Deposit Insurance
Government is considering increasing the bank deposit insurance cover above current limit of ₹ 5 lakh.
About Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC)
|
About Deposit insurance
- It is a measure of protection to depositors, particularly small depositors, from the risk of loss of their savings arising from bank failures.
- Background: Deposit insurance was introduced in India in 1962 under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Act, 1961.
- India was the second country (after the US in 1933) in the world to provide for such provision.
- Coverage: The insurance protection extends to ₹ 5 lakh per depositor, which covers the aggregate of all accounts maintained by that depositor across all branches of the insured bank.
- However, if the deposits are held with more than one bank, deposit insurance coverage limit is applied separately to the deposits in each bank.
- Covered Bank: Insures all commercial banks, including branches of foreign banks functioning in India, local area banks, regional rural banks, and cooperative banks.
- Deposit insurance scheme is compulsory and no bank can withdraw from it.
- Exceptions: Land development banks, Non-Banking Financial Company’s (NBFCs) etc.
- Insures: Savings, fixed, current, and recurring deposits are insured.
- Exceptions: Does not provide insurance for deposits by foreign, central, and state governments, and for inter-bank deposits.
- It insures both the principal and interest amount held by a depositor in a bank.
- Through amendment in 2021, Section 18A amendment to the DICGC Act allowed depositors to receive time-bound (within 90 days) interim payments up to the insured amount when the RBI imposes restrictions on banks.
- Deposit insurance premium is borne entirely by the insured bank.
- DICGC collects premiums from member banks at flat or risk-based differentiated rates.
- Tags :
- deposit insurance
- DICGC
New Harmonised System Codes For GI Tagged Rice
India reportedly introduces New Harmonised System (HS) Codes for GI Tagged Rice.
- An amendment to the Customs Tariff Act (1975) was introduced to provide an HS (Harmonised System) code for GI-recognised rice varieties.
- The amendment will make it possible for the exports of GI-tagged rice without any problem or special notification from the Ministry of Finance.

About HS
- Definition: HS is a global product classification system developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO).
- Classification Structure:
- HS assigns specific six-digit codes for varying classifications and commodities.
- Countries are allowed to add longer codes to the first six digits for further classification.
- Governance and Updates
- HS is governed by "The International Convention on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System".
- HS Committee, made up of member countries, oversees the HS classification system and also updates HS every 5 – 6 years.
- Widespread adoption
- Classifies approximately 98% of international trade
- Encompasses over 5,000 commodity groups
- Implemented by more than 200 countries
- Benefits of HS
- Common coding method helps countries organize and track products in global trade.
- Extensively used by governments, international organizations and private organisations for internal taxes, trade policies, etc.
- Reduces international trade costs and supports economic research.
- Tags :
- HS Code
‘AI For Entrepreneurship’ Micro-Learning Module
Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship launched the ‘AI for Entrepreneurship’ micro-learning module.
‘AI for Entrepreneurship’ Micro-learning Module
- Launched in collaboration with National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and Intel India
- Purpose: To simplify AI concepts and encourage entrepreneurial thinking among young innovators across India.
- Target: To empower 1 lakh youth by 2025 by equipping them with essential skills to thrive in a technology-driven economy.
- Tags :
- Entrepreneurship
- AI For entrepreneurship
E-Shram Microsites & Occupational Shortage Index (OSI))
Union Minister for Labour & Employment launched the State and Union Territory Microsites under the e-Shram initiative and the Occupational Shortage Index (OSI).
About e-Shram Microsites
- State-specific digital platforms seamlessly integrated with the National e-Shram database.
- Benefits
- For States/UTs: Ready-to-use digital infrastructure, real time data analytics dashboard, etc.
- For Workers: Seamless registration process, multilingual facility, etc.
About OSI
- Purpose: Identify workforce demand-supply gaps using ILO methodology and PLFS data.
- Key Functions: Tracks job shortages in high-demand sectors, Supports workforce planning and skill development etc.
- Tags :
- E-Shram
Articles Sources
Time Use Survey (TUS)
Recently, National Statistics Office (NSO) released the 2nd Time Use Survey (TUS) for the year 2024.
