Why in the news?
The RBI has imposed a six-month moratorium on New India Co-operative Bank Limited, restricting loans, deposits, and withdrawals.
More on the news
- According to the RBI, these measures have been taken due to concerns over the bank's financial stability and liquidity situation.
- The RBI also superseded its Board of Directors for 12 months, citing "poor governance standards".
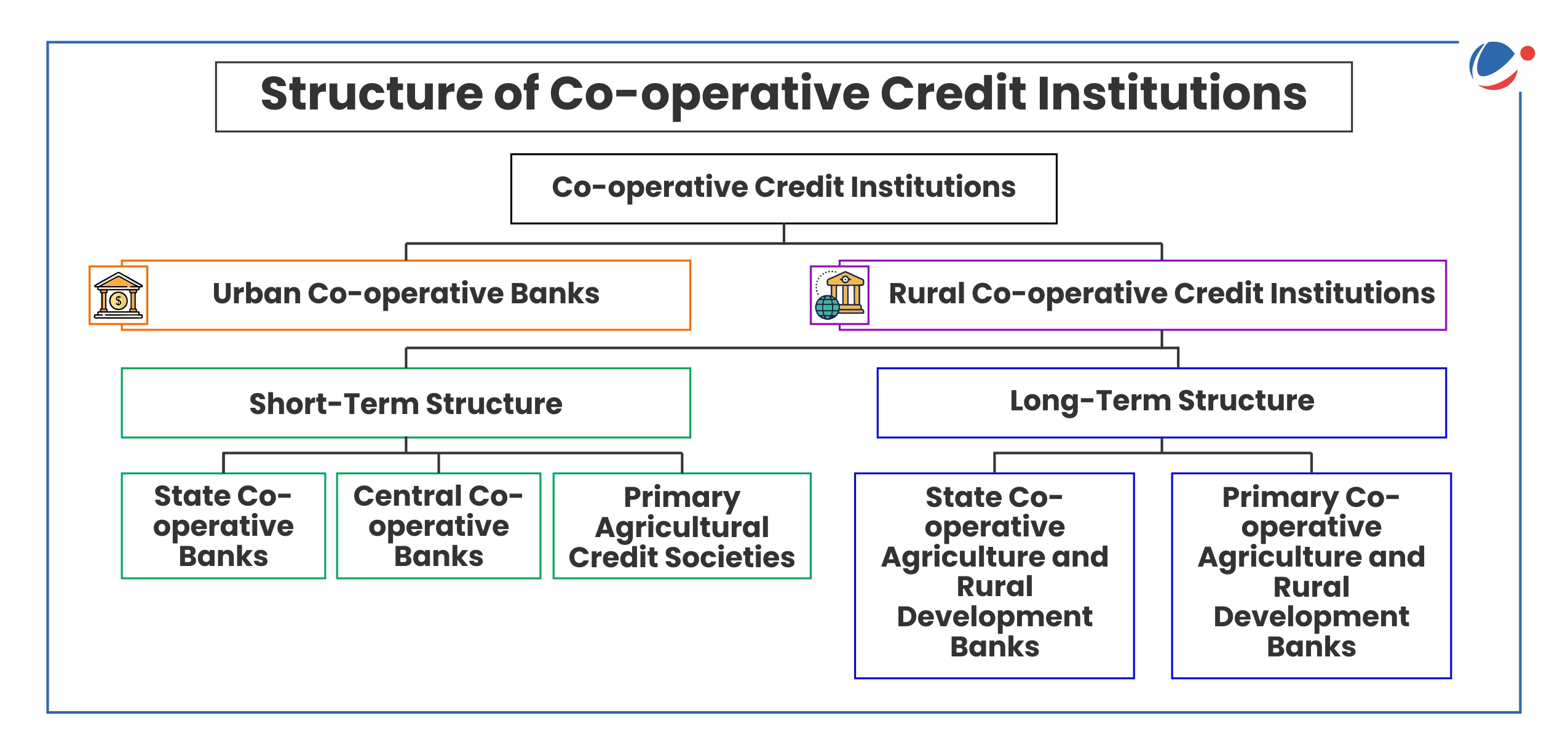
About Urban Cooperative Banks
- Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) are a subset of cooperative banks in India that operate primarily in urban and semi-urban areas.
- History: The Cooperative Credit Societies Act of 1904 (during Lord Curzon's tenure) and its 1912 amendment laid the legal foundation for these institutions.
- The first urban cooperative credit society was established in 1889 in Baroda (Anyonya Sahakari Mandali).
- Currently, they are registered as cooperative societies under the respective State Cooperative Societies Acts (for single-state operations) or the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 (for operations across multiple states).
