Why in the News?
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the Intensified Special NCD Screening Drive.
About Screen Drive on NCD
- Aim: To achieve 100% screening of all individuals aged 30 years and above for prevalent NCDs and three common cancers—Oral, Breast, and Cervical.
- Implementation: Through Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs) and various healthcare facilities nationwide, under National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD).
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs are established under Ayushman Bharat initiative by upgrading existing Rural and Urban PHCs/Sub Centers.
About NP-NCD:
- Background:
- Launch: NP-NCD, formerly known as National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardio- vascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) was launched in 2010 across 100 districts in 21 states to combat NCDs as part of 11th Five Year Plan.
- 12th Five Year Plan: Proposed phased expansion to cover all districts.
- 2013-14: Subsumed under National Health Mission (NHM) which is a flagship centrally sponsored scheme to achieve universal access to affordable and quality health care services?
- Objectives of NP-NCD:
- Health promotion through behavior change with involvement of community, civil society, media etc.
- Screening, early diagnosis, management and follow-up at each level to ensure continuum of care.
- Capacity building, Strengthening supply chain management for drugs, equipment and logistics, Monitoring and evaluation through a uniform ICT application.
About Non Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
- NCDs are chronic diseases that are not transmissible from one person to another.
- Main types of NCDs are Cardiovascular Diseases (such as heart attacks and Stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
- When these are caused by an unhealthy lifestyle, these diseases are also called lifestyle diseases.
- NCDs tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioral risk factors.
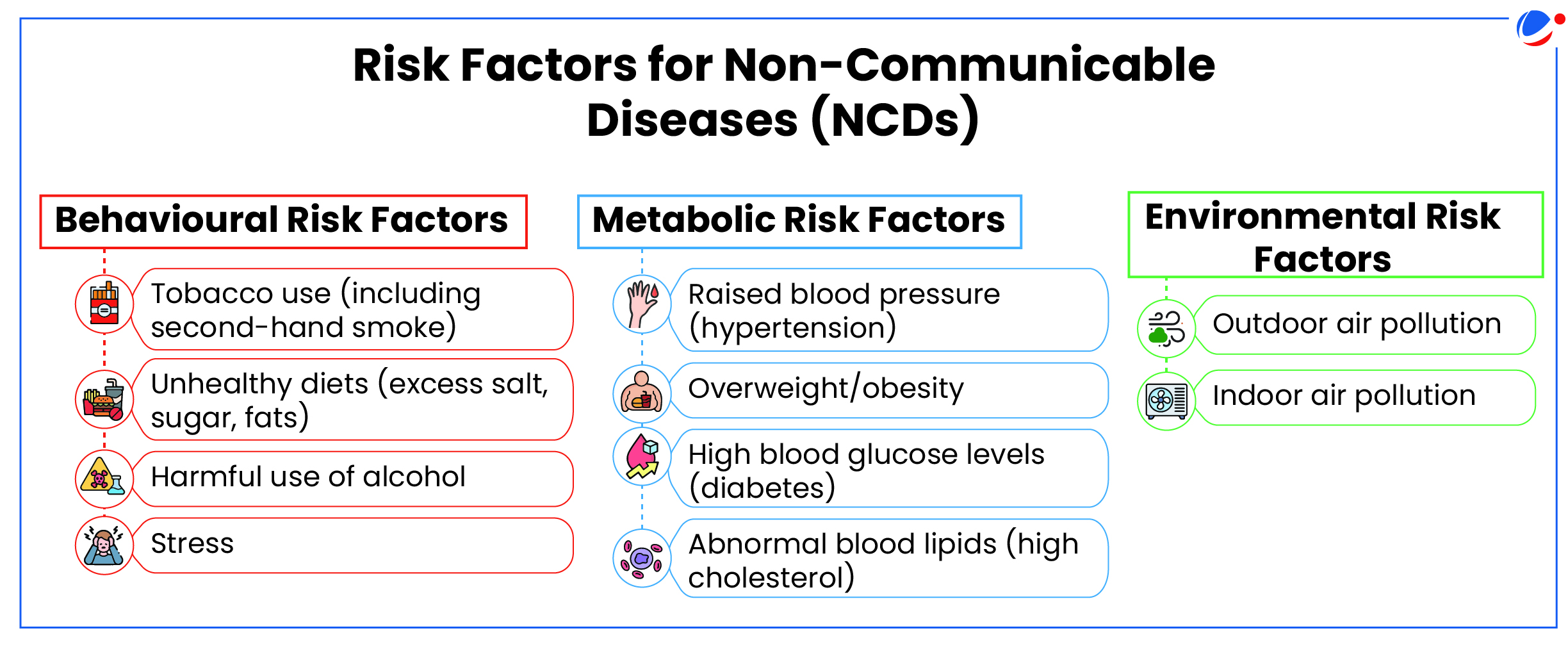
Burden of NCDs
- Global Scenario:
- NCDs are number 1 cause of death and disability worldwide, accounting for 74% of all deaths and more than three out of four years lived with a disability.
- Burden is greatest within low- and middle-income countries, where 77 percent of all NCD deaths occurred.
- Four top killers that together account for more than 80% of all premature NCD deaths annually include cardiovascular diseases (17·9 million), cancers (9.3 million), chronic respiratory diseases (4.1 million), and diabetes (2.0 million).