About Time Use Survey (TUS)
- Purpose: It provides a framework for measuring time dispositions by the population on different activities.
- Objective: To measure the participation of men and women in paid and unpaid activities.
- Key findings
- Increase in women participation in employment related activities (paid activities).
- There is increased acknowledgement of caregiving activities regardless of gender within Indian families.
- Time spent in Culture, leisure, mass-media and sports practices has increased in both men and women.
- Tags :
- time use survey
Articles Sources
FDI Limit Hiked in Insurance Sector
Finance Minister announced proposal to raise FDI limit in Insurance sector from 74% to 100%.
- This enhanced limit will be available for those companies which invest entire premium in India.
- To enhance FDI limit, government will have to bring amendments to Insurance Act 1938, Life Insurance Corporation Act 1956, and Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999.
Significance of 100% FDI in insurance sector
- Higher Investment: More foreign capital for growth and expansion.
- Enhanced Competition: Better products, improved services, and competitive pricing.
- Technological Advancements: Adoption of advanced tech and innovative products.
- Improved Penetration: More people brought under insurance coverage and help achieve the target of 'Insurance for All' by 2047.
Status of India’s Insurance sector (Economic Survey 2024-25)
- Total insurance premium grew 7.7% in FY24, reaching Rs.11.2 lakh crore.
- Insurance penetration declined from 4% in FY23 to 3.7% in FY24.
- Insurance Density rose from USD 92 in FY23 to USD 95 in FY24.
- Insurance penetration is measured as percentage of insurance premium to GDP whereas insurance density is calculated as ratio of premium to population (per capita premium).
Challenges Faced by Insurance Sector in India
- Absence of top companies: Out of 25 world’s top insurance firms, 20 are not present in India now.
- Economic Constraints: Affordability issues restrict insurance adoption.
- Cultural Preferences: Preference for traditional financial practices over insurance.
- Tags :
- FDI
- Insurance
- FDI in Insurance
Articles Sources
Enhanced Certificate of Origin (ECOO) 2.0 System
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) has launched the enhanced Certificate of Origin (eCoO) 2.0 System.
About eCoO 2.0
- It is a significant upgrade to simplify the certification process for exporters and enhance trade efficiency.
- Offers several user-friendly features, such as multi-user access, which enables exporters to authorize multiple users under a single Importer Exporter Code (IEC).
- Supports Aadhaar-based e-signing alongside digital signature tokens, providing greater flexibility.
About Certificate of Origin
- It is a document used in international trade to certify that the goods being exported originated in a specific country.
- Tags :
- ECOO
Tonnage Tax Scheme
The Budget 2025-26 has expanded the tonnage tax scheme.
Tonnage Tax Scheme
- The Scheme was previously available to sea going ships.
- Now it is available to inland vessels registered under the Indian Vessels Act, 2021 to promote water transport.
- Inland Vessels Act, 2021 aims to promote safe, economical inland water transport, ensure legal uniformity and vessel procedures.
- Ministry: Ministry of Shipping (now part of the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways).
- Genesis: Introduced in 2004 under the Indian Finance Act, 2004.
- Significance: Encourage more cargo movement; will further incentivises shipping companies to invest in inland waterways vessels.