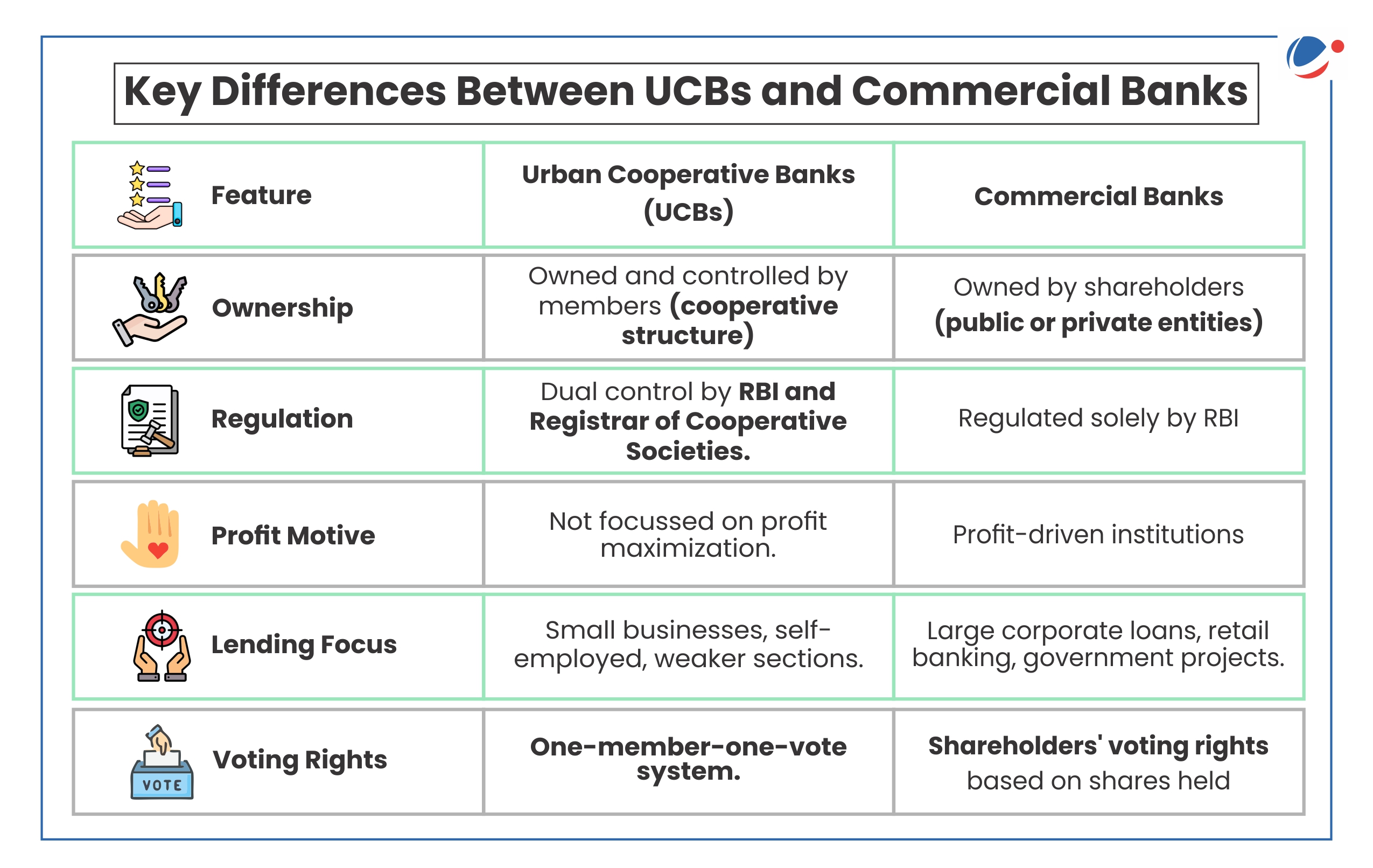
- Control and Regulation: UCBs function under a dual regulatory framework:
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949: Since 1966, RBI has been supervising UCBs regarding licensing, capital adequacy, loan policies, and financial stability.
- The Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2020 has given RBI more control over UCBs, allowing it to intervene in their management and governance.
- Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS): The respective state governments or the central government control administrative functions through the RCS.
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949: Since 1966, RBI has been supervising UCBs regarding licensing, capital adequacy, loan policies, and financial stability.
Significance of UCBs
- Financial Inclusion: UCBs primarily cater to small borrowers, micro-businesses, and lower-income groups in urban and semi-urban areas.
- Local Focus: UCBs operate within specific communities, allowing them to understand local needs and provide tailored financial services.
- Priority Sector Lending: UCBs have to allocate 65% to PSL in FY 2024-25 but increasing it to 75% by March 2026.
- Developmental Support: UCBs are catering the needs of the non-agricultural sector, particularly small borrowers in urban and semi-urban areas.
- UCBs, till 1996, were allowed to lend money only for non-agricultural purposes. This distinction does not hold today.
Challenges Faced by UCBs
- Weak Governance and Fraud Risks: Many UCBs suffer from political interference, nepotism, and financial mismanagement, leading to fraud and operational inefficiencies.
- During 2023-24, licenses of 24 UCBs were cancelled.
