Why in the News?
Recently, DRDO successfully conducted flight-tests of the Phase-2 Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) System.
More on the News
- Phase-II Air Defence (AD) Endo-atmospheric missile was launched from Integrated Test Range, Chandipur, post detection of target missile by weapon system radars deployed on land and sea.
- Phase-II Air Defense Endo-atmospheric missile is an indigenously developed 2-stage solid propelled ground launched missile system.
- It is meant for neutralizing enemy ballistic missile threats in the altitude bracket of endo to low exo-atmospheric regions.
- Test has demonstrated India's indigenous capability to defend against the Ballistic Missiles of 5000 km class.
About Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Systems
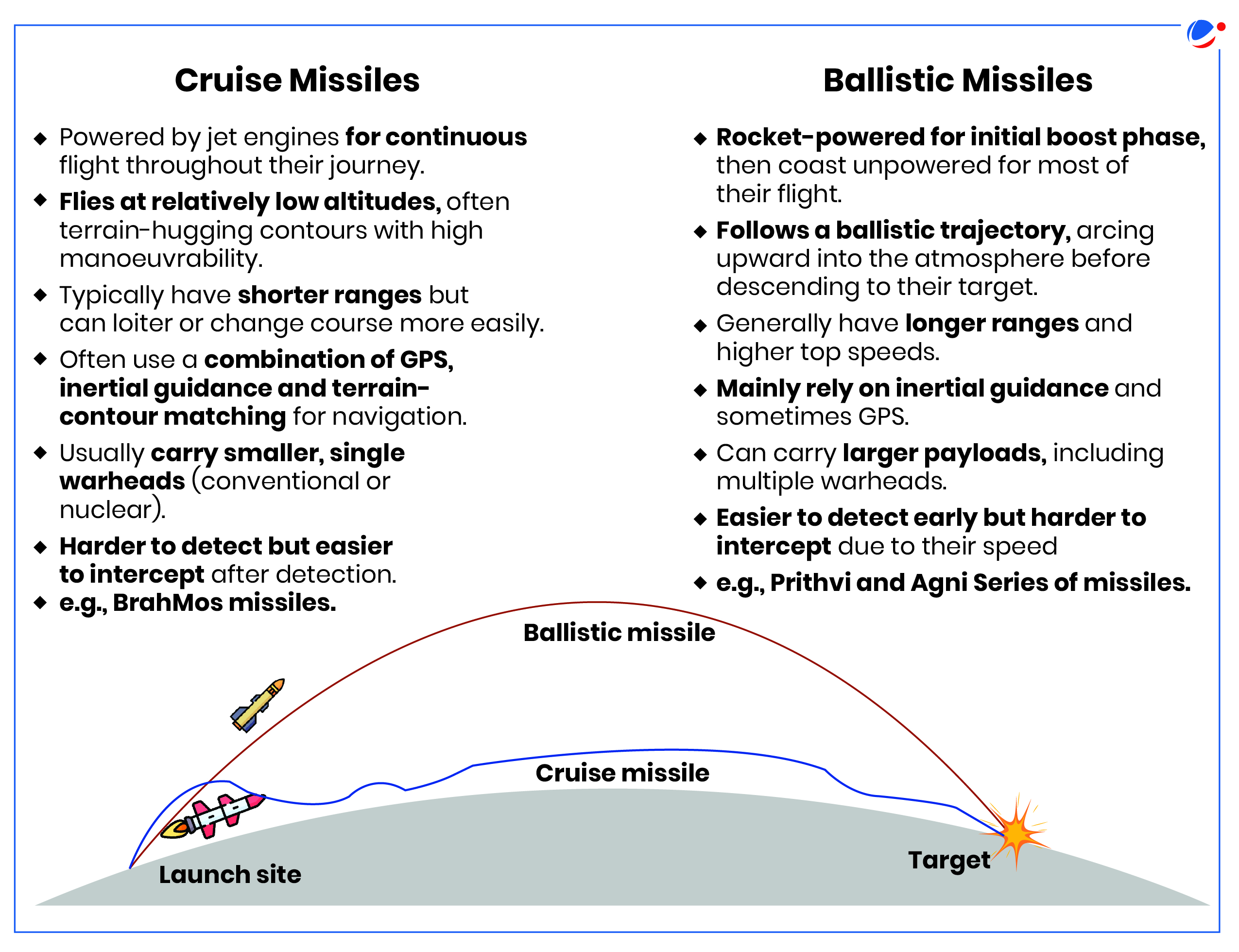
- BMD systems seek to defend against an aerial attack like drones, fighter jets, and ballistic and cruise missiles by launching interceptors that would hit incoming missiles and destroy them on impact.