- Tags :
- tonnage tax
Articles Sources
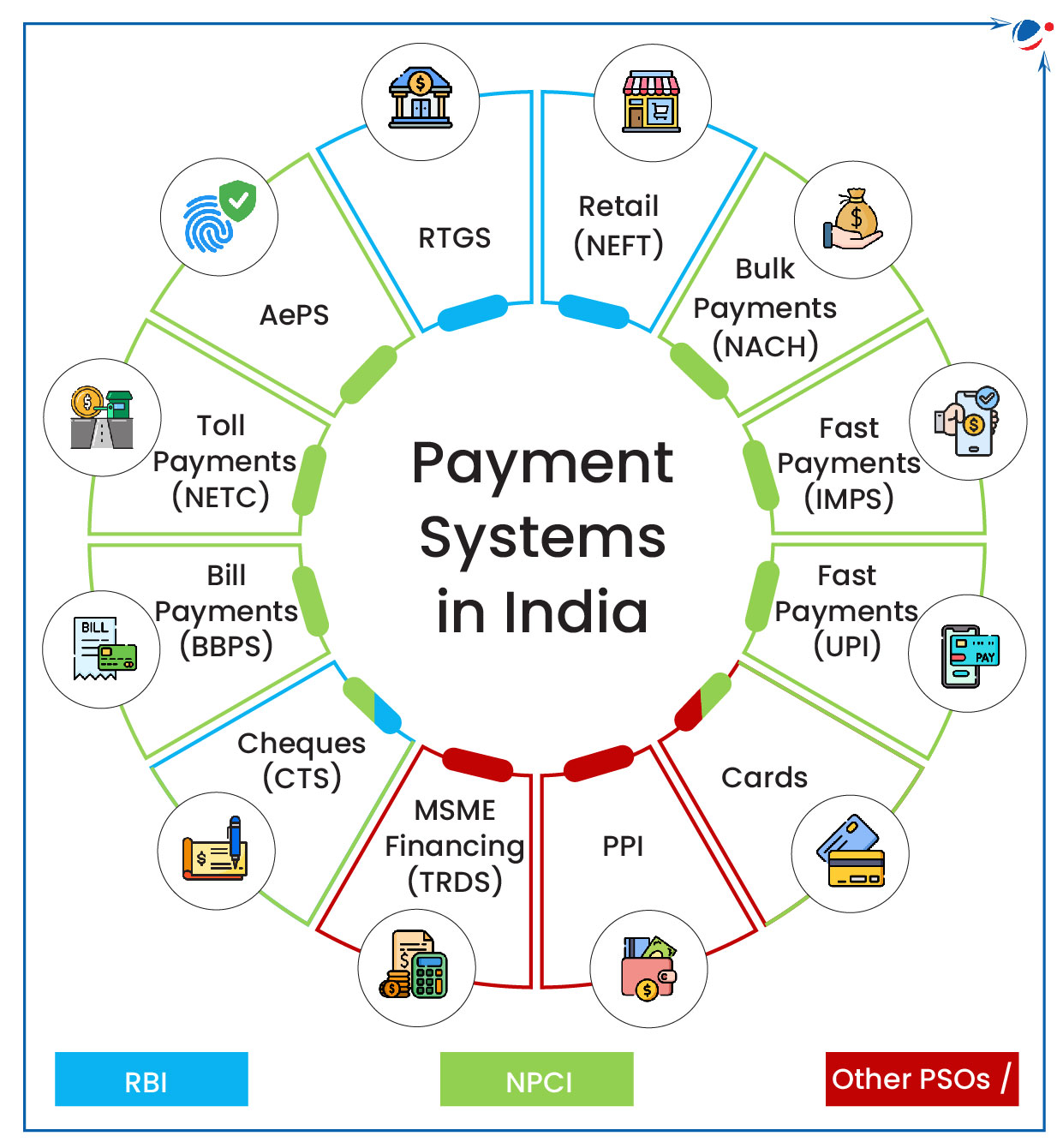
Regulation of Payment Systems in India
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released ‘Payment System Report, December 2024’.
- It is a bi-annual report which analyses the trends in payment transactions carried out using different payment systems in the last 5 calendar years (CY) up to CY-2024.
Key findings:
- Digital payment transactions: In 2013 there were 222 crore digital transactions valued at Rs 772 lakh crore, it has increased 94 times in volume and more than 3.5 times in value in CY-2024.
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI): Volume of UPI transactions reflects a CAGR of 74.03 %, value of the transactions represented a CAGR of 68.14% in last 5 years.
- Credit cards & Debit cards: Number of credit cards has more than doubled in five years whereas debit cards have remained relatively stable in last 5 years.
- Global trends: India joined Project Nexus, facilitating multilateral linkage of fast payment systems (FPS) of four ASEAN Nations (Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand) and India.
