Recently, Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023 has been released by DARPG.
About GRAI
- Conceptualized: by Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) based on recommendation of Parliamentary Standing Committee of Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- Index is based on Four Dimensions (Efficiency, Feedback, Domain and Organizational Commitment) And 11 Indicators Assessing Grievance Redressal Mechanism Adopted By Central Ministries And Departments.
- Objective: Highlight strengths and areas of improvement regarding grievance redressal mechanisms of various organizations.
- Ranking: Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare Topped The Ranking Followed By Department Of Posting Group A.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, Union Home Minister launched Civil Registration System (CRS) mobile application.
- Application, developed by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India, is expected to reduce the time required for these registrations seamlessly.
About CRS
- It is a unified system for continuous, mandatory, and permanent documentation of vital events, including births, deaths, and stillbirths, along with their associated details.
- The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969 mandates that all births and deaths must be officially registered
- It operates under the authority of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India
- It is included in the concurrent list under Schedule Seven.
Article Sources
1 sourceSupreme Court ruled that prior sanction is mandatory to prosecute public servants in money laundering cases.
- Thus, establishing a key procedural safeguard under the stringent Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) and adding a layer of accountability to PMLA prosecutions.
Key highlights of the Directorate of Enforcement vs. Bibhu Prasad Acharya Case

- Supremacy of CrPC: The court asserted that the PMLA doesn't supersede the requirement for prior sanction under Section 197 of CrPC.
- The provision corresponds to Section 218 of the Bhartiya Nagrik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023, which has replaced the CrPC with effect from July 1, 2024
- Section 197 of CrPC: To protect the public servants from prosecutions & from being prosecuted for anything they do in the discharge of their duties.
- Exception: Protection is not unqualified & public servants can be prosecuted with a previous sanction from the appropriate government.
Provision towards protection of Civil Servants
- Articles 311 (1) and 311 (2): They provide Constitutional protection to Civil Servants.
- Public Servants (Inquiries) Act, 1850: Ensures inquiries are conducted fairly and transparently, upholding principles of natural justice within public administration.
Recently, President of India released report on ‘Prisons in India: Mapping Prison Manuals and Measures for Reformation and Decongestion’.
- Report, prepared by Centre for Research & Planning, the research wing of Supreme Court of India, seeks to highlight the complexities of India's prison system, with a focus on the potential for technology-driven solutions.
Key insights from the report
- Stereotyping: Prison manuals often refer to essential sanitation and conservancy work as "menial" or "degrading," perpetuating a hierarchical view of labour.
- Bail Rejection: Rejection rate for bail applications is high (32.3% in Sessions Courts and 16.2% in Magisterial Courts).
- Slow Trial: Over 52% of cases where accused were in custody for more than a year were still pending at evidence stage in 2023.
- Others: Persistence of Manual Scavenging in prisons; Division of prison work based on caste system (held unconstitutional in Sukanya Shantha Case); Underutilization of open prisons etc.
Use of Technology for Prison Reforms
- E-prisons: Developed by National Informatics Centre to integrate all activities related to prison and prisoner management.
- Model Prison and Correctional Services Act, 2023: Introduced the use of electronic monitoring technology as a condition for granting prison leaves for prisoners.
- FASTER (Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records) system of Supreme Court resolved delay in communication of bail orders from courts to prison.
- Interoperable Criminal Justice System (ICJS): It can create an automatic channel between courts, police and prisons and reduce unjustified delay in custody cases.
Recently, Justice Sanjiv Khanna took oath as 51st Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- The oath of office was administered by the President of India during a ceremony at the Rashtrapati Bhavan.
