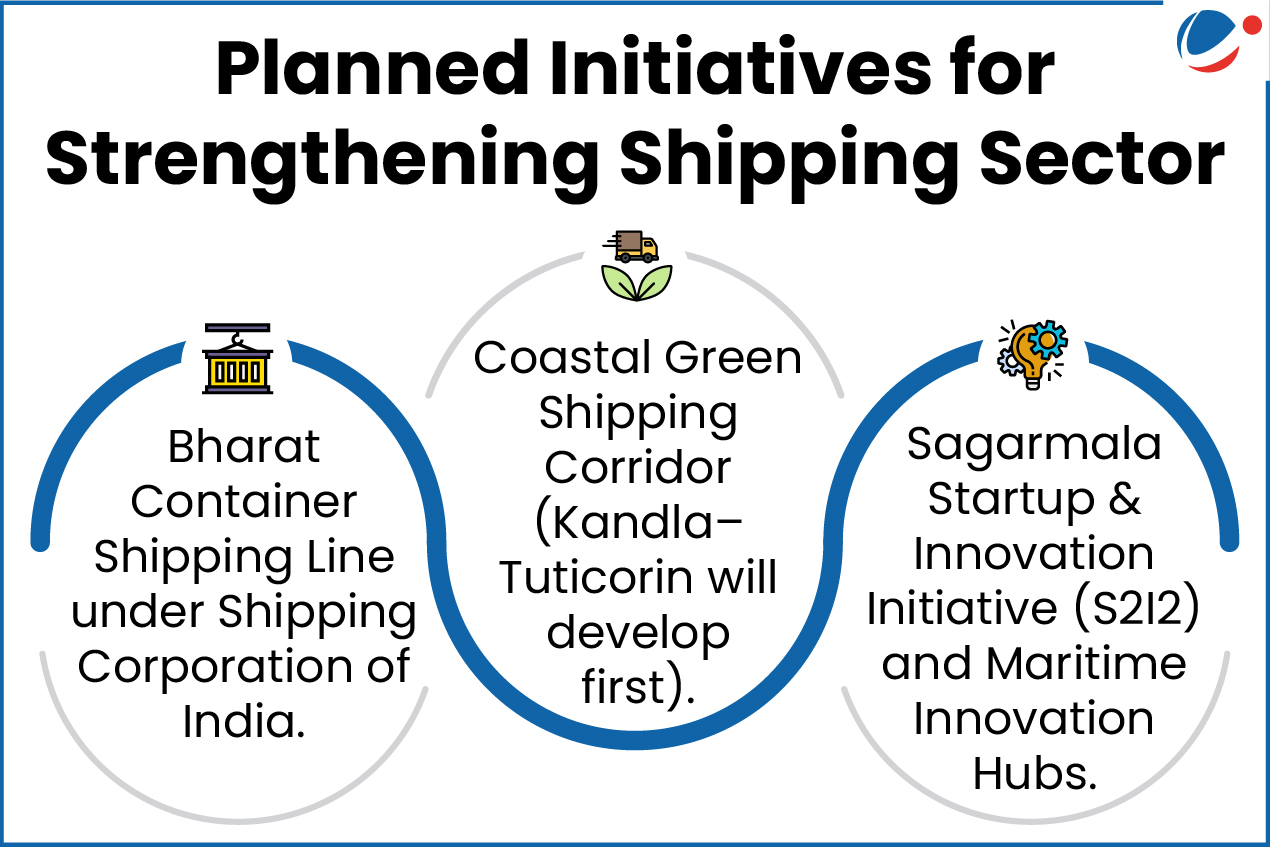
Large ships are now included in ‘Transport and Logistics’ category of the Infrastructure Harmonized Master List (HML) of Infrastructure Sector, aimed to strengthen domestic shipbuilding and maritime industry.
- A large ship is defined as Commercial Vessel:
- Having a gross tonnage (GT) of 10,000 or more, under the Indian ownership and flag; or
- Having a GT of 1,500 or more which are built in India and are under Indian ownership and flag.
- Significance of inclusion in HML: Access to infrastructure lending at easier terms with enhanced limits, access to larger amounts of funds as external commercial borrowings (ECB), viability gap funding, tax incentives etc.
Status of India’s Shipping Sector
- Foreign Dependence: 95% of India’s trade relies on foreign ships and India pays nearly $75 billion every year to foreign shipping companies for shipping services.
- Share in Shipbuilding: India currently accounts for only 0.06% of global shipbuilding.
- Target: Government is aiming at becoming one of the top five shipbuilding nations by 2047 and according to Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, government foresees an investment of ₹54 trillion into building indigenous shipping and shipbuilding capabilities by 2047.
- Issues in Shipping Sector: Capital constraints with high borrowing costs, ageing fleet, tax anomalies, skill gaps etc.
