INDIA BECOMES FOURTH-LARGEST STOCK MARKET
- India overtakes Hong Kong to become the world’s fourth-largest stock market.
- According to data compiled by Bloomberg, the combined value of shares listed on Indian exchanges reached USD 4.33 trillion, versus USD 4.29 trillion for Hong Kong, on Jan 22, 2024.
- Top three stock markets are the US, China, and Japan.
- Stock market is where investors, both individual and institutional, trade a wide range of securities such as stocks, bonds, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), derivatives, etc.
- Two types of stock market:
- Primary Market: New shares, bonds, etc., are offered for the first time.
- Secondary Market: Existing securities (equities, bonds, etc.) are traded. e.g., Stock exchanges like Bombay Stock Exchange.
- Two types of stock market:
- Significance of stock market
- For Businesses: Access to capital, risk diversification, business expansion, etc.
- For Investors: Better returns compared to traditional savings instruments, tax benefits, capital growth, etc.
- For Society: Social Impact bonds, Sustainable investment though Green bonds, etc.
- For Economy: Mobilization of idle savings, boost to entrepreneurship through venture capital funds, etc.
- Issues with Indian Stock markets: High volatility, limited issuer and investor base adversely affects liquidity, sub-optimal corporate debt market due dominance of government bonds, etc.
Regulation of Stock markets in India
|
- Tags :
- Capital Markets
DIRECT LISTING OF PUBLIC INDIAN COMPANIES
- Centre allowed direct listing of public Indian companies on international exchanges of GIFT International Financial Services Centre (GIFT-IFSC). This was enabled by:
- Companies (Listing of Equity Shares in Permissible Jurisdictions) Rules, 2024 and
- Amendment to Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) Rules, 2019.
- Direct Listing Scheme of FEMA rules 2019 provides framework for issuing and listing of equity shares of public Indian companies on international exchanges.
- Prior to this, Indian companies were not allowed to issue or list equity shares abroad.
- Expected benefits: Give Indian companies access to cheaper foreign capital, boost foreign investment, etc.
- Tags :
- Society
- Capital Markets
AADHAAR-BASED PAY MANDATORY FOR MGNREGA
- Recently, Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) became mandatory for MGNREGS workers.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) gives a legal guarantee of a hundred days of wage employment in a year to adult members of a rural household willing for unskilled manual work.
- MGNREGS has utilized APBS since 2017 and is made mandatory now (from 1st January).
- Government may consider exemption on a case-to-case basis if any Gram Panchayat has either a technical problem or an Aadhaar-related problem.
- ABPS working
- ABPS uses the worker’s unique 12-digit Aadhaar number as their financial address.
- To be paid under ABPS,
- A worker’s Aadhaar details must be seeded to her job card;
- Her Aadhaar details must be seeded to her bank account;
- Her Aadhaar must be mapped with the National Payments Corporation of India (NCPI) database.
- Significance of the move
- Curbing corruption by weeding out fake beneficiaries.
- Will ensure speedy payments and reduce rejection (due to change of bank account of beneficiaries).

More than 1100 government schemes and programs run by Center and States have been notified to use Aadhaar. Some of them are
|
- Tags :
- MGNREGA
16TH FINANCE COMMISSION
- It was constituted with the approval of the President of India in pursuance of Article 280(1) of the Constitution.
- The government appointed Arvind Panagariya (former vice-chairman of NITI Aayog) as the chairman and members would be notified separately.
- The Commission’s work involves redressing the vertical imbalances between the taxation powers and expenditure responsibilities of the center and the States respectively and equalization of all public services across the States.
- The commission shall make recommendations on the following
- Distribution between the Union and States of the net proceeds of taxes and allocation between the States of such proceeds.
- Principles for governing the grants-in-aid and revenues of the state under Article 275 of the Constitution.
- Measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the Panchayats and Municipalities based on state finance commission recommendation.
- The commission may review present arrangements for financing Disaster Management initiatives, concerning the funds constituted under Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- The 16th FC recommendations, upon acceptance by the government, would cover the period of five years commencing April 1, 2026.