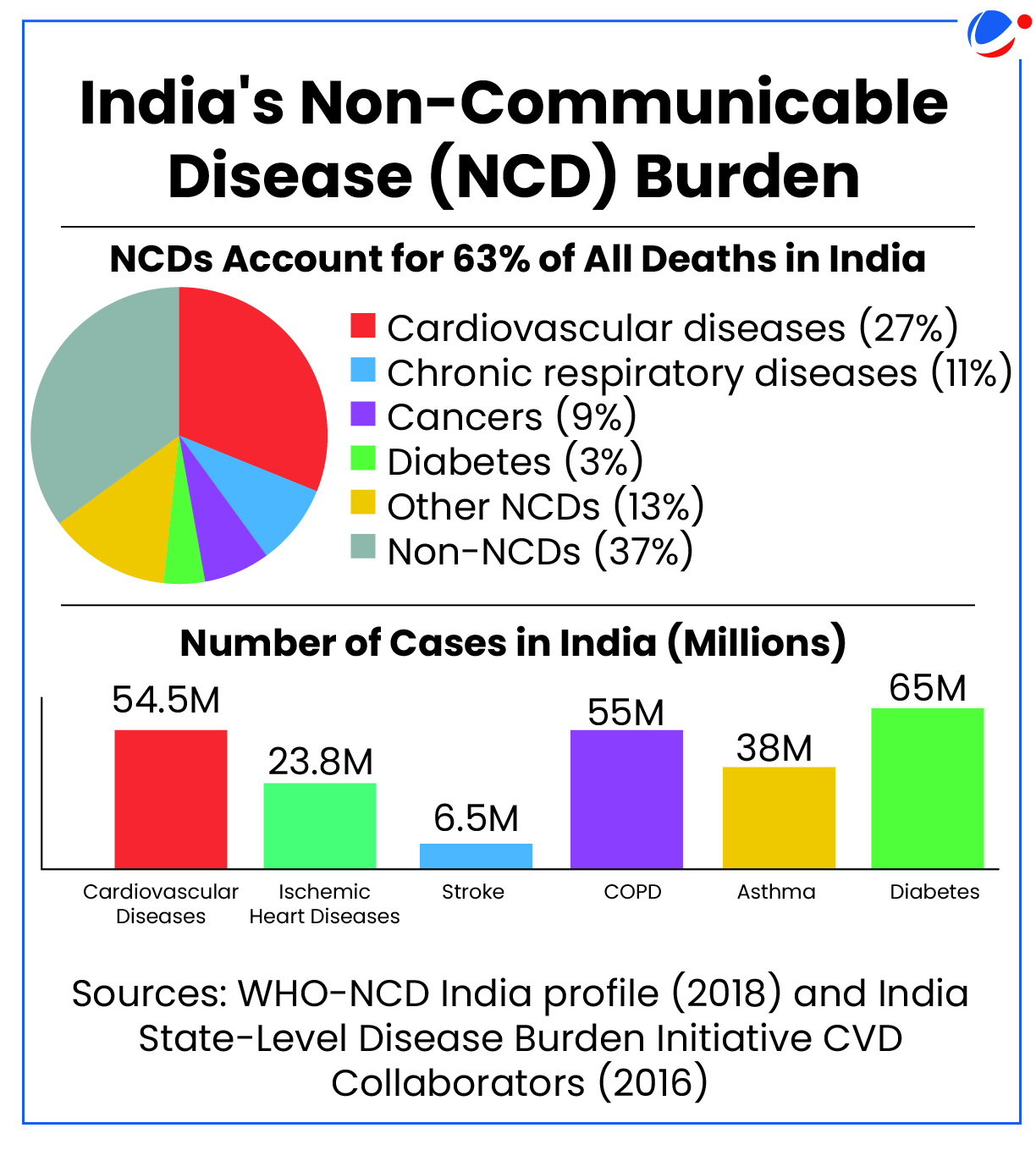
- Indian Scenario (Please refer Infographic)
Impact of NCDs:
- NCDs in childhood: Causes about 1.2–4.2 fewer years of completed education.
- Higher out of pocket medical expenditure: Overall, travel costs are the primary out-of-pocket expense for many Indian patients with NCDs.
- Life expectancy: Life expectancy is lowest at the age of 15 among lowest education groups due to higher death rates during 30–69 years from NCDs.
- Economic impact: WHO projects the economic burden of NCDs (E.g. Household health expenditure, Budget expenditure etc.) in India to surpass ₹280 lakh crore by 2030.
- Poverty: The rapid rise in NCDs is predicted to impede poverty reduction initiatives in low-income countries, particularly by increasing household costs associated with health care.
- Gendered Impact: The prevalence of NCDs among women is 62 per 1,000, as compared to 36 per 1,000 men.
- Other Impact: Low human capital, unhealthy labor force, revenue loss, etc.
|
Recommendations for Prevention and Control of NCDs:
- Comprehensive Approach: To lessen the impact of NCDs collaboration across sectors like health, finance, transport, education, and agriculture is crucial.
- NCD Management: Investing in better management of NCDs is critical. It includes detection, screening, treatment, and palliative care, ideally through primary healthcare for early intervention.
- Digital Health Interventions (DHIs): An additional US$0.24 per patient per year in DHIs, including telemedicine, mobile messaging, and chatbots, could Save over 2 million lives from NCDs over next decade.
- Leveraging fiscal tools: To reduce risk factors e.g. raising taxes on tobacco, Salt, sugar etc.
- Life-course approach to NCDs: Prevention and Management of NCDs along with other policy reforms like labor markets, social protection and long-term care.
- Policy Efforts: Increased government expenditure, encouraging private sector investments to address issue of regional imbalance in availability of human resources & infrastructure for treatment of chronic NCDs.