About appointment of CJI
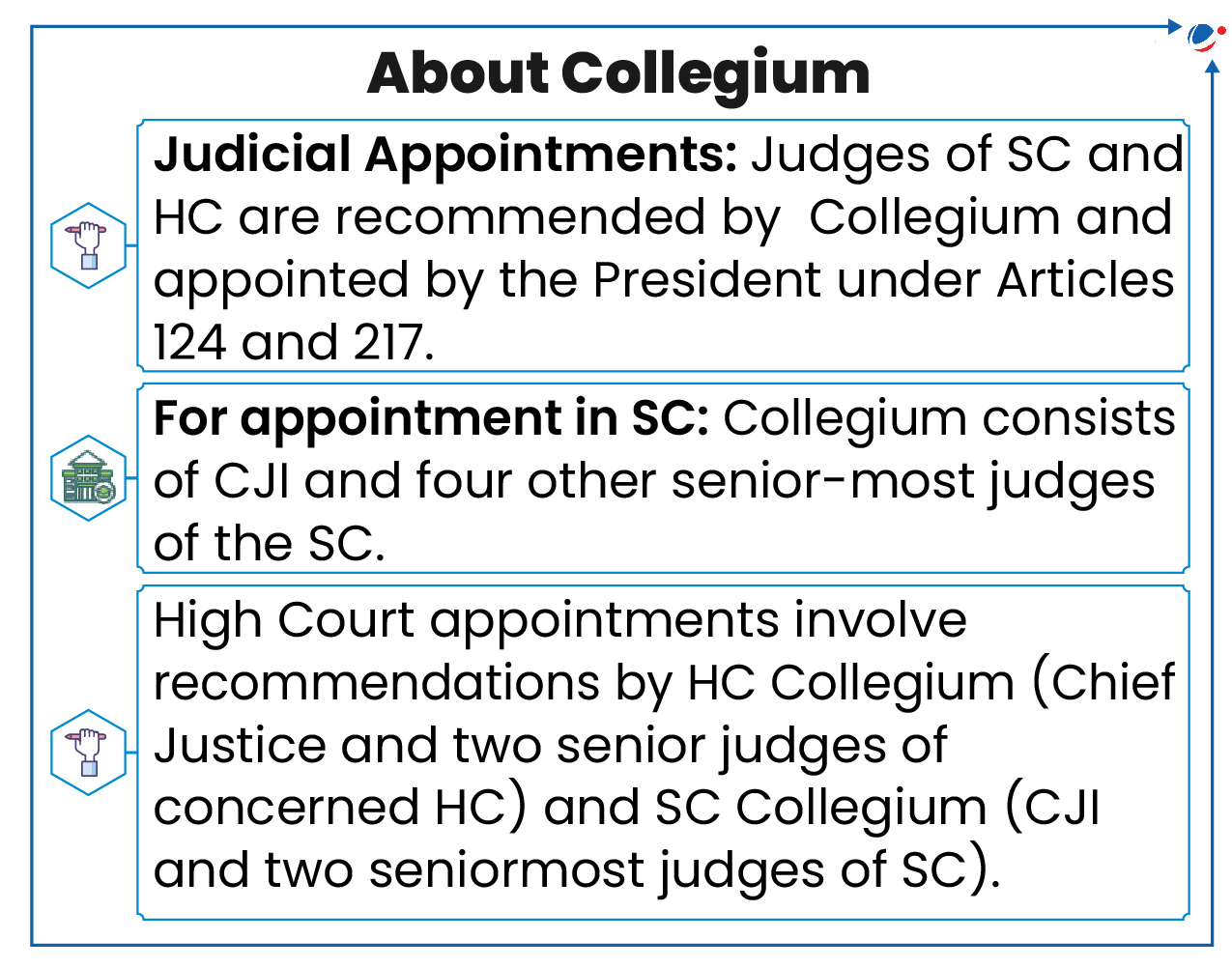
- The senior-most Supreme Court judge, considered fit for the role, is usually appointed as CJI on the recommendation of the outgoing CJI.
- This convention was breached in 1964, 1973, and 1977.
- The Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs seeks this recommendation, which is then sent to the Prime Minister, who advises the President on the appointment.
- Under Article 124 (2), every Judge of the SC be appointed by the President and shall hold office until he/she attains the age of 65 year.
Key Role of CJI
- First amongst the equals: SC in the State of Rajasthan vs Prakash Chand (1997) ruled that the CJI is the head of the judiciary and holds a leadership position, they do not hold any superior judicial authority over the other SC judges.
- Master of the Roster: It is the exclusive power of the CJI to constitute Benches (including Constitution benches), to hear cases.
- Head of Collegium: CJI heads the Collegium for judicial appointments and transfers in the higher judiciary.
- Appointment of officers and servants of SC: It shall be made by the CJI or such other Judge or officer of the Court as he may direct (Article 146).
The Inter-State Council has been reconstituted.
About ISC
- It is a forum through which Centre and the state co-ordinate and co-operate with each other.
- Genesis: Established under Article 263 of Constitution through a Presidential Order in 1990 on recommendation of Sarkaria Commission.
- Composition: It consists of:-
- Chairman: Prime Minister
- Members:
- CM of all States.
- CM of Union Territories having a Legislative Assembly and Administrators of UTs not having a Legislative Assembly.
- 6 Ministers of Cabinet rank in Union Council of Ministers to be nominated by Prime Minister.
Recently, Supreme Court (SC) overturned its decision which denied Aligarh Muslim University’s (AMU) status as a minority institution.

- The Supreme Court (by 4:3 majority), overruled its S. Azeez Basha vs. UoI (1967) judgment which held that AMU cannot claim minority status under Article 30 (1) as it was established by a statute.
- SC in S. Azeez Basha vs. UOI had held that AMU was neither established nor administered by Muslim minority, and it is a central university established through AMU Act, 1920.
- Later on, Parliament through AMU (Amendment) Act, 1981 restored AMU’s minority status.
- However, Allahabad High Court struck down the minority status of AMU in 2006 which has been subsequently challenged in SC in 2019.
- SC has now referred ‘issue of AMU's minority status under Article 30’ to a regular bench based on principles established in this judgment.
Key Highlights of the Judgment
- No need for minority control over administration to prove that it is a minority educational institution.
- Courts should trace Genesis and identify Brain behind the Institution to determine who established the institution
- Minority Status is not surrendered because an institution was created by a statute or upon incorporation of the University.
- Communities that weren't a minority before the Constitution are also entitled to Article 30 (1) protection for institutions established before independence.