- Tags :
- Finance Commission
DIRECT TAX TO GDP RATIO ROSE TO 15-YEAR HIGH
- Direct Tax to GDP ratio rose to 15-year high in FY23 Central Board of Direct Taxes data shows.
- Key highlight:
- Direct Tax to GDP ratio reached a 15-year high at 6.11% of GDP in FY23.
- Direct Tax to GDP ratio gives an estimate of a country’s ability to mobilise resources to fuel its development.
- Direct Tax to GDP ratio reached a 15-year high at 6.11% of GDP in FY23.
- Tax Buoyancy, however, declined from 2.52 to 1.18 compared to the previous year.
- Tax buoyancy indicates the measure of efficiency or responsiveness in tax collection in response to the growth in GDP.
- Tax revenues are considered as buoyant when they increase more than proportionately in response to the increase in GDP even when the rates of taxes remain unchanged.
- The recent decline indicates that the current economic growth did not lead to as much of an increase in direct tax collections for FY 23 as seen in FY22.
- Gross direct tax collections increased by over 173% to Rs 19.72 trillion in FY23 from Rs 7.22 trillion in FY14.
- Tax buoyancy indicates the measure of efficiency or responsiveness in tax collection in response to the growth in GDP.
- Initiatives prompting rise in Direct Tax to GDP
- Corporate tax rate has gradually decreased since the Finance Act of 2016.
- Phasing out of exemptions and incentives for the corporate sector.
- Vivad se Vishwas Scheme for reducing litigations in the direct tax payments.
- Finance Act of 2020 allows individual taxpayers to pay income tax at lower slab rates by forgoing specified exemptions.
- Other reforms: Aadhaar – PAN linkage, digital technology (Faceless Assessment, Faceless Appeal) to improve tax administration, Taxpayers Charter, etc.
About direct tax
|
- Tags :
- Taxation
- Tax-to-GDP
REVERSE FLIP
- Many Startups are reverse flipping i.e. moving their overseas holding entities to India.
- ‘Reverse flipping’: It is a term used to describe the trend of overseas start-ups shifting their domicile to India and listing on Indian stock exchanges.
- Reasons for Reverse Flipping:
- Capitalise on India’s large and growing economy
- Access to deeper pools of venture capital
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 recognized the concept of reverse flipping and proposed ways to accelerate the process, such as simplifying corporate laws and capital movements, simplification of taxation, etc.
- Tags :
- Startups
MOMENTUM INVESTING
- Many academic studies have shown that momentum investing can generate high returns.
- About Momentum Investing
- It refers to a style of investing wherein investors purchase assets such as stocks or bonds that are consistently rising in price, while selling assets whose prices are falling.
- Momentum investor hope that the upward price momentum of these assets would continue, thus allowing them to sell these assets at higher prices in the future to make profits.
- The buy high, sell higher philosophy of momentum investing is in stark contrast to the traditional approach of buy low, sell high.
- Tags :
- Investment
MODEL BASED LENDING
- RBI governor has cautioned banks and NBFC against model-based algorithmic lending.
- It is a remote and automated lending process.
- It uses digital technologies for customer acquisition, credit assessment, loan approval, disbursement, recovery, and associated customer service.
- Benefits: financial inclusion, quick processing, increased collaboration with fintechs, facilitation of innovative products.
- Concerns: accuracy and information asymmetries, algorithmic biases, exclusion of various sections.
- Tags :
- Lending
MODERN MONETARY THEORY (MMT)
- MMT argues that countries that issue their own currencies can never “run out of money” the way people or businesses can.
- As long as there is unemployment, it calls for government spending without being concerned about fiscal deficit.
- At full employment, MMT prescribes taxes and government borrowing to counter inflation.
- The monetization of fiscal deficit aligns with this theory.
- It involves central bank printing currency for emergency spending by government.
- India ceased this practice in 1996 via an MOU between the RBI and the government.