- The package introduces a four-pillar approach designed to
- Strengthen domestic capacity
- Improve long-term financing
- Promote greenfield and brownfield shipyard development
- Enhance technical capabilities and skilling, and implement legal, taxation, and policy reforms
- The package includes
- Extension of the Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Scheme (SBFAS) until March 31, 2036, to incentivize shipbuilding
- A Maritime Development Fund (MDF) will provide long-term financing for the sector.
- MDF use cases would be for shipbuilding, shipbuilding clusters, ship repairs, ship ownership, port expansion, inland waterway transport, and coastal shipping.
- Shipbuilding Development Scheme (SbDS) to expand domestic shipbuilding capacity to 4.5 million Gross Tonnage annually.
- A National Shipbuilding Mission will oversee all initiatives.
Article Sources
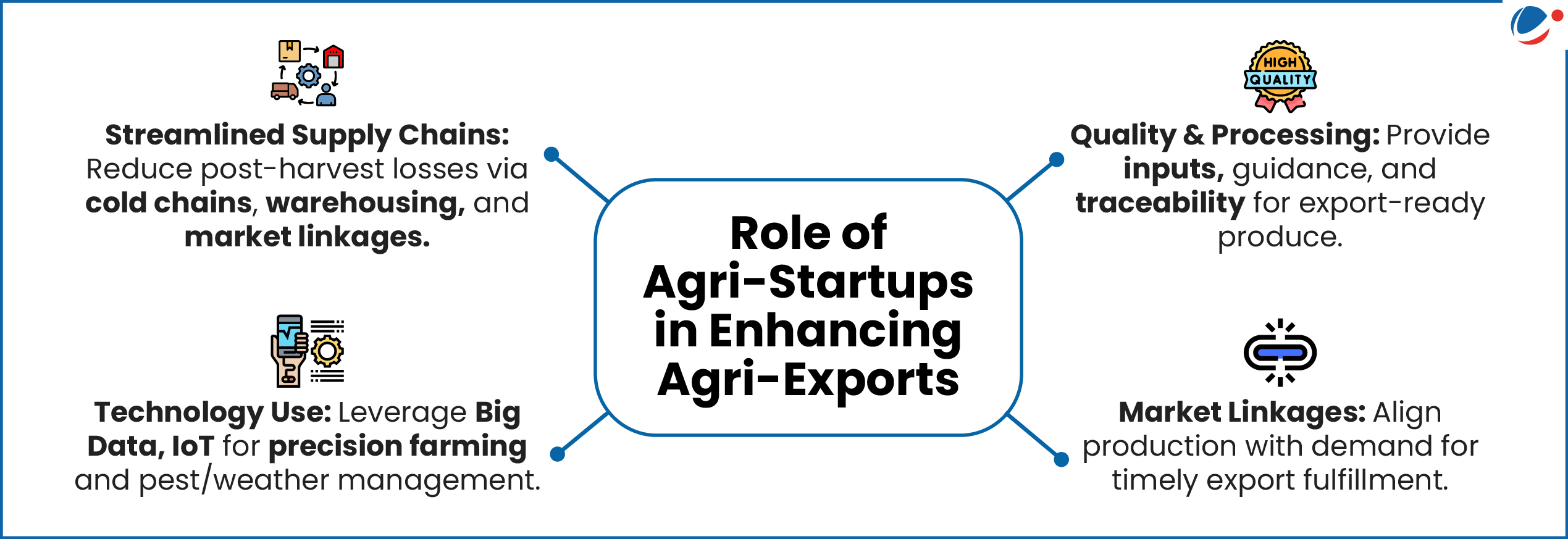
1 sourceAPEDA has launched BHARATI to support Agri Food Startups and boost India’s agri Food Export.
About BHARATI
- It stands for Bharat’s Hub for Agritech, Resilience, Advancement and Incubation for Export Enablement.
- Key Objectives:
- It aims to support 100 agri-food startups, and achieve $50 billion in exports by 2030.
- Selected startups will undergo a 3 month acceleration programme on product development, export readiness, regulatory compliance, market access etc.
- Attract startups working on advanced technologies: E.g. AI-based quality control, blockchain-enabled traceability, IoT-enabled cold chains and agri-fintech.
- Drive Innovation in high-value categories: E.g. GI-tagged agri-products, Organic foods, Superfoods, Novel processed Indian agri-foods, Livestock products, AYUSH products
- Resolve export challenges: E.g. related to product development, value addition, quality assurance, perishability, wastage and logistics.
- It aims to support 100 agri-food startups, and achieve $50 billion in exports by 2030.
