ISRO and Department of Biotechnology (DBT) join forced to advance Space Biotechnology research.
- The key challenges in space missions are the lack of continuous availability of nutrients, waste management, preservation of food, microgravity, radiation, health hazards such as cancers, cataracts, bone muscle loss, etc.
- In this regard, Space biotechnology would study how living organisms adapt, function, and evolve in microgravity conditions so as to advance space exploration and human survival.
Space biotechnology applications and their Significance:
- Microgravity Research: Space’s microgravity enables better-quality protein crystal growth, enhancing understanding of structures for precise drug development.
- Radiation Research: E.g., BioSentinel (a NASA programme) will predict how human cells will repair double-strand breaks in response to ionising radiation in space.
- BioSentinel was launched in 2022 on Artemis I.
- Environmental Monitoring: Study of microbes can be used for bioremediation to convert Mars and Moon regolith into soil capable of plant growth.
- Disease Modelling: Space biotechnology research can help model diseases to address the challenges astronauts face during long-duration space missions.
- Bioregenerative Life Support Systems: It enables self-sustaining missions through waste recycling, advancing Earth’s sustainability and resource management solutions.
Initiatives
- India: Axiom-4 mission and Gaganyaan mission.
- Global Initiatives: Space Biology Program (NASA); Biolab (European Space Agency); Space breeding programs (China National Space Administration (CNSA)).
ISRO has launched India’s first analog space mission in Leh (Ladakh) to plan lunar mission experiments.
- It has been developed by joint collaboration of ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Center, AAKA space studio, university of Ladakh and IIT Bombay.
About Analog Space Mission:
- Analog space missions are field tests done in locations that have physical similarities to that of the extreme space environments.
- It may include testing of new technologies, robotic equipment, vehicles, study of behavioral effects (isolation and confinement).
- Reasons for choosing Leh (Ladakh)
- geographical features dry and cold climate, barren land, high-altitude terrain and extreme isolation closely resemble Martian and lunar landscapes.
- Other analog missions: NEEMO (NASA), SIRIUS Program (UAE)
Recently SpaceX’s Falcon-9 deployed India’s GSAT-N2 satellite into orbit.
About GSAT-N2 (Geostationary Satellite-20)
- It is a communication satellite of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- NSIL is commercial arm of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Features: Geosynchronous transfer orbit; Life span – 14 years; Mass around 4,700 kg.
- India’s primary launch vehicle, LVM-3, can carry payloads up to 4,000 kg, thus rendering it incapable of carrying the GSAT payload (SpaceX’s Falcon-9
- Significance: It will enhance broadband services and in-flight connectivity across the Indian region. It offers pan-India coverage, including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands.
The world’s first wooden satellite, developed by Japan, has been launched.
- The satellite will study how wood withstands space’s extreme conditions.
About LignoSat
- It is a small, palm-sized satellite made from honoki wood, a type of magnolia tree native to Japan.
- It also incorporates traditional aluminium structures and electronic components.
- Significance:
- Wooden satellite is part of a plan to use renewable materials for space structures.
- Wood can better withstand space conditions than metal, as there’s no water or oxygen to cause decay.
- When decommissioned, wooden satellites burn up without releasing harmful pollutants, unlike metal ones.
Ministry of Science and Technology launched Operation Dronagiri and Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI)
- These initiatives have been launched in efforts to liberalise geospatial data, and developing geospatial infrastructure, geospatial skill and knowledge.
- Geospatial data is information that describes objects, events or other features with a location on or near the Earth’s surface.
- Examples: Satellite imagery, census data, social media data etc.
- Geospatial data is widely accepted as a critical national infrastructure and information resource.
About Operation Dronagiri
- It is a pilot project under National Geospatial Policy 2022, and will be implemented by Geospatial Innovation Cell, Department of Science and Technology.
- Purpose: To demonstrate the potential applications of geospatial technologies and innovations in improving the quality of life of citizens and ease of doing business.
- First Phase Implementation: In the states of UP, Haryana, Assam, Andhra Pradesh & Maharashtra.
- Pilot projects and use cases will be demonstrated to showcase potential applications of integration of geospatial data and technology in 3 sectors: Agriculture, Livelihoods, Logistics and Transport.

About Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI)
- Interface is being built for making spatial data accessible with advanced data exchange protocols and privacy-preserving features.
- Significance: Enabling seamless data sharing, enabling data-driven decisions for public good, fostering responsible use of geospatial data.
BSNL launched India’s first Direct-to-Device(D2D) Satellite connectivity.
- It marks a major event in extending satellite communications to everyday consumers which were earlier limited to emergency and military use.
- Global initiatives such as AST SpaceMobile, Lynk Global, Constellation Global, SpaceX- Starlink are also uses D2D technology.
Working of Direct-to-Device Satellite Technology
- Principle: Satellites act as cell towers in space, bypassing the need for terrestrial cell towers as used in traditional mobile connectivity.