- Tags :
- Monetary Policy
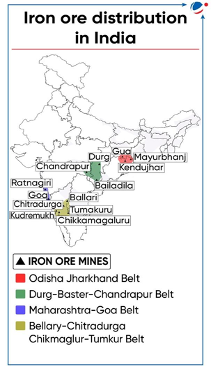
INDIAN IRON ORE MARKET
- Competition Commission of India (CCI) published a study examining competition in the iron ore market.
- Iron ore is predominantly composed of iron oxides called magnetite and hematite and yields metallic iron (Fe) when heated with a reductant.
- CCI study shows India's self-sufficiency in iron ore production, contributing 7% globally and ranking as the 4th largest producer.
- Concerns raised by CCI
- Recent years have seen increase in iron ore exports (iron ore has low value as compared to finished products like Steel).
- Allocation of captive mines (owned by companies for self -use) to some players creates entry barriers.
- Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2021 allows the captive mines to sell up to 50% of surplus iron ore in the open market.
- Differential pricing of iron ore for different end-users is likely to create competition concerns.
- Key Recommendation:
- Discourage export: Iron ore is a non-renewable national resource and crucial to various industries.
- Prioritise the export of higher value-added products such as finished steel to promote Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Upgrade quality: Use cutting-edge technologies to upgrade low-grade iron ore to higher grades.
- Sustainable mining: Promote clean technology adoption and transformation of production processes into sustainable mineral production modes.
- Discourage export: Iron ore is a non-renewable national resource and crucial to various industries.
- Tags :
- Iron Industry
AUDIT QUALITY DEFICIENCIES
- National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) found deficiencies in audit quality of big four audit firms.
- NFRA as a regulator oversees accounting standards and auditing profession in India.
- NFRA is a statutory body constituted in 2018 under Section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Act mandates NFRA to monitor compliance with Auditing Standards and to oversee the quality of service of the professions associated.
- Under this mandate, NFRA initiated audit quality inspections in big four audit firms.
- Namely Deloitte, Haskins & Sells LLP; BSR & Co LLP; SRBC & Co LLP; and Price Waterhouse Chartered Accountants LLP.
- Key Issues Highlighted
- Independence Issues: Firms are not in full compliance with the independence related requirements of the Code of Ethics.
- Quality of Audit Documentation: Deficiencies in documentation can lead to challenges in justifying audit conclusions and procedures.
- Inadequate Risk Assessment: Concerns raised about effectiveness of internal risk management processes within organization.
- Regulatory Compliance Issues: Violations of Companies Act 2013 seen in policies of SRBC & Co.
- It did not fully recognize the relationships between SRBC and its network members.
- Tags :
- Quality
- Audit
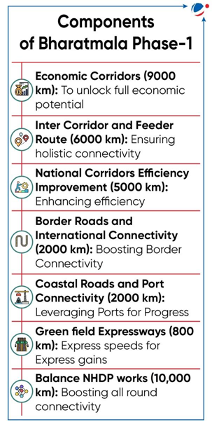
BHARATMALA PHASE 1 EXTENDED
- Bharatmala Phase 1 deadline extended by Six years to 2027-28.
- Bharatmala Pariyojana, launched under Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, is an umbrella program for highways sector.
- Phase I was approved in 2017 to focus on bridging critical infrastructure gaps through development of 34,800 km of National Highways by 2022.
- Till November-2023, 42% of project has been completed.
- Objectives of Bharatmala Pariyojana
- Optimize efficiency of freight and passenger movement across country by bridging critical infrastructure gaps.
- Improving connectivity in North East.
- Improving efficiency of existing corridors through development of Multimodal Logistics Park.
- Features of Bharatmala Pariyojana
- Satellite mapping of corridors to identify upgradation requirement.
- Technology-based automated traffic surveys of over more than 1,500 points.
- Origin-Destination study of freight movement across 600 districts.
- What are the gaps in highway infrastructure?
- Inadequacy in optimization of National Highway network & Road network due to resource constraints and absence of a national plan.
- Lack of integrated planning in connectivity of major corridors and ports with hinterland.
- Presence of Congestion Points, with multiple points of local congestion present even on already developed corridors.
- Lack of accident response infrastructure.
