Global INDIAai Summit 2024 summit hosted by India (lead chair of GPAI in 2024) was recently concluded.
Key Highlights and Outcomes of the Summit
- India emphasized on democratizing AI and making it accessible to all.
- A new integrated partnership on AI announced by OECD and GPAI (Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence)
- GPAI members came to a consensus about the future vision of GPAI, giving recognition to the New Delhi 2023 GPAI Ministerial Declaration.
Recently, the University of Oxford has cautioned against inflated expectations of quantum technologies.
- In spite of quantum technologies potential (e.g., quantum computing, quantum sensors, etc.,) it carries risks of misuse due to potential dual-use applications, especially in digital security.
- In this regard, many have called for Quantum Governance to create awareness of its concepts and explore its benefits for humankind.
About Quantum Governance
- World Economic Forum (WEF) was one of the first organisations to discuss quantum computing governance.
- ‘Quantum Governance’ framework for this is based on the principles of transparency, inclusiveness, accessibility, non-maleficence, equitability, accountability, and the common good.
Significance
- Accelerate the development of responsible quantum computing by building trust in the technology.
- Early ethical consideration by addressing quantum computing ethics during design and development phases.
- Learning from other technologies by applying ethical principles from AI, nanotech, nuclear, etc.
Challenges
- Researchers favor open quantum frameworks, while national policies prioritize strong intellectual property protections for quantum technologies.
- Private sector's profit-driven approach may hinder responsible, open quantum development.
- There is limited evidence on the impact of responsible innovation policies in quantum governance.
About Quantum Technologies
- Quantum Technology is based on the principles of Quantum mechanics developed in the early 20th century to describe nature at the scale of atoms and elementary particles.
- Application: secure communication, disaster management through better prediction, computing, simulation, chemistry, healthcare, cryptography, etc.
Initiatives taken by India
- National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications, 2023.
- 21 Quantum hubs in the country and 4 Quantum research parks across India.
Click here to read more about Quantum Technology in India.
A new malware called ‘Snowblind' is targeting Android phones.
About Snowblind Malware
- It is a malware that targets Android devices to steal banking and other sensitive information.
- Malware, or malicious software, is any program or file that's intentionally harmful to a computer, network or server.
- People usually get this virus by downloading a malicious app that looks legitimate.