- Project Nexus, conceptualized by Bank for International Settlements (BIS), enables instant cross-border retail payments by interlinking domestic FPSs.
Payment Systems in India
- Payment systems are mechanisms established to facilitate the clearing and settlement of monetary and other financial transactions.
- Tags :
- ‘Payment System Report
Digital Payments Index (DPI)
Recently, RBI published the Reserve Bank of India–Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI).
About RBI-DPI
- Objective:capture the extent of digitisation of payments systems & measure the adoption of online transactions
- Released frequency: Semi-annual (March & September).
- Base Period: March 2018.
- Parameters involved:
- Payment Enablers
- Payment Infrastructure (demand-side factors)
- Payment Infrastructure (supply-side factors)
- Payment Performance and
- Consumer Centricity.
- Tags :
- Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI)
Market infrastructure institutions (MIIs).
The SEBI issues guidelines for the evaluation of the performance of statutory committees of market infrastructure institutions (MIIs).
- Under the guidelines, MIIs are required to appoint an independent external agency to evaluate their performance and the functioning of their statutory committees.
- This needs to be done once every three years.
About Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs)
- These are organizations that provide the infrastructure for trading securities & are regulated by SEBI.
- It includes stock exchanges, depositories, and clearing corporations.
- Purpose: Enabling trading, securing investor holding, transaction settlement etc.
- Tags :
- market infrastructure institutions (MIIs).
Algorithmic Trading
SEBI proposed Retail Algo Trading Framework.
- Algo trading automates buy/sell orders using preset conditions for precise execution.
- Erstwhile, only institutional investors were allowed to use it via Direct Market Access (DMA).
Key highlights of Regulatory Framework
- Categorization of Algorithms
- White-box: Logic is disclosed and replicable i.e. Execution Algos
- Black-box: Algos where the logic is not known to the user and is not replicable
- Trading Limits for Retail Traders: Retail traders must follow exchange-set limits (yet to be decided).
- Registration of Algo Providers: Algo providers are not regulated by SEBI, but must register with exchanges and partner with a broker to sell algos.