- Tags :
- Roadways
2023 LIST OF D-SIBS
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) releases 2023 list of Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
- D-SIBs are systemically important due to their size, cross-jurisdictional activities, complexity and lack of substitute and interconnection.
- It also means that the bank is too big to fail.
- If DSBs fail, there would be significant disruption to the essential services to the banking system and the overall economy.
- It also means that the bank is too big to fail.
- Declaration/Regulation of D-SIBs:
- It is based on the D-SIBs Framework of RBI which was released in 2014.
- This Framework is based on Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s (BCBS’s) framework for dealing with D-SIBs.
- Banks are placed in 5 buckets.
- As per latest list, India’s D-SIB’s are State Bank of India (bucket 4) and HDFC Bank (bucket 2), ICICI Bank (bucket 1).
- D-SIBs have to maintain Additional Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) requirement as a percentage of Risk Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- Bucket 1 banks have to maintain lowest CET1 i.e. 0.20% and Bucket 5 have to maintain highest CET i.e. 1%.
- In case a foreign bank having branch presence in India is a Global Systemically Important Bank (G-SIB), it has to maintain additional CET1 capital surcharge.
- Financial Stability Board (FSB) releases the list of G-SIBs.
- Tags :
- Banking
- D-SIBS
PAYMENTS INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT FUND (PIDF) SCHEME
- RBI extends Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) Scheme till 2025.
- About PIDF Scheme
- It was first operationalized in 2021 for three years.
- Aims to encourage deployment of payment acceptance infrastructure such as physical Point of Sale (PoS) terminals, Quick Response (QR) codes, in tier-3 to tier-6 centres, North eastern states and UTs of J & K and Ladakh.
- It was extended to street vendors covered under PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi Scheme) in Tier-1 and Tier-2 centres.
- PIDF is governed through an Advisory Council and managed and administered by RBI.
- Types of Acceptance Devices Covered: Physical PoS, mPoS (mobile PoS), GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) etc.
- To widen the scope of beneficiaries and acceptance infrastructure, following enhancements are being made under the scheme:
- Beneficiaries of PM Vishwakarma Scheme in all centres included as merchants under PIDF Scheme.
- Sound Box devices and Aadhaar-enabled biometric devices are eligible for claim of subsidy under Scheme.
- Subsidy for special focus areas has been made uniform at 90% of the cost of device, irrespective of the type of device.
- Tags :
- Payment System
NATIONAL TRANSIT PASS SYSTEM (NTPS)
- Union Minister launches National Transit Pass System (NTPS)-‘One Nation-One Pass’.
- It is under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change to facilitate the seamless transit of timber, bamboo, and other Minor Forest Produce (MFP) across the country.
- Currently, transit permits are issued for the transport of timber and forest produce based on state-specific transit rules.
- NTPS enables managing records for both inter-state and intra-state transportation of timber, bamboo, and MFP from private lands/government/private depots.
- States have exempted some species grown on private land from the purview of transit permits, to transport these species No Objection Certificate is provided.
- Benefits of NTPS:
- Will contribute to ease of doing business by streamlining the issuance of transit permits by providing a unified, online mode across the country.
- Provide a significant impetus to the agroforestry sector.
- Saving transportation costs and time, and Seamless movement across state borders.
- Under the Forest Rights Act (FRA) of 2006, MFP includes all non-timber forest produce of plant origin including bamboo, brushwood, stumps, etc.
- The forest dwellers are legally empowered with the ownership and governance of the MFP through the Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas Act, 1996, and FRA, 2006.
- Tags :
- Logistics
ATAL SETU NHAVA SHEVA SEA LINK
- Inaugurated by PM, it is the country’s longest Sea bridge, also referred to as Mumbai Trans Harbour Link.
- It is a 21.8 Kms long bridge of which 16.5 km is built completely over the Sea.
- It connects Sewri in Mumbai with Nhava Sheva in Raigad district, thereby easing travel between Mumbai-Navi Mumbai.