- It uses satellites in orbit to transmit signals directly to devices on the ground.
- Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) technology : It allows for seamless two-way communication between devices and satellites.
- BSNL uses Viasat’s Geostationary L-band satellites positioned 36,000 kilometers above which bypasses ground-based cell towers, making it ideal for remote coverage.
Significance
- Reliable connectivity: Uninterrupted internet connectivity, regardless of weather conditions.
- High-speed internet and wider coverage even in the remotest areas where cellular or Wi-Fi networks are unavailable.
- Support UPI payments: Empower people in rural or underserved regions to make digital transactions.
- Emergency calls and SOS messaging: Communication in emergency situations where cellular or Wi-Fi networks are unavailable (useful for adventurers, travellers etc).
Challenges
- Latency: Ensuring minimal delay for real-time applications like voice calls and video streaming.
- Regulatory Challenges: AsD2D service may cross geographical borders.
- Spectrum allocation: Obtaining sufficient bandwidth for seamless satellite-to-ground communication.
- Device compatibility: Ensuring technology works across various smartphones and operating systems.
- Propagation challenges: Overcoming signal loss and interference in diverse environments.
GES is emerging as an alternative to battery energy storage for solar and wind power.
About GES:
- It is a type of mechanical energy storage system that uses gravitational potential energy to store and generate electricity.
- It involves lifting a heavy mass during excess energy generation and releasing it to produce electricity when demand rises or solar energy is unavailable.
- Types of weights used are often water, concrete blocks or compressed earth blocks.
- It involves lifting a heavy mass during excess energy generation and releasing it to produce electricity when demand rises or solar energy is unavailable.
- Advantages: High efficiency, large storage capacity, low environmental impact, longevity etc.
- Limitations: High initial cost and space requirement, complexity etc.
- Applications: Renewable energy integration, grid stabilization etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, a new complex of India’s first Biomanufacturing Institute, named BRIC-NABI, was inaugurated at Mohali (Punjab).
About BRIC-NABI
- Formed through the strategic merger of National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) and the Centre of Innovative and Applied Bioprocessing (CIAB).
- Funded by: Department of Biotechnology
- Aims:
- Promote cutting-edge research in genetic manipulation, metabolic pathways, etc.
- Address India’s biomanufacturing gap by creating large-scale production facilities and nurturing startups.
Recently, Union Minister of Science and Technology launched the first indigenous antibiotic “Nafithromycin” for resistant infections.
About Antibiotics
- They are chemical substances (produced both synthetically and by some microbes) used as drugs to kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms.
- They have low toxicity for humans and animals and can be mixed with livestock feed to check microbial infections in animals.
- They work against bacterial and not viral infections (like common cold, flue).
- Viruses lack cell wall that is attacked by antibiotics.
- Common Examples: Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin.
Jeddah Commitments adopted at Fourth Global High-Level Ministerial Conference on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- It is a comprehensive framework for global action to combat AMR through a One Health approach.
- Commitments aim to translate the Political Declarations of the UNGA’s High-Level Meeting on AMR into practical commitments for urgent actions.
- AMR occurs when germs like bacteria, viruses, etc. develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them.
Key highlights of Jeddah commitments (Non-legally binding instrument)
- One Health AMR learning hub: Focused on sharing best practices and building capabilities for implementing multi sectoral National Action Plans on AMR.
- One Health Approach is an integrated, unified approach aimed to sustainably balance and optimize health of people, animals and ecosystems.
- Independent Panel for Evidence on Action Against AMR by 2025: To avoid duplication of ongoing efforts.
- National AMR coordinating mechanism: To implement and ensure sustainable financing and monitoring of National Action Plans (NAPs).
