Shift in Earth’s Magnetic North
Earth’s Magnetic North Pole is shifting toward Siberia, according to updated World Magnetic Model (WMM).
About WMM
- WMM is a standard model of the core and large-scale crustal magnetic field.
- New version of model is updated every five years to address changes in Earth’s magnetic field.
- It is produced by the United States’ National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and the United Kingdom’s Defence Geographic Centre (DGC).
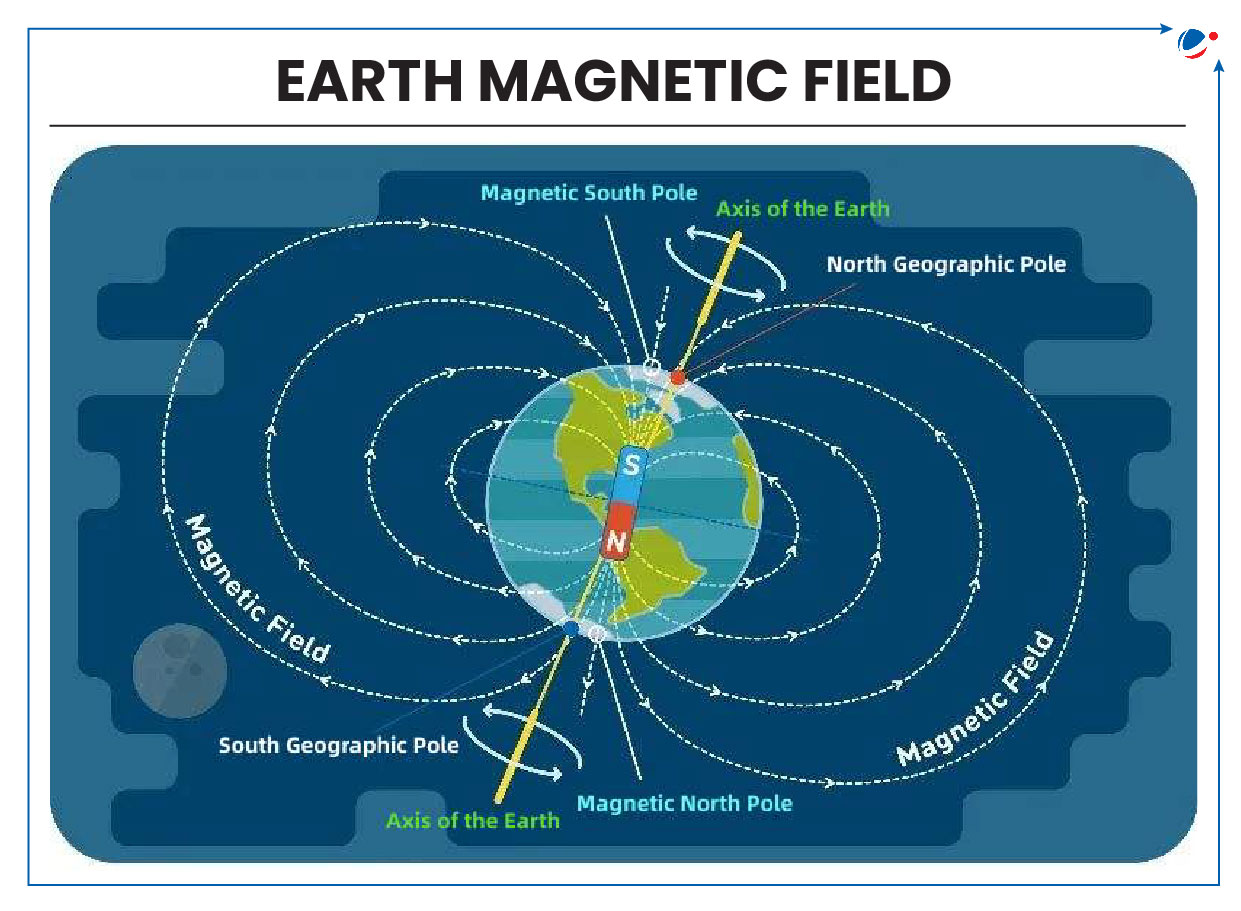
Shift in Earth’s Magnetic North Pole
- Magnetic North is where the Earth’s magnetic field lines enter Earth in the North while Geographic North is where lines of longitude (meridians) converge in the north.
- Earth rotates on the geographic north and south poles.
- Since Earth’s Magnetic North Pole was first discovered in 1831 by explorer James Clark Ross, it has gradually shifted.
- Over past century, its movement from Canada toward Siberia (Russia) has accelerated reaching a peak of 31 miles annually by 2000s but rate of movement has slowed in last five years.
- Positions of Earth’s Magnetic North and South Poles gradually change due to variations in Earth’s magnetic field over time.
- Magnetic declination – the angle between magnetic North and Geographic North – at a given location also changes over time.
- Sometimes, Magnetic Poles also undergo Pole Reversal i.e. swapping of magnetic north and south poles.
- According to Paleomagnetic records, Earth’s magnetic poles have reversed 183 times in the last 83 million years.
- Potential Implications: Errors in navigation systems, impact on migratory species, risks from solar storms to satellites and power grids etc.
- Tags :
- Magnetic Pole
Mount Dukono
Recently, a volcano erupted at Mount Dukono in Indonesia.
About Mount Dukono
- About: With a height of 1,087 metres above sea level, it is one of Indonesia’s 127 active volcanoes.
- Location: on Halmahera Island
Other major volcanoes erupted recently in Indonesia
- Mount Merapi: Located near the city of Yogyakarta.
- Mount Ruang: It is a stratovolcano located in the Sulawesi Islands.
- Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki: Located in Flores island
- Tags :
- Indonesia
- Mount Dukono