- Tags :
- Bridge
STANDARDISATION IN INDIA
- India should be a Pioneer of Standards says Union Minister for Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- Speaking at 77th Foundation day of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Minister also highlighted recent progress related to standards in India stating:
- Mandatory jewellery hallmarking covers 343 districts and 90% jewellery that people are buying is hallmarked.
- About 156 Quality Control Orders (QCOs) of 672 products are being processed.
- Standards Development is the process of creating and establishing agreed-upon guidelines or criteria to ensure quality and operability of various products or services.
- Significance of standardization:
- Supports economic growth and enhances competitiveness.
- Fosters technological development and supports innovation.
- Addresses health, safety and environmental concerns.
- Standards Development process in India is largely government led with BIS acting as National Standard Body.
- Established under BIS Act 2016.
- Involved in harmonious development of activities of standardization, marking and quality certification.
- Administered by Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution with its Minister being President of BIS.
- Other initiatives for standards development:
- Standards National Action Plan (SNAP)
- Indian National Strategy for Standardization (INSS)
- Quality Council of India (QCI) and its Scheme for Accreditation of Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs)
- One Nation One Standard Scheme of BIS.

- Tags :
- Quality
UREA GOLD
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved launch of Urea Gold.
- Urea gold will support the other initiative of government in the sphere of Environmentally Friendly Fertilizers (EFFs).
- Urea gold is a Sulphur-Coated Urea (SCU).
- It is a non-organic slow-release fertilizer and is generally prepared by coating preheated urea granules with molten sulphur.
- Sulphur coating ensures a more gradual release of nitrogen.
- It prolongs the urea action, thus helping plants to stay greener for longer time.
- It will increase efficiency and reduce frequent application of fertilizer, thus enhancing soil health.
- As per Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) study, use of SCU leads to reduction in urea consumption by 25%.
- EFFs are fertilizers that can reduce environmental pollution from nutrient loss by retarding, or even controlling, the release of nutrients into soil.
- EFFs also include organic fertilizers such as Biocompost, Vermicompost, etc.
- Development of Nano Urea and Neem Coated Urea.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samruddhi Kendras (PMKSK) will facilitate these fertilizers.
- GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan), helps in preparing organic manure.

- Tags :
- Urea
- Fertilizer
PROTECTION OF PLANT VARIETIES AND FARMERS’ RIGHTS ACT
- Delhi High Court permits PepsiCo to claim patent for potato variety grown for its potato chips.
- Judgement came on PepsiCo’s appeal under Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPVFR) Act, 2001 against order of PPVFR Authority.
- PPVFR Authority had revoked PepsiCo’s registration with respect to plant variety - FL 2027.
- FL 2027 is chipping potato variety with low external defects which is grown exclusively for PepsiCo by some farmers.
- It has high dry matter/high solids content and stable sugars, making it highly suitable for manufacture of chips.
- Under WTO’s TRIPS (Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights), it is obligatory for a member to provide protection to new plant varieties.
- Under this, India enacted PPVFR Act.
- A plant variety which conforms to criteria of Distinctiveness, Uniformity and Stability (DUS) is eligible for registration under PPVFR Act.
- PPVFR Act recognizes following rights:
- Farmers’ rights: Registration and protection of new variety, farmers' variety, and extant variety, rewards for conservation of plant genetic resources etc.
- Researchers’ rights: Use of any registered variety for experiments.
- Breeders’ rights: Exclusive rights to produce, sell, import or export etc.
PPVFR Authority
|
- Tags :
- Farmers
- IPR
SOLAR POWER SCHEME FOR PVTGS HABITATIONS
- President has sanctioned implementation of the scheme under new solar power Scheme for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) Habitations/ Villages.
- The scheme was launched under Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN).
- Key features of scheme
- Two components:
- Electrification of 1 Lakh PVTG households (HHs) through Off-grid solar powe: Solar Home Lighting System (SHLS) for scattered un-electrified HHs in PVTG areas and Solar Mini-grids for cluster of HHs in a PVTG habitation/ hamlet.
- Solarization of multi-purpose centers (MPCs) by installation of Off-grid Solar power pack with battery bank.