- Tags :
- Algorithmic Trading
Potash
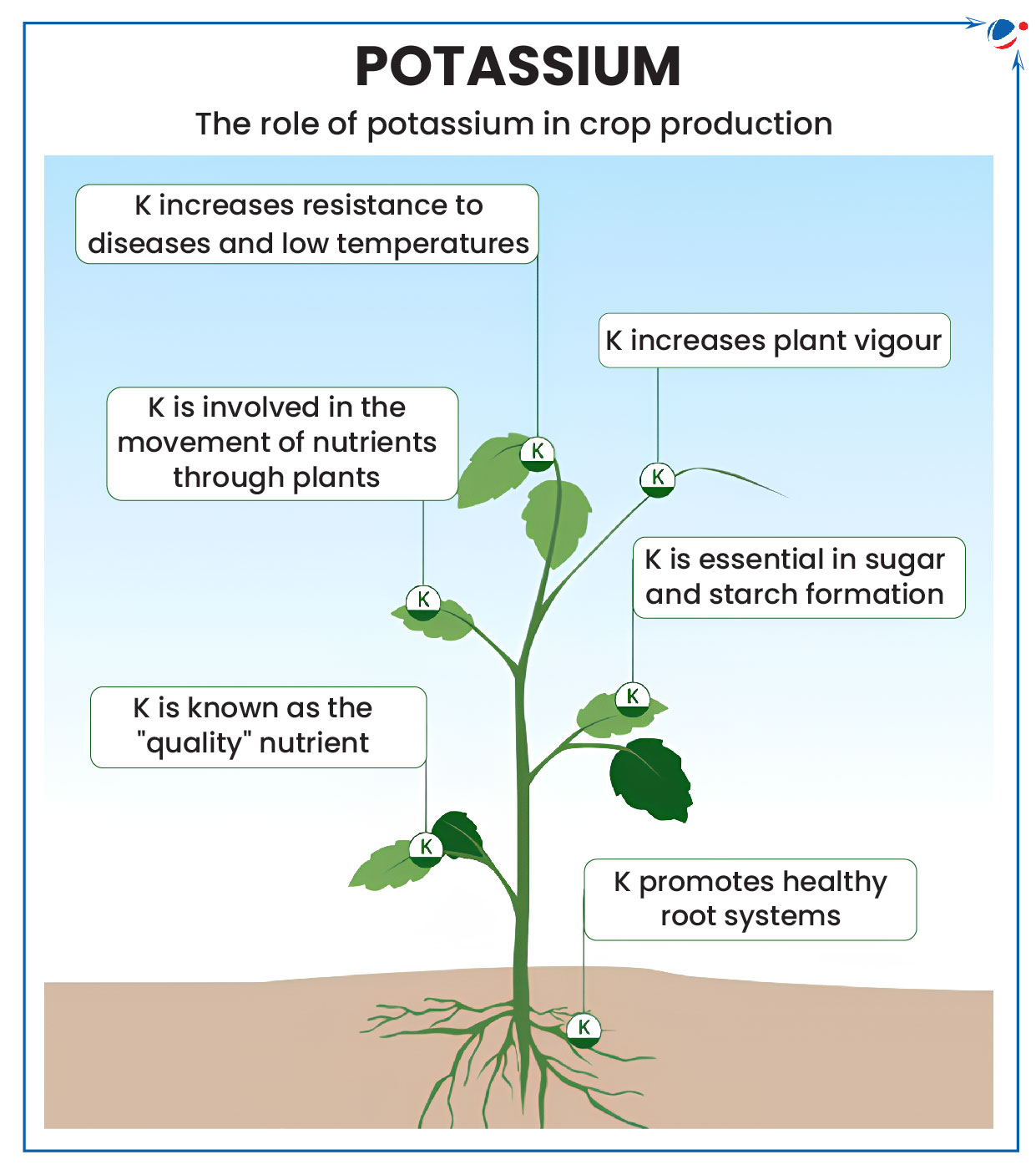
Government will explore Potash Mining in Punjab’s Fazilka and Sri Muktsar Sahib Districts.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) surveys have also identified potash reserves in Rajasthan, highlighting potential to reduce India’s import reliance.
About Potash
- Definition: Potash is an impure combination of potassium carbonate & potassium (K) salts.
- Principal ore: Sylvinite.
- Uses of Potash:
- Agriculture: Over 90% of potash is utilized as fertilizer, making it one of the three primary nutrients in agriculture, alongside nitrogen and phosphorus, collectively known as N-P-K.
- The ideal nutrient ratio for optimal plant growth is 4:2:1 (N:P: K).
- Purification of water: Potash alum removes hardness of water & has anti-bacterial properties.
- Other industrial Uses: Manufacturing of Glass ceramics, Soaps and detergents, Explosives etc.
- Agriculture: Over 90% of potash is utilized as fertilizer, making it one of the three primary nutrients in agriculture, alongside nitrogen and phosphorus, collectively known as N-P-K.
- Common Types of Potash Fertilizers: Sulphate of Potash (SOP) & Muriate of Potash (MOP).
- Potash Derived from Molasses (PDM): It is 100% indigenous fertilizer under the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme.
- NBS: Provides fertilizer subsidies to farmers based on actual nutrient content (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
- Potash classified as Critical Mineral: Under “The Mines & Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment (MMDR) Act, 2023”.
Economic Status of Potash in India
- Deposits: Rajasthan (89%), Madhya Pradesh (5%) and Uttar Pradesh (4%).
- Import: India meets 100% of its Potash requirement through imports (Indian Mineral yearbook 2022).
- Tags :
- Potash
Electronic manufacturing
After China, India has become the World's 2nd largest mobile manufacturing country and is followed by Vietnam.
- Presently, 99.2% of all mobile phones sold in India are made in India.
- Mobile phones constitute 43% of India’s total electronics production.
Electronic manufacturing sector status
- Total valuation: India’s electronics sector has experienced rapid growth, reaching USD 155 billion in FY23.
- Production: Production nearly doubled from USD 48 billion in FY17 to USD 101 billion in FY23.