- It repackages an app to avoid detection and misuses accessibility features to steal sensitive information and control the app remotely.
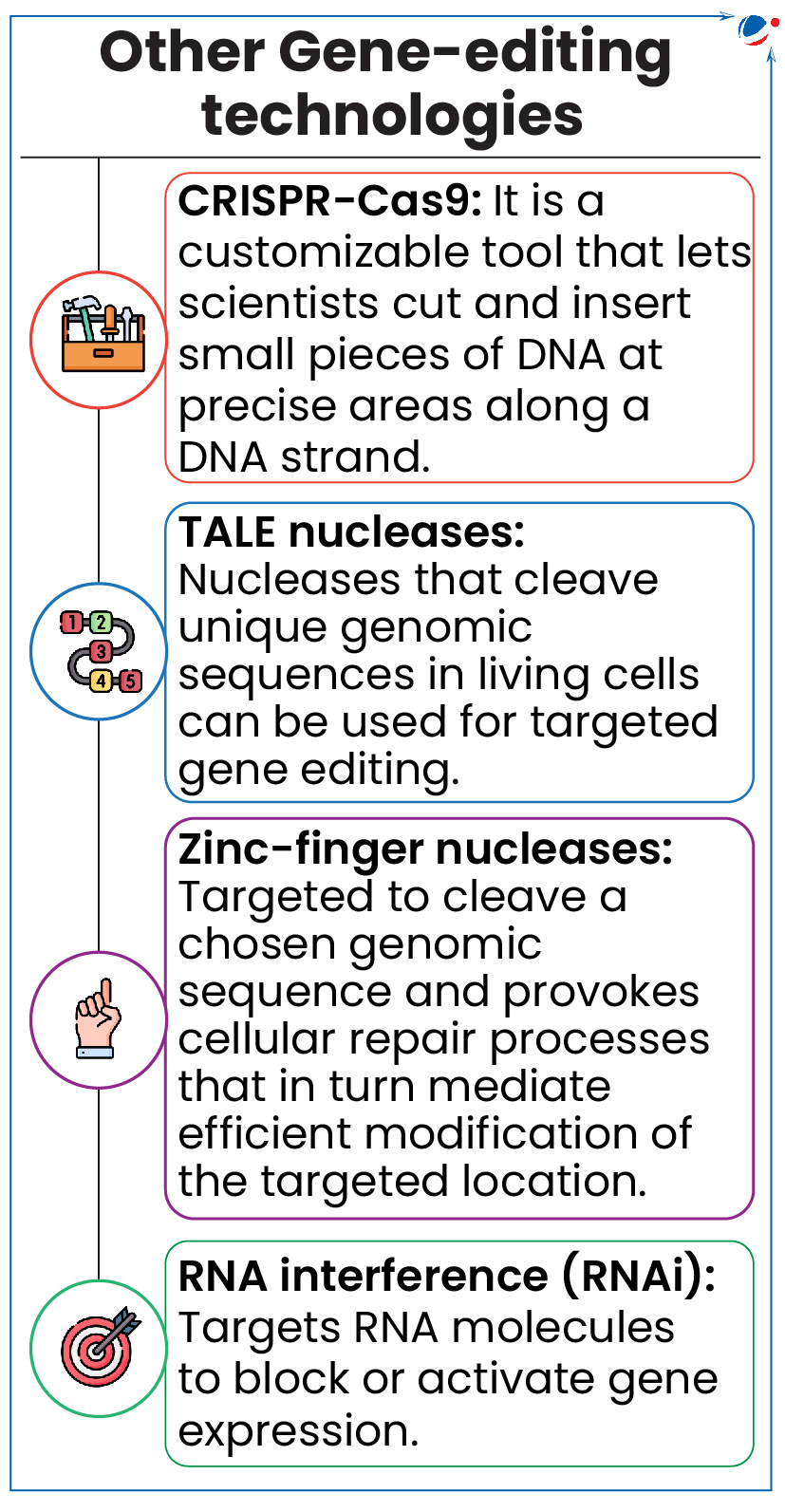
Scientists discovered naturally existing DNA editing tool - Bridge Recombinase Mechanism (BRM).
- BRM utilizes mobile genetic elements or “jumping genes”, which cut and paste themselves into genomes, performing on-the-go DNA manipulation and are present in all forms of life.
- Jumping Genes are small DNA segments with a recombinase enzyme along with extra DNA segments at the ends of the genes that binds and manipulates DNA.
- Gene editing is alteration of genetic material of a living organism by inserting, replacing, or deleting a DNA sequence, with the aim of improving some characteristic of a plant/ animal or correcting a genetic disorder.
About BRM
- Extra DNA at the ends of jumping genes gets joined together and converts the DNA double helix structure into a single-stranded RNA molecule.
- This bridge RNA molecule can bind to two DNA segments (donor and target), allowing for flexible DNA modifications.
- Donor and target loop can be programmed independently, offering great flexibility in inserting or recombining sequences to DNA.
Significance of BRM
- It will allow researchers to rearrange, recombine, invert, duplicate, move, and perform other editing operations on very long DNA sequences.
- It can lead to development of more advanced gene editing therapeutics and treatments for diseases.
New IVF procedure called mitochondrial donation (currently under trial in Australia) offers a cure to Mito.
- Mitochondria is the Powerhouse of the cells producing 90% of the energy needed to sustain life.
About Mito
- Inherited metabolic condition caused by genetic mutation in the DNA.
- It impairs the ability of mitochondria to convert food and oxygen into energy.
- Two Kinds (as there are two types of DNA):
- Nuclear DNA, inherited from both parents.
- DNA of the mitochondria, passed down through the mother.
Nipah monoclonal antibody trials may begin in India in 2025.
About Monoclonal Antibodies
- Monoclonal antibodies (moAbs or mAbs) are lab-made proteins mimicking natural antibodies.
- Antibodies are parts of body’s immune system which seeks out antigens (foreign materials) and destroy them.
- Applications:
- Diagnostics (e.g., ELISA),
- Treating diseases (cancer, infections, autoimmune disorders, etc.)
- Analyzing cell types in blood/tissue (with the use of fluorescent tags).
2024 marks the 100th year of electroencephalography (EEG)
About EEG
- It is a medical test which measures brain electrical activity generated by neurons.
- It uses small, metal discs called electrodes that attach to the scalp.
- Brain cells communicate via electrical impulses, and this activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording.
- Uses: Detecting epilepsy, neurological disorders, or any other brain related tumors, damage, etc.