- Implementing agency: Respective DISCOMs in PVTG area.
- Timeline: 2023-24 to 2025-26.
- Monitoring: By Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) and Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA).
- Grievance Redress mechanism: Vendors shall operationalize helpline number in local language/ language of PVTG area.
- Two components:
- PM JANMAN
- Aim: To saturate PVTG HHs and habitations with basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, etc.
- Comprises 11 critical interventions through 9 ministries, including MoTA, over 3 years.
- Implemented as combination of:
- Centrally Sponsored Schemes in partnership with State Governments/ UT Administrations and
- Central Sector Schemes through line Ministries/Departments.

- Tags :
- Solar Power
- PVTG
ELECTRICITY (AMENDMENT) RULES, 2024 NOTIFIED
- Ministry of Power notified Electricity (Amendment) Rules, 2024 to amend Electricity Rules, 2005.
- In exercise of powers conferred by Section 176 of Electricity Act 2003, government has prescribed new rules for-
- promoting ease of doing business by industries like Green Hydrogen manufacturers, facilitate energy transition and energy security.
- Key highlights of rules
Parameters | Rules | Significance |
Transmission Lines |
|
|
Open Access (OA) |
|
|
Power Tariff |
|
|
- Tags :
- Electricity
GLOBAL HYDROGEN TRADING MECHANISM (GHTM)
- Indian Gas Exchange or IGX (India's only gas exchange) and Gujarat State Petroleum Corporation (GSPC) signed a MoU to establish a GHTM in collaboration with IFSC-GIFT City in Gandhinagar (Gujarat).
- They will develop a global hydrogen price index, a benchmark for price discovery and market information on India's growing green hydrogen market.
- Benefits: Enhance transparency, boost investor confidence, and facilitate the growth of the green hydrogen market on a global scale.
- Tags :
- Hydrogen
POINT OF PRESENCE (POP) REGULATIONS FOR NPS SUBSCRIBERS
- Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) notifies new point of presence regulations for NPS subscribers.
- PFRDA has notified the Point of Presence (PoP) Regulations 2023, requiring only one registration for the National Pension System (NPS).
- POPs are the first points of interaction of the NPS subscriber with the NPS architecture.
- The authorized branches of a POP, called Point of Presence Service Providers (POPSPs), will act as collection points.
- Banks and non-banks can now act as PoPs to onboard NPS subscribers, and they will require only a single registration for NPS, instead of multiple registrations earlier.
- The timeline for disposing of applications has also been reduced from 60 days to 30 days.
- POPs are the first points of interaction of the NPS subscriber with the NPS architecture.
- The simplification is in line with the Union Budget 2023-24 announcement to review regulations to reduce the cost of compliance and enhance the ease of doing business.
- About National Pension System (NPS):
- Introduced by the Central Government in 2004 to help the individuals have income in the form of pension.
- Any citizen of India, whether resident or NRI, can join NPS.
- It is mandatory to all employees joining services of the Central Government (except Armed Forces) and Central Autonomous Bodies on or after 1st January 2004.
- PFRDA regulates NPS under the PFRDA Act, 2013.

- Tags :
- National Pension System
FUTURE OF GROWTH REPORT 2024
- The report, published by the World Economic Forum (WEF). introduces a multidimensional framework to assess the quality of economic growth across 107 countries globally.
- It characterizes nations’ economic growth across four dimensions: Innovativeness; Inclusiveness; Sustainability; and Resilience.
- Framework produces an aggregate result for each pillar on a 0-100 scale, where 100 is an ideal and country is perfect in every pillars.
Pillar | Description |
Innovative-ness |
|
Inclusiveness |
|
Sustainability |
|
Resilience |
|
- The report also classifies clusters of countries with similar growth characteristics into 7 groups based on inclusion, innovation, and sustainability.
- India is grouped among countries with traditionally efficiency-driven growth pathways, building up innovativeness, inclusiveness and resilience from a low base, with comparatively low environmental footprint.