Article Sources
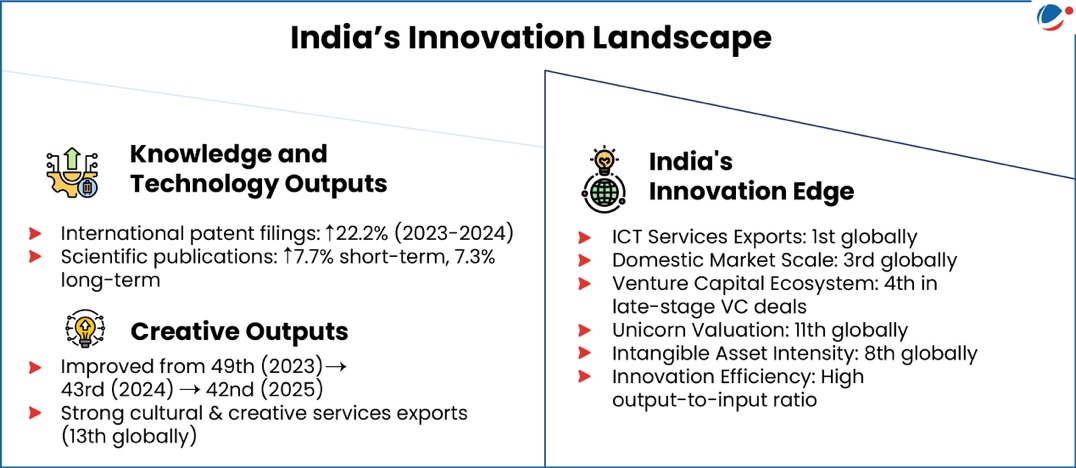
1 sourceWorld Intellectual Property Organisation released the Global Innovation Index (GII) 2025.
GII measures innovation performance of 139 economies through investment patterns, technological progress, adoption rates, and socioeconomic impacts.
- Launched in 2007, GII is recognized by the UN General Assembly as an authoritative reference for Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) policies.
Key Highlights of GII 2025
- India’s Rise: India’s rank rises to 38th position, a big leap from 81st in 2015.
- India along with Vietnam is the longest-standing overperformer, performing above expectation for their level of development for 15th year.
- Most Innovative Economies: Switzerland has been ranked first, followed by Sweden, USA, South Korea and Singapore.
- Top Innovation Clusters: Shenzhen–Hong Kong–Guangzhou (China and Hong Kong), followed by Tokyo-Yokohama (Japan), and San Jose-San Francisco (USA).
- India has four clusters in top 100: Bengaluru (21st), Delhi (26th), Mumbai (46th) and Chennai (84th).
India’s Initiatives for Improving Innovation
- Startup India Program: Provides handholding support for startups, funding through Fund of Funds, credit guarantee, tax exemptions etc.
- Atal Innovation Mission: Develop new programmes and policies for fostering innovation in different economic sectors.
- National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI): Umbrella programme for nurturing ideas into successful startups.
- Other: Accelerating Growth of New India's Innovations (AGNIi) Mission, NITI Frontier Tech Repository, Prime Minister’s Research Fellowship Scheme etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe report released by the World Trade Organization (WTO) recognizes the transformative potential of AI as a general-purpose technology that can reshape wealth distribution and income across economies.
How AI can act as catalysts for Trade and Inclusive Growth?
- Reducing Trade cost and improving productivity: By optimizing logistics, streamlining regulatory compliance, overcoming language barriers, and improving contract enforcement, AI could lead to 34-37% rise in global trade by 2040.
- Reducing ‘Skill Premium’: AI is expected to substitute tasks performed by medium- and high-skilled workers more than those of low-skilled workers, thereby reducing the relative demand for higher-skilled labor.
- Skill premium is the wage ratio of high-skilled to low-skilled workers which is projected to decline by 3-4% globally.
- Knowledge diffusion: Economies more open to trade experience stronger innovation spillovers - a 10% increase in digitally deliverable services trade is associated with a 2.6% rise in cross-border AI patent citations.
- New Development Pathways: Economies rich in critical minerals or renewable energy can become hubs for upstream inputs like hardware manufacturing or data hosting and other labor-intensive activities like data collection and annotation.
What are the concerns demanding urgent Policy action?
- Concentration of AI: AI development is highly concentrated in a few firms and economies, which poses risks to equitable access.
- Labor market disruption: Displacement of some workers by automating tasks, requiring investment in education and active labor market policies to help workers adapt.
Conclusion
To realize the inclusive potential of AI and trade, there is a need for proactive and coordinated policies, including investing in digital infrastructure and skills, promoting regulatory coherence, ensuring competition, and leveraging international cooperation through organizations like the WTO.
Article Sources
1 sourceOECD Upgrades India’s 2025 GDP Forecast to 6.7% While Moderating Inflation Projection to 2.9%.
About Economic Outlook Report
Released by: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- Report: Biannual publication analyzing global and national economic trends.
- Coverage: Includes GDP, inflation, employment, trade, and investment.
- Risks: Highlights inflationary pressures, financial instability, and geopolitical tensions.