- Other Important Missile Defence systems of the world include THAAD (USA), Iron Dome (Israel), Patriot (USA), etc.
Evolution of India's BMD Program
- India's BMD program was sanctioned in 2000 in the backdrop growing threats from China and Pakistan and nuclearization of the sub-continent.
- Work for its development commenced in 2 phases:
- Phase-I: Designed to intercept missiles with a range of up to 2000 km.
- It includes 3 things - Prithvi Air Defence (PAD), Ashwin Advanced Air Defence (AAD), and Swordfish RADAR (long-range tracking radar developed for the BMD system).
- Phase 1 has been successfully tested and has been deployed.
- Phase-II: It is capable to intercept missiles with range up to 5000 km.
- It consists of two missiles, AD-1 and AD-2.
- AD-1 is a long-range interceptor missile designed for both low exo-atmospheric and endo-atmospheric interception of long-range ballistic missiles as well as aircraft.
- AD-2 missile is meant to intercept intermediate-range ballistic missile targets with a range between 3000-5500 km.
- It consists of two missiles, AD-1 and AD-2.
- Phase-I: Designed to intercept missiles with a range of up to 2000 km.
Significance of BMD Program
- Strategic: Domestic BMD capability aligns with India's goal of strategic autonomy in defense matters and the vision of becoming net-security provider in the Indo-Pacific.
- e.g., Delay in delivery of the S-400 air-defence missile system due to ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict essentially points to the problem of relying on foreign countries for security needs.
- It can also have implications for regional and global balance of powers by influencing adversaries' perceptions of India's defence capabilities and potentially impact their strategic calculations.
- Security: Changing security environment in the Indo-Pacific and simultaneous threats from two nuclear states necessitates development of BMD system.
- An effective BMD system would also help India negate nuclear coercion while still maintaining a no-first-use policy regarding nuclear weapons.
- It is also important in the context of contingencies, like irrational actions by States and the growing threats from non-state and transnational actors in South Asia.
- Technological: An effective BMD system may also lead to advancements in other critical domains such as Radars and tracking systems, dual-use technologies like telecommunication and aerospace, etc.
- Diplomatic: It can influences India's relationship with major powers like the US, Russia, etc., and its role in global non-proliferation efforts.
Challenges/ Concerns with BMD Systems
- Arms race: BMD can change the nuclear order and alter strategic stability encouraging adversaries to develop technology to thwart BMD systems and restore mutual vulnerability.
- Cost and resources: Securing adequate funding and allocating resources for research, development, testing, and deployment has always been a significant challenge in India due to lack of economies of scale.
- Inter-operability and evolution: Integrating the BMD capabilities with the existing military infrastructure requires careful planning to ensure smooth coordination and functioning during real-world scenarios.
- Defense capabilities also need to evolve as per the evolving advanced and unpredictable missiles capabilities from potential adversaries.
Conclusion
India's efforts to develop and deploy its BMD capabilities along with projects such as 'Project Kusha' which envisages to detect and neutralize aerial threats such as stealth fighters, aircraft, ballistic and cruise missiles, precision guided munitions, UAVs, etc., can significantly enhance India's deterrence posture and its ability to protect against potential threats, marking a new chapter in country's defense modernization efforts.