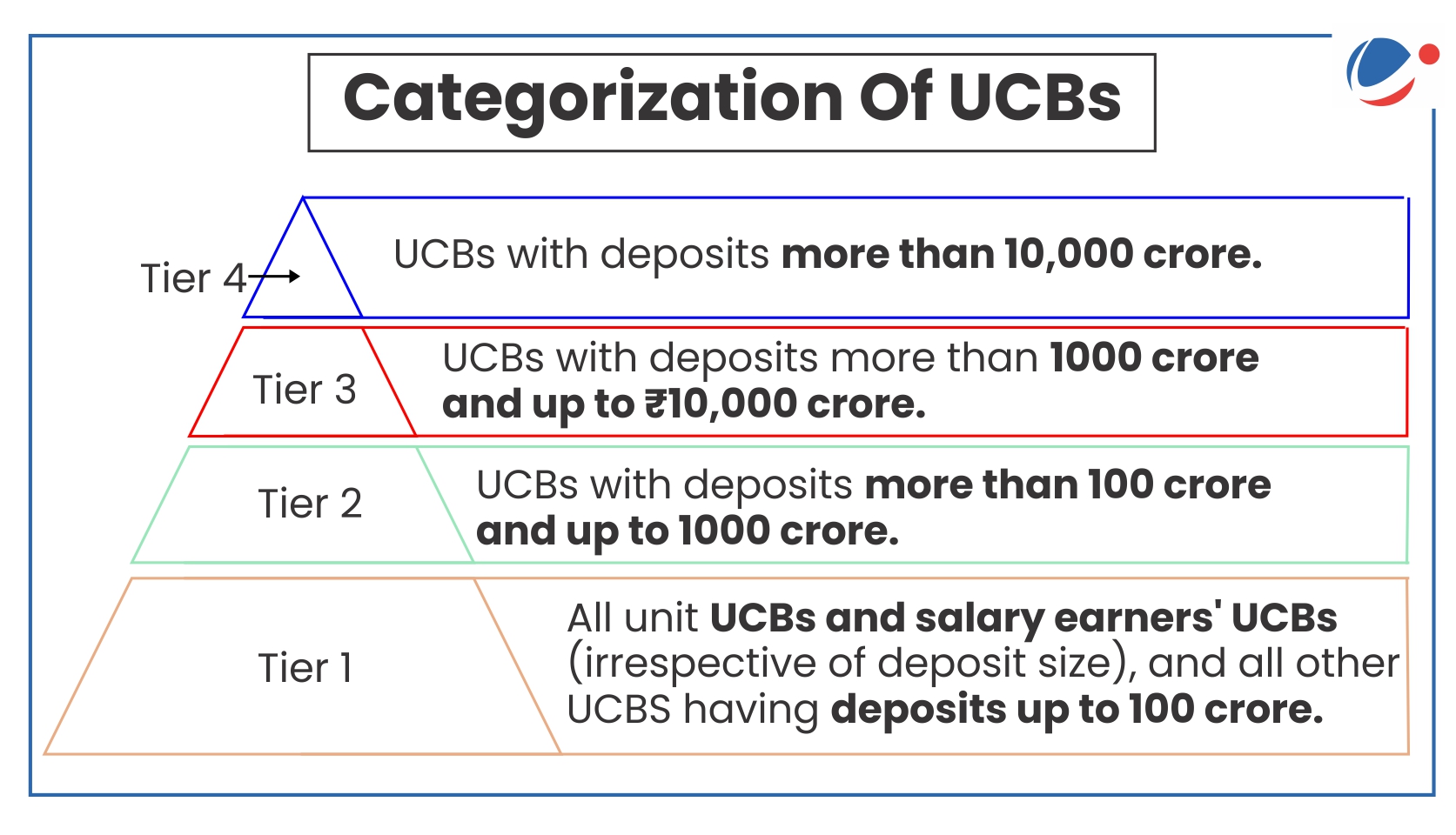
- Competition from Commercial Banks and Fintechs: UCBs share in the banking sector declined to 2.5% of total banking assets in March 2024, down from 3.8% in 2017.
- High Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): High levels of NPAs erode profitability and weaken the financial health of UCBs.
- Gross NPAs of UCBs were 8.8 per cent at the end of March 2024.
- Capital Adequacy Shortfalls: Limited access to capital markets restricts their ability to meet regulatory capital requirements and expand operations.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Dual regulation by RBI and state cooperative bodies leads to compliance challenges and operational inefficiencies.
- Technological Obsolescence: Many UCBs lag in adopting digital banking technologies, impacting efficiency and customer experience.
 Recent measures taken
|
Way forward
- Strengthening Governance and Supervision: Mandate professionalization of UCB boards by requiring at least 50% of directors to have expertise in banking, finance, or law.
- Consolidation and Mergers: Encourage voluntary mergers of weak UCBs with stronger ones to create financially resilient entities.
- Independent Audits: Conduct regular audits by autonomous bodies for all UCBs to ensure financial discipline.
- Technology Adoption: Cooperative banks are encouraged to adopt modern technology for efficient operations and better customer service.
- Social Audits: Enable stakeholder-led audits to assess policies and fund allocation.