- Exports: Electronics has become the country's fifth largest export commodity, but India represents less than 1% of global share.
- Tags :
- Electronic manufacturing
Articles Sources
Union Budget 2025: Developing 50 Top Tourist Destinations in 'Challenge Mode'
These destinations will be developed in partnership with states to elevate tourism infrastructure, improve ease of travel, and strengthen connectivity to key sites.
- States will be required to provide land for critical infrastructure, which will be classified under the Infrastructure Harmonized Master List (HML).
Key Focus of Budget
- Employment-Led Growth: Skill development programs, MUDRA loans for homestays, improved travel and connectivity to tourist spots.
- Spiritual Tourism: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage tourism, especially Buddhist sites.
- Medical Tourism: Promote "Heal in India" initiative to boost India’s global healthcare position.

- Gyan Bharatam Mission: Documentation and conservation of India’s manuscript heritage.
Contribution of Tourism Sector:
- Accounted for 5% of GDP in FY23. The sector also created 7.6 crore jobs during the same period.
- India received 1.8 per cent of world tourism receipts and attained a rank of 14th worldwide in world tourism receipts during 2023.
Measures taken by government
- Infrastructure Development: Swadesh Darshan 2.0, PRASHAD Scheme, RCS-UDAN for regional connectivity.
- Policy & Legal: National Tourism Policy, E-Visa for multiple categories.
- Thematic Tourism: Promoting wellness, culinary, rural, and eco-tourism.
- NIDHI (National Integrated Database of Hospitality Industry): Digital system for ease of business in hospitality & tourism.
- Tags :
- Union Budget 2025
- Tourist Destinations
Articles Sources
RuTAGe Smart Village Center (RSVC)
Rural Technology Action Group (RuTAGe) Smart Village Center (RSVC) launched in Mandaura, Haryana.
- RSVC was developed under aegis of Office of Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA).
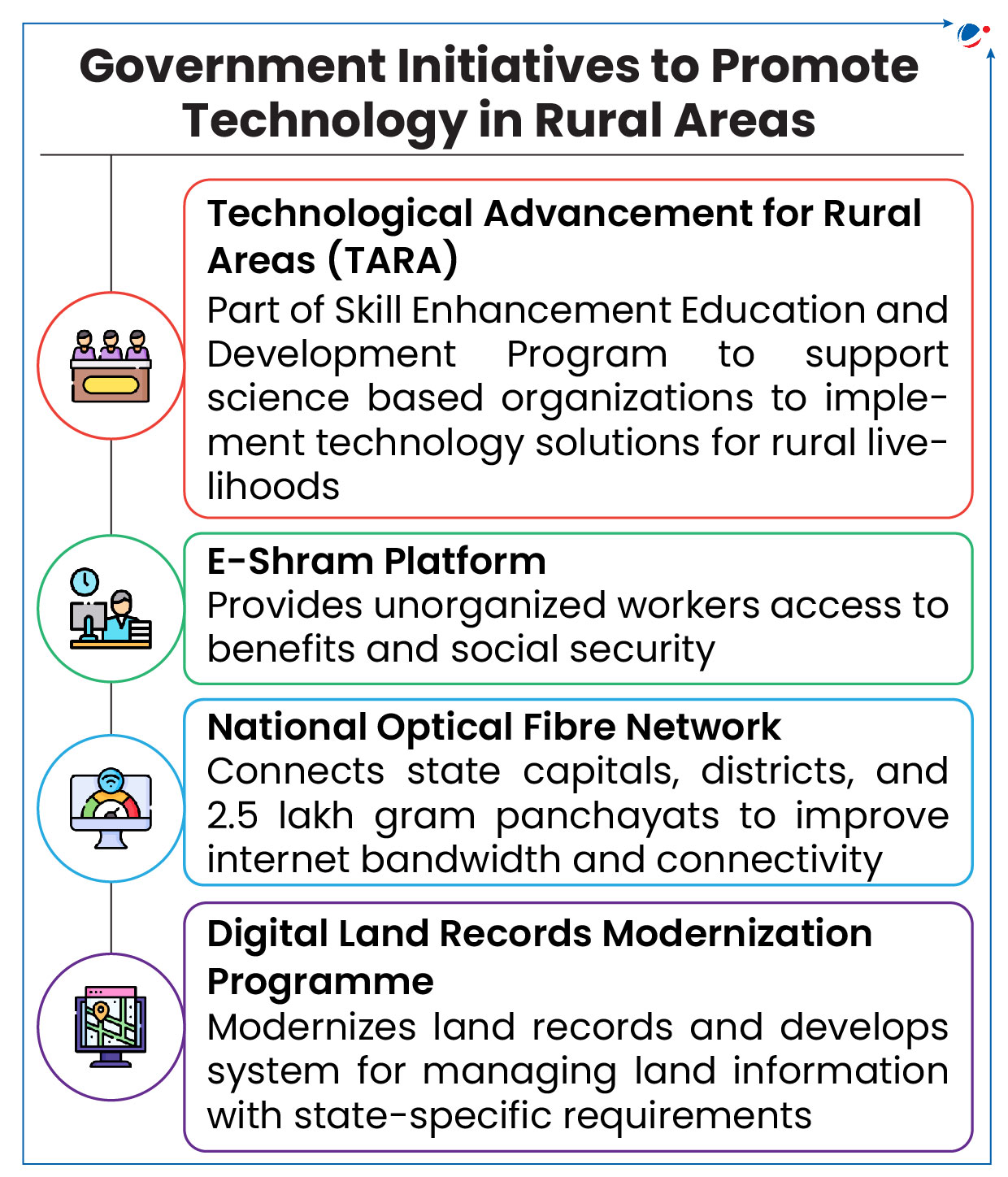
- It aims to integrate cutting-edge technologies with rural needs, enhancing quality of life and empowering communities through sustainable solutions.
- PSA conceptualized RuTAGe in 2003-04.
Key Features of RSVC Model