- Tags :
- Growth
- World Economic Forum (WEF)
INCLUSIVE ACCESS TO ADVANCED AI
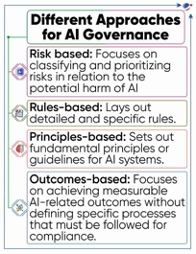
- World Economic Forum’s AI Governance Alliance (AIGA) Calls for Global Efforts for Inclusive Access to Advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- AIGA (launched in 2023) aims to accelerate the development of ethical guidelines and governance frameworks for Generative AI.
- Generative AI is a type of AI technology that can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data.
- World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-profit organization based in Geneva (Switzerland) committed to improving state of the world.
- At recent WEF Annual Meeting 2024, AIGA released new reports on advanced AI focusing on generative AI governance. Key highlights are below,
- Challenges: Absence of a standardized perspective on the generative AI model lifecycle, vague definitions etc. are impacting development of safe generative AI.
- AI Governance: Global landscape for AI governance is complex and rapidly evolving, AIGA recommended for,
- International coordination: A multi-stakeholder approach involving government, civil society, academia, industry for legitimate governance of AI.
- Compatible standards: To avoid significant differences in standards, national bodies should work together and align their efforts.
- Flexible regulatory mechanisms: To match AI's rapid advancements, investment in innovation and governance frameworks must be agile and adaptable.
- Role of Global South: Include Global South at all AI stages for innovation, ensuring everyone benefits and minimizing global harms.
- Tags :
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
LABOUR RULES FOR WORKERS ABROAD
- Trade Unions have opposed UP and Haryana governments’ recruitment of workers to work in Israel, primarily for construction activities.
- They have cited that it is against Indian ethos of bringing back citizens from conflict zones.
- Issues faced by migrant labourers
- Vulnerability to regional conflicts: Risk of conflict and violence due to volatile political landscape. e.g., Ongoing Israel – Hamas conflict.
- Exploitation and unfair labour practices: Wage theft, poor working conditions, etc., due to limited legal knowledge and language skills.
- Denial of social security: Due to lack portability, etc.
- Other issues: Lack of proper accommodation, poor standard of living, etc.
- Measures taken by India for protection of migrant labourers
- Bilateral and multilateral arrangements: India has signed Labour Manpower Agreements (LMAs) with six West Asian countries including Kuwait, Oman, etc.
- Welfare programmes: National Pension scheme for NRIs, Indian community welfare fund, etc.
- India has signed Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration (2018).
- Other measures: e-Migrate Application system, MADAD portal for grievance redressal, etc.
ILO conventions for protection of migrant workers
Note: India has not ratified both conventions. |
- Tags :
- Labour
RULES EXPLORATION LICENSE FOR MINING
- Ministry of Mines notified four rules to implement the Exploration License (EL) regime.
- Notified under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957, these rules include:
- Mineral (Auction) Amendment Rules, 2024
- Mineral Conservation and Development (Amendment) Rules, 2024
- Minerals (Evidence of Mineral Contents) Amendment Rules, 2024
- Minerals (Other than Atomic and Hydro Carbons Energy Minerals) Concession Amendment Rules, 2024
- Exploration License (EL)
- EL means a licence granted for undertaking reconnaissance operations or prospecting operations or both.
- It was introduced through MMDR Amendment Act, 2023.
- Issued in respect of 29 minerals specified in Seventh Schedule of MMRD Act including Cobalt, Lithium, Nickel, Gold, etc.
- Granted by: State governments through competitive bidding.
- Tenure: 5 years from date of execution of EL.
- Central government through rules can prescribe the details such as manner of auction, bidding parameters, etc.
- EL means a licence granted for undertaking reconnaissance operations or prospecting operations or both.
- MMDR Act 1957 is the principal legislation regulating mines and mineral sector in India.
- It classifies mining related activities into-
- Reconnaissance (preliminary survey to determine mineral resources),
- Prospecting (exploring, locating, or proving mineral deposits), and
- Mining (commercial extraction).
- It classifies mining related activities into-
- Tags :
- Mining
- Exploration
COAL/LIGNITE GASIFICATION PROJECTS
- Cabinet approves Viability Gap Funding of Rs 8500 crore for promotion of Coal/Lignite Gasification Projects.