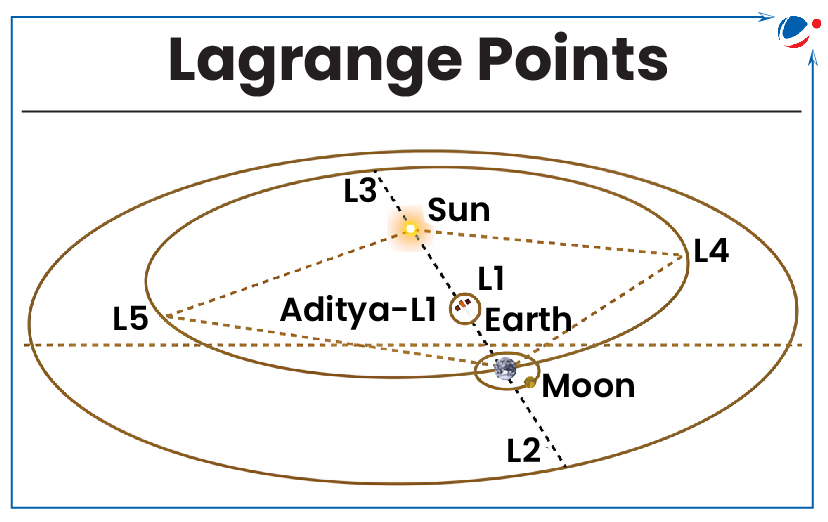
Aditya-L1 was inserted in its halo orbit in early 2024 and takes 178 days to complete a revolution around the Langrange L1 point.
- At Lagrange point, the gravitational pull of the two large bodies equals the necessary centripetal force required for a small object to move with them.
- For two body gravitational systems, there are a total five Lagrange points denoted as L1, L2, L3, L4 and L5. Out of these L4 and L5 are stable.
What are halo orbits?
- These are periodic and three-dimensional orbits resulting from an interaction between the gravitational pull of the two planetary bodies and centrifugal force on a spacecraft.
- Halo orbits exist in any 3-body system. E.g., Earth-Moon orbiting satellite system.
- Mainly linked to L1, L2 or L3.
Benefits of placing Aditya-L1 in Halo Orbit
- Ensuring a mission lifetime of 5 years
- Reducing fuel consumption (minimising station-keeping manoeuvres)
- Ensuring an unobstructed view of the sun
About Aditya-L1 Mission (2023)
- First Indian space mission to study the Sun.
- Objectives: Study the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds and flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and will carry out round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
- Payload: Carries 7 payloads (Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) etc.)

ISRO is keen to be a part Global Planetary Defense Efforts.
- At an international workshop on Asteroid Day 2024, ISRO Chairperson said that ISRO is looking to study asteroid Apophis when it is 32,000 km away from Earth in 2029 to prepare for planetary defense efforts.
About Asteroid Apophis
- Discovered in 2004, it is a near-Earth object (NEO) and was identified as one of the most hazardous asteroids that could impact Earth.
- There are billions of comets and asteroids in our solar system. The vast majority never approach Earth. When a comet or asteroid’s orbit brings it close to Earth, it is classified NEO.
- However, a radar observation campaign in March 2021, combined with precise orbit analysis, allowed astronomers to conclude that there is no risk of Apophis impacting our planet for at least a century.
Planetary Defense
- It refers to efforts and strategies aimed at protecting Earth from potential impacts by NEOs such as asteroids and comets.
- It involves multiple strategies including detection, tracking, impact assessment, deflection, etc.
- Need of Planetary Defense: If NEOs path intersects with that of Earth’s orbit, then depending on their size, speed, angle and impact region, could threaten billions of lives on impact and in the ensuing tsunamis, earthquakes and fires.
Recently, NASA’s Mars Odyssey Orbiter captured the view of largest volcano in our solar system, Olympus Mons, located on Mars.
About Mars Odyssey
- Launched in 2001, it is the longest continually active orbital mission.
- It was the first spacecraft to make a global map of chemical elements and minerals that make up Martian surface.
- Objective of Mars Odyssey
- Determine abundance of hydrogen in shallow subsurface.
- Acquire high spatial and spectral resolution images of surface mineralogy.
- Characterize Martian near-space radiation environment as related to radiation-induced risk to human explorers.
Researchers have found evidence of an underground cave on the moon that is accessible from the surface.
- The cave was recorded at the Sea of Tranquillity, a large, dark, basaltic plains on lunar surface.
About Lunar cave
- Lunar caves are believed to be the underground passageways formed through volcanic processes that are connected to the pits covering the moon’s surface.
- Significance of the discovery:
- New insight into the evolution of the moon and lunar volcanism.
- Caves could provide shelter for future astronauts from radiation, micrometeorites, and temperature extremes.
Budget 2024-25 announced that Centre will partner with private sector to develop Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs).
- This announcement marks a historic shift in India's nuclear policy, as the Atomic Energy Act of 1962 did not permit private sector participation in nuclear energy generation.
