UNESCO launched “Imagine A World With More Women In Science’’ campaign.
- The campaign marks the 10th anniversary of International Day of Women and Girls in Science and highlights positive impact of diverse perspectives by using hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience.
- UNGA has in 2015 declared 11th February as International Day of Women and Girls in Science.
Gender Gap in Science
- Global:
- Low Representation: Women make up only one-third of the global scientific community
- Leadership Gap: Just 1 in 10 STEM leadership roles are held by women.
- India:
- Women constitute 43% enrolment in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics & Medicine)
- The number of women scientists is 18.6%, R&D projects run by Women are ~25%.
Challenges
- Social & Cultural Norms (restrictive gender roles), Lack of role models (few visible female leaders in science limits aspirations), workplace inequality (biased work cultures) etc.
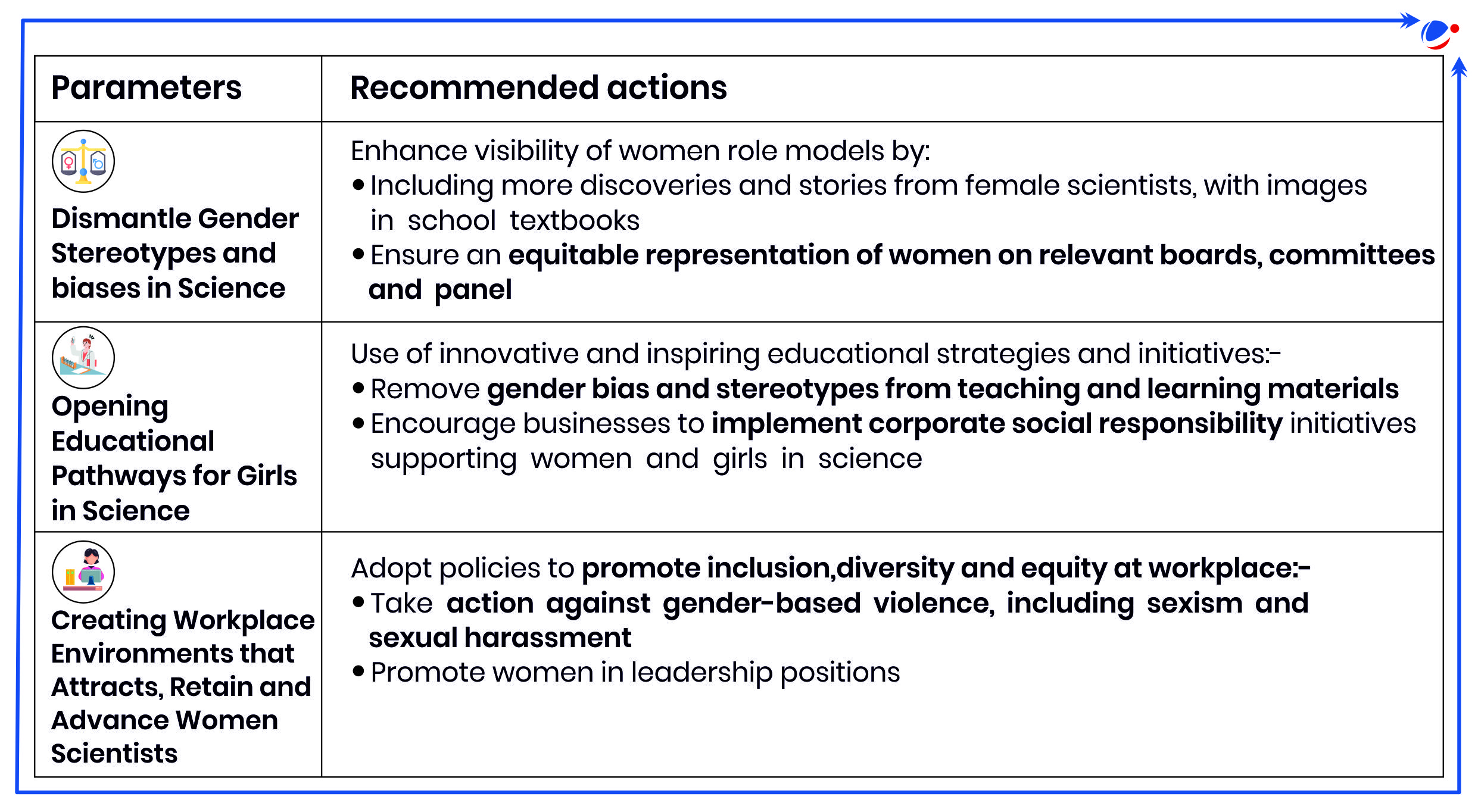
Steps to be Taken
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with NITI Aayog launched Swavalambini.
About Swavalambini
- A Women Entrepreneurship Programme, initially introduced across Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Eastern regions has been now expanded to other regions of the country.
- Implementation: By National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD) in joint partnership with NITI Ayog.
- Aim: To establish a structured and stage-wise entrepreneurial journey for young women. The programme will take participants through various stages, including awareness-building, skill development, training, mentorship, policy support and funding support.
- It also provides six months of mentorship and handholding support to help participants translate their ideas into sustainable prospects.
The Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) is a nationwide rural household-based survey of children's schooling and learning status.
- It tests the schooling status for children in the age group of 3-16, and the ability to read simple text & do basic arithmetic in the age group of 5-16.
- The ASER survey was conducted annually from 2005 till 2014. Thereafter, an alternate-year cycle was introduced.
Key Findings
- Reversing the Learning Gap: Improvements in basic reading and arithmetic among students of classes 3 and 5 in rural areas reverting back from the post-pandemic damage.
- Improvement in both reading & arithmetic levels for all elementary grades (Std I-VIII) since 2022 with arithmetic levels being highest over the decade.
- Digital Literacy: In 2024, for the first time, it includes a component of ‘Digital Literacy’ among the age group 14-16.
- Access to smartphones is close to universal: Almost 90% of both girls and boys report having a smartphone at home.
- Gender Gap in Smartphone Ownership: 36.2% of boys own a smartphone compared to just 26.9% of girls.
- Smartphone Usage More for Social Media than Education: Only 57% of teenagers use smart devices for educational purposes, while approximately 76% use them for social media.
- School Infrastructure: All Right to Education indicators in ASER show slight improvements, including functional girls' toilets, drinking water facilities etc.
WHO marked 20 years of its first global treaty, the WHO FCTC.
About WHO FCTC
- Genesis: Adopted in 2003, enforced in 2005.
- Purpose: Provides a legal framework for tobacco control which includes large pictorial health warnings, smoke-free laws, and higher taxes.
- India’s Role: Ratified in 2004, served as South-East Asia’s regional coordinator.
- Impact: 5.6 billion people covered by at least one policy, contributing to declining global smoking rates.