- Key highlights of the scheme
- Incentive for coal gasification projects is provided to Government PSUs and Private Sector under three categories.
- Category I: For Government PSUs, upto 3 projects will be supported.
- Category II: For Private Sector and Government PSUs.
- Category III: For demonstration Projects (indigenous technology) and/or small-scale product-based Gasification Plants.
- Selection of entities under category II and III shall be carried out through a competitive bidding process.
- Grant will be paid to the selected entity in two equal instalments.
- Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS), chaired by the Secretary Coal, is fully empowered to modify the scheme's modalities except total outlay.
- Incentive for coal gasification projects is provided to Government PSUs and Private Sector under three categories.
- Coal gasification
- Underground Coal gasification is a process by which coal is converted to useful gases without the need for mining.
- Gases can subsequently be used to produce heat, generate power or synthesize a variety of chemical products.
- It helps in harnessing the coal reserves that are deep, scattered and covered by forests.
- India has a target to gasify 100 million tonnes of coal by 2030.
- Underground Coal gasification is a process by which coal is converted to useful gases without the need for mining.
Related News Cabinet approved two joint venture projects for coal gasification
|
- Tags :
- Coal Sector
STEEL MAKING
- Government is aiming to increase share of scrap in steel making process to 50 % by 2047 says Union Minister of Steel.
- Steel Scrap in Steel making
- Steel is a material most conducive for circular economy as it can be used, reused and recycled infinitely.
- While iron ore remains the primary source of steel making, used or re-used steel in form of Scrap is secondary raw material for steel industry.
- Benefits of Steel scrap
- Resource Conservation: Use of every ton of steel scrap shall save 1.1 ton of iron ore, 630 kg of coking coal and 55 kg of limestone.
- Reduced carbon footprints: Use of scrap cuts emission by 25 % in comparison to primary route of steelmaking.
- India’s steel sector accounts for 12% of India’s CO2 emissions.
- Energy Savings: Production of steel from recycled steel requires less energy.
Recent Steps Taken
- National Steel Policy, 2017: Aspires to achieve 300MT of steel-making capacity by 2030 with a contribution of 35-40% from EAF route.
- Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) route produce steel mostly from scrap collected for recycling.
- EAF and Blast Furnace-Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF) route are methods of steelmaking.
- Steel Scrap Recycling Policy, 2019: Enhances availability of domestically generated scrap to reduce consumption of coal in steel making.

- Tags :
- Steel Industry
DECLINE IN INDIVIDUAL INCOME INEQUALITY: SBI RESEARCH
- SBI Research report reveals decline in individual income inequality in the country in past 8 years.
- Key highlights of the report: From 2013-2014 to 2021-2022:
- In terms of Gini coefficient, income inequality of taxable income group has declined from 0.472 to 0.402.
- 36.3% of taxpayers have moved from lower income to higher income tax bucket.
- Top 2.5%of taxpayer’s contribution in income has declined from 2.81% to 2.28%
- Female labour force participation is rising.
- Micro firms are transitioning towards small, medium and large size firms.
- These findings dispel the notion of 'K '-shaped growth or recovery.
- K-shaped recovery happens when different sections of an economy recover at starkly different rates.
- Many experts have suggested that post the COVID-19 pandemic, India is experiencing a 'K-shaped' recovery, where the rich thrive while the less privileged face challenges.
- K-shaped recovery happens when different sections of an economy recover at starkly different rates.
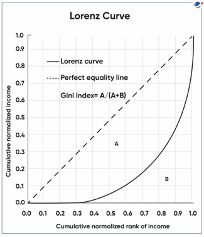
- About Gini coefficient
- Gini coefficient is a statistical measure of income or wealth inequality, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality).
- Theoretically, values over 1 are possible due to negative income or wealth.
- Gini coefficient larger than 0.40 is considered high.
- Gini coefficient is a statistical measure of income or wealth inequality, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality).
- Tags :
- Inequality