- BSRs are aligned with global trends where Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are gaining attention.
- Unlike SMRs, which are an entirely new concept involving factory-made, easily assembled reactors, BSRs are based on India's existing Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor technology.
- They can enhance the contribution of Nuclear energy in India’s energy basket (current share of nuclear energy is 1.6%).
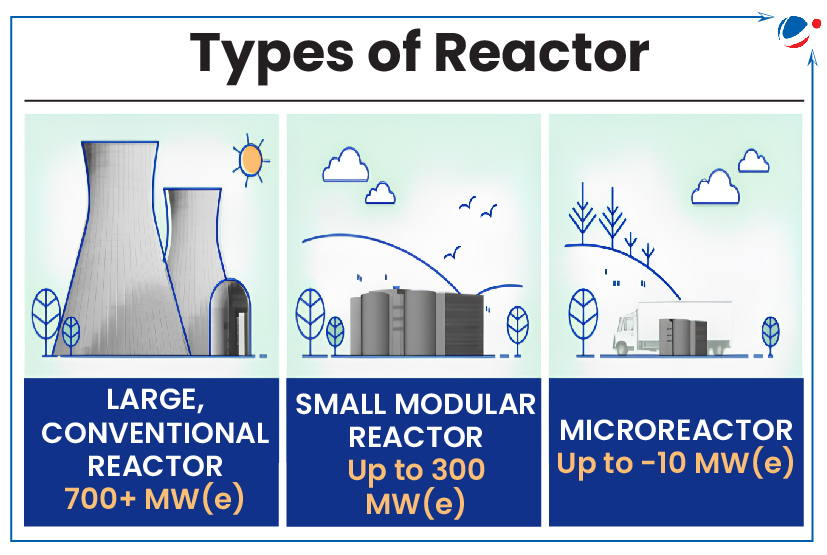
About Small Modular Reactors
- They are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit.
- There are more than 80 SMR designs and concepts globally. Most of them are in various developmental stages.
Significance of the SMRs
- Reduced fuel requirements, require less frequent refueling, every 3 - 7 years, compared to 1 -2 years for conventional plants (IAEA).
- Saves construction time as prefabricated units of SMRs can be manufactured, shipped and installed on site.
- Eliminate or significantly lower the potential for unsafe releases of radioactivity to the environment.
China has made world’s first high-temperature superconducting Tokamak device - ‘HH70’.
- Previously, the EU and Japan inaugurated JT-60SA, the world's largest and most advanced Tokamak fusion reactor in Japan and pledged support to advance fusion research for International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER).
- Tokamak is a machine for controlled thermonuclear fusion with a toroidal shape, similar to a doughnut.

About Nuclear Fusion
- A process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy.
- In nuclear fission, on the other hand, large atomic nuclei are split into smaller atomic nuclei to release energy.
- Most fusion reactors use a mixture of deuterium and tritium — hydrogen atom isotopes that contain extra neutrons.
About ITER
- ITER is a global scientific partnership between China, Europe, Japan, India, the Republic of Korea, Russia and the US.
- It’s currently under construction in France.
- Objective: To prove the viability of fusion as an energy source.
- It will be the largest Tokamak device to test magnetic confinement to produce fusion energy.
- ITER has been designed for high fusion power gain with about 10-fold return (expressed as Q ≥ 10), i.e., ratio of heating input power to thermal output power.
- Current record for fusion power gain in a Tokamak is Q = 0.67 by European JET facility in the UK.
MoD funded a start-up under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) will secure Li-Fi technology for the Indian Defence sector, particularly focusing on the Navy.
- iDEX fosters innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace sector.
- Managed by Defence Innovation Organization under MoD.