- Physical Presence: Offers long-term tech support at Panchayat level, assisting 15-20 villages with 12 technology tracks, including Agriculture & Waste Management etc.
- Market Access: Emphasizes collaboration with platforms like ONDC, Amazon, and Market Mirchi to connect rural producers with larger markets.
- Scalability: Plans to expand with 20 new centers and empower women entrepreneurs through Techpreneurs program to ensure sustainability.
Role of Technology in Rural Growth
- Agricultural Innovation: Platforms like e-NAM connect farmers to markets, offering better prices and transparent trade.
- Entrepreneurship: E-commerce and 3D printing support small businesses, allowing them to access global markets and reduce dependency on imports.
- Education: Programs like PM e-VIDYA and SWAYAM offer online education, improving access to quality learning and bridging digital divide.
- Financial Inclusion: DBT program and PM Jan Dhan Yojana facilitate direct, cashless transfers, reducing fraud and increasing transparency.
- Water Management: National Program on Aquifer Mapping and Management uses technology to manage groundwater resources, ensuring efficient water use in agriculture.
- Tags :
- • RuTAGe Smart Village Center (RSVC)
Global Capability Centre (GCC)
Madhya Pradesh has become the first state in the country to bring a dedicated Global Capability Centre (GCC) policy.
About GCCs
- GCCs are designed to leverage global talent pools and technological advancements to enhance organizational capabilities and drive business transformation.
- India’s GCC are emerging as strategic hubs reshaping the Indian corporate landscape while influencing global business dynamics.
- Present Scenario: Number of GCCs in India has grown from ~1430 (FY 2019) to >1700(FY 2024) in FY24.
- As of FY24, GCCs in India employ nearly 1.9 million professionals.
- Tags :
- Global Capability Centre (GCC)
SwaRail Application
The Ministry of Railways has introduced the ‘SwaRail’ SuperApp, a one-stop solution to streamline various railway services.
About SwaRail
- Offers services like Reserved Ticket Bookings, Unreserved Ticket & Platform Ticket Bookings, etc.
- A key focus of the App is enhancing user experience with a seamless and clean user interface (UI).
- Developed by Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- Tags :
- SwaRail Application