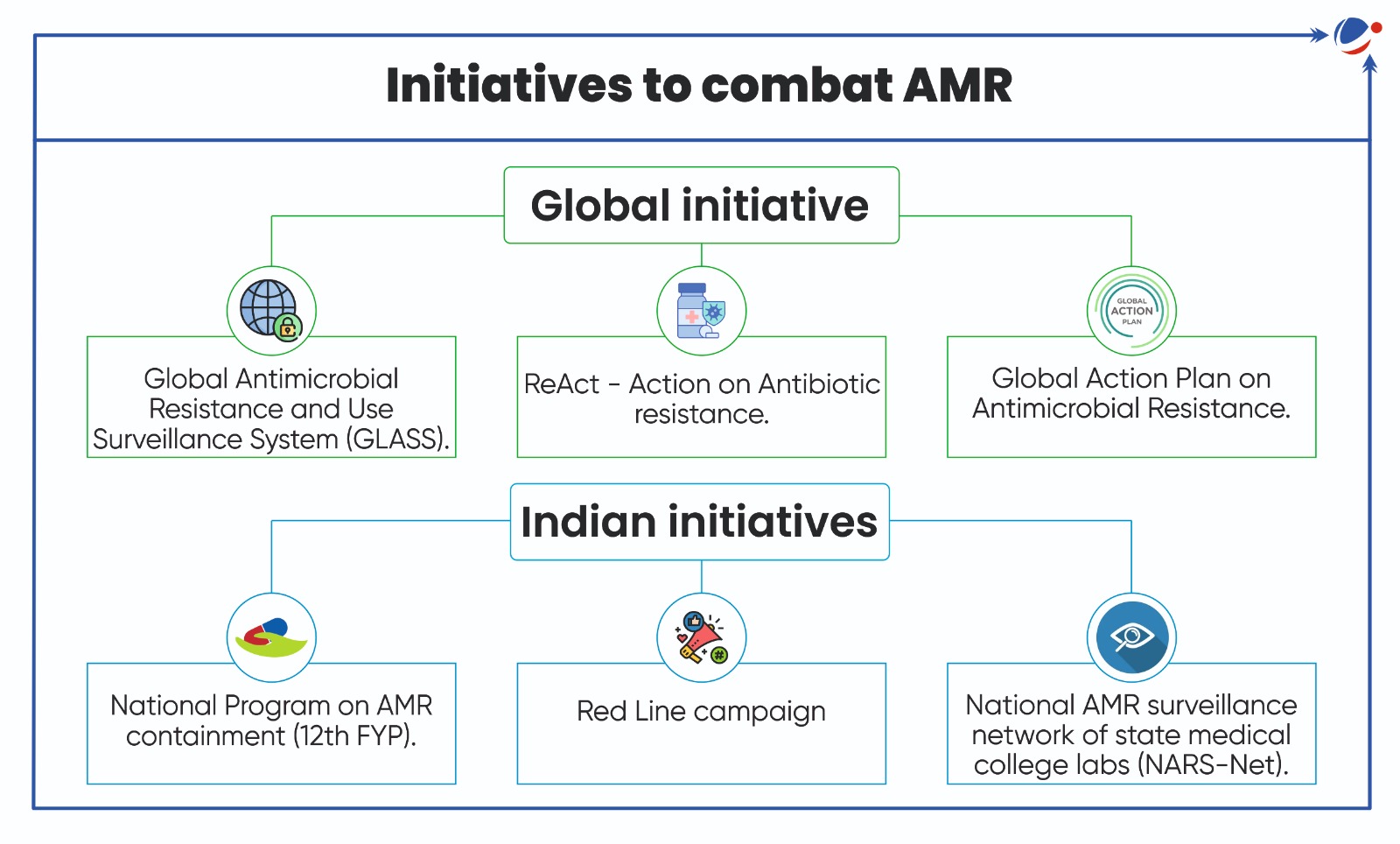
- Promotes global data sharing through platforms such as GLASS AMR/AMC, ANIMUSE, and INFARM.
- Adherence to Codex Alimentarius Commission guidelines: To ensure the prudent and responsible use of antimicrobials.
- Supports Quadripartite organizations (FAO, WHO, WOAH, UNEP): To achieve 2030 goals of UNGA Political Declaration on AMR.
Article Sources
1 source- It focuses on “Animal Health Security Strengthening in India for Pandemic Preparedness and Response”.
- The minister also released documents on Standard Veterinary Treatment Guidelines (SVTG) and Crisis Management Plan (CMP) for animal diseases.
About Pandemic Fund Project

- It is a $25 Million initiative funded by the G20 Pandemic Fund and was established under Indonesia’s G20 Presidency (2022).
- Aim: enhance low- and middle-income country’s capacity to respond to animal health threats and pandemic through financing investments
- Implementing Entities: Asian Development Bank (ADB), World Bank, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Need to focus on animal disease outbreaks
- Prevent Zoonotic Diseases: 5 of 6 public health emergencies declared by WHO had animal origin
- Minimize socio-economic impacts: E.g. SARS and Avian flu are estimated to have caused global economic loss of $50 B, and $30 B, respectively.
- Major Interventions under the Project includes:-
- Upgradation and expansion of animal health laboratories and vaccine manufacturing facilities.
- Enhancing early warning and surveillance mechanisms to detect outbreaks and facilitate timely interventions.
- Upgrading Data Management and Analytical systems to enable better risk assessment.
- Addressing Cross-Cutting Institutional Capacity Gaps at National and Regional Levels through a disaster management framework for the livestock sector.
Article Sources
1 sourceWHO and partners, activated the GHEC for the first time in response to a recent Mpox outbreak.
About GHEC
- Genesis: WHO founded the GHEC in 2023 after the response to COVID-19 pandemic revealed the need to ensure better-coordinated support to countries.
- Objective: Strengthening the response to health emergencies, and a collaboration platform for countries and health emergency networks.
- Role: It supports countries on their health emergency workforce, the surge deployment of experts and the networking of technical leaders.