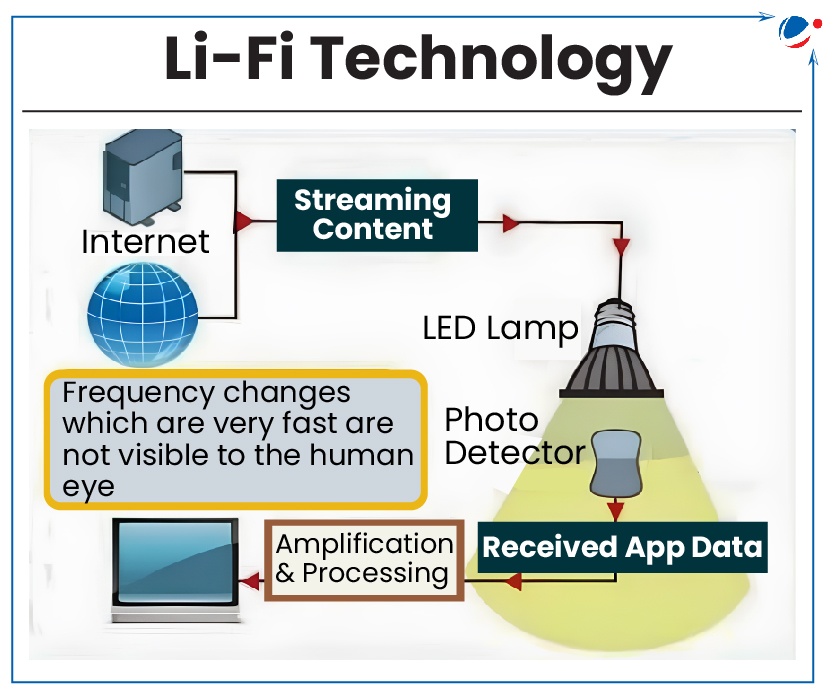
About Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) Technology
- A bidirectional wireless system that uses visible light (400-800 Terahertz) for communication, unlike Wi-Fi which uses radio waves.
- Transmits data with the help of Light Emitting Diode (LED).
- Working:
- On/off activity of the LED transmitter enables data transmission in accordance with the incoming binary codes (switching ON is a logical '1', switching it OFF is a logical '0').
- Applications: Aircrafts, hospitals (operation theatres), power plants etc. where electromagnetic (Radio) interference creates security issues.
Advantage of Li-Fi over Wi-Fi
- Faster: Combination of low interference, high bandwidths provide high data rate.
- Cheaper and sustainable: It is up to 10 times cheaper than Wi-Fi, requires fewer components and uses less energy.
- Secure: Since light does not pass through walls like radio waves do, it prevents interception.
Disadvantages
- Much shorter range than Wi-Fi.
- Can’t be accessed beyond the illumination range of light, etc.
Guidelines for Utilization and Processing of Steel Slag in Road Construction, released by Central Road Research Institute (CRRI).
About Steel slag
- It is a solid waste generated in the process of steel making.
- It is composed of oxides of calcium, iron, silicon, magnesium, etc.
- Key Applications: Road base course material (Steel Slag Road Technology (SSRT)), Blending material for Portland cement, Fertilizer and soil improvement etc.
- Benefits of SSRT
- Technical: Improved durability of road; Improved skid resistance; Economical than bituminous etc.
- Environmental: Utilization of 19 million tons of steel slag waste, generated annually; Reduction of carbon footprint in road construction.
Scientists discovered 'dark' oxygen 13,100-feet deep in the Pacific Ocean.
About Dark oxygen
- It is believed that Dark Oxygen is the oxygen that is produced without the process of photosynthesis.
- According to the study, it is generated by metallic nodules present on the seafloor.
- These natural metal formations appear to catalyze the splitting of seawater (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Previously, it was believed that most of the oxygen came from marine plants performing photosynthesis, a process which is dependent on sunlight.
- Discovery challenges existing paradigms about oxygen production in Earth’s most inaccessible marine environments.
Scientists have identified bone remains found in a Tibetan Baishiya Karst Cave as belonging to a Denisovan individual.
About Denisovans
- An extinct species of hominid and a close relative to modern humans.
- May have ranged from Siberia to Southeast Asia during the last Ice Age.
- DNA evidence suggests Denisovans are related to both Neanderthals and modern humans, and may have interbred with both.
- Share a common ancestor - Homo heidelbergensis (most likely lived in Africa) - with both modern humans and Neanderthals.
Scientists suggest LUCA could have formed just 300 million years after Earth's formation.
- This is estimated to be around 4.2 billion years ago.
About LUCA
- Researchers believe all the three branches of life i.e. bacteria, archaea, and eukarya have originated from a single microbe, called LUCA.
- However, there is no fossil evidence to support the existence of LUCA.
- Suggested Characteristics:
- Anaerobic: Grew in an environment devoid of oxygen.
- Thermophile: Heat loving microbe.
- Metabolism: Depended upon hydrogen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen, turning them into compounds such as ammonia.
A six-member student team from India have secured 4 Gold medals, 1 silver medal, and 1 honourable mention in the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) 2024.
- This is the best performance by an Indian in IMO since the country’s debut in 1989.
About IMO
- It is the World Championship Mathematics Competition for High School students and is held annually in a different country.
- First IMO was held in 1959 in Romania.
- Gold, Silver and Bronze medals are awarded, as well as Honorable Mentions for good effort.





