About Staple Cotton Fibre A staple is an individual cotton fibre. Based on the length of the staple, cotton is classified as:
|
Why in the News?
The 'Mission for Cotton Productivity' was announced during Budget 2025-26.
Mission for Cotton Productivity
- It is a five-year mission to facilitate improvements in productivity and sustainability of cotton farming, and promote extra-long staple (ELS) cotton varieties.
- Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- It will provide science & technology support to cotton growing farmers.
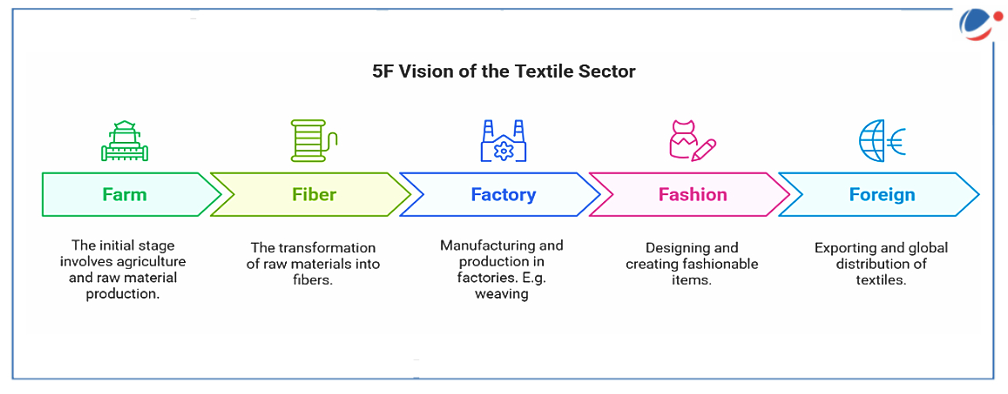
- Aligned with the Government's integrated 5F vision for the textile sector, the mission will help in increasing incomes of the farmers as well as ensure a steady supply of quality cotton for rejuvenating India's traditional textile sector.
- It will aid in reducing import dependence and enhance the global competitiveness of India's textile sector, where 80% of capacity is driven by MSMEs.
Need for the Mission
- Stagnant Productivity: Challenges of stagnant cotton productivity. For instance, in 2023-24 the cotton yield was 435kg/hectare which is similar to 2024-25's yield of 447kg/hectare.
- Rainfed Crop: Majority cotton area is rainfed, mainly in the Central and Southern States.
- Approximately 67% of India's cotton is produced on rain-fed areas and 33% on irrigated lands.
- Pests Menace: Cotton crop is highly prone to pests and diseases. E.g. Pink Bollworm, Whitefly etc.
- Unstable Prices: Wide fluctuation in cotton prices, inadequate market infrastructure and cotton export policy.
Cotton Production, Productivity and Consumption in India
Significance of Cotton in India
|
Cotton (Scientific name: Gossypium spp)
- Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll (protective case) around its seeds.
- It is a shrub (semi-xerophyte) native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India.
- Four species of cotton are G. Arboreum & G. Herbaceum (Asian cotton), G. Barbadense (Egyptian cotton) and G. Hirsutum (American Upland cotton).
- India is reportedly the only country which grows all four species of cotton.
- G. Hirsutum represents 90% of the hybrid cotton production in India and all the current Bt cotton hybrids are G. Hirsutuim.
Bt Cotton
|
- Climate & Soil Requirement
- Temperature:
- At germination stage, minimum temperature required is 15°C whereas in vegetative growth the optimum temperature is 21-27°C.
- It can tolerate temperature to the extent of 43°C but temperature below 21°C is detrimental to the crop.
- It requires at least 210 frost-free days and 50 to 100 cm of rainfall for its growth.
- Warm days of cool nights with large diurnal variations during the period of fruiting are conducive to good boll & fibre development.
- Soil: Cotton is grown on a variety of soils like well drained deep alluvial soils in the north, black clayey soils of varying depth in central region and black and mixed black and red soils in south zone.
- Cotton is semi-tolerant to salinity and sensitive to water logging and thus prefers light well drained soils capable of retaining moisture.
- Crop Season: April-May in northern India and is delayed as we proceed down south (monsoon based in southern zone).
- Temperature:
Other Steps taken for development of cotton sector:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) for Cotton: Cotton is procured by Government at MSP through Cotton Corporation of India (CCI).
- There is no maximum quantity limit of purchase of produced cotton from farmers.
- Based on the recommendations of CACP, Ministry of Agriculture declares MSP for two basic varieties of Fair Average Quality (FAQ) cotton viz. Medium Staple length and long staple length.
- Branding of Indian Cotton: Brand "KASTURI Cotton India" launched to attain the objective of making India Atmanirbhar and vocal for local in the field of cotton.
- E.g. Encourage self-regulation by industries by owning complete responsibility of Traceability, Certification and Branding of KASTURI Cotton India.
- Mobile App "Cott-Ally": A farmer-friendly app to increase awareness about MSP of cotton, best farm practices and nearest procurement centres of CCI in regional languages.
- Technological Interventions: High Density Planting System (HDPS), scientific assessment of quality, processing of cotton in modernized Ginning & Pressing factories, Extension services etc.
Conclusion
There is a need to improve processing of cotton beyond yarn and weaving to production of finished products. The role of MSMEs is primary in promotion of the cotton textile industry. The Mission promotes production of quality cotton to help cotton farmers increase their income along with promoting exports. It is vital for the growth of Brand India and making India self-reliant.






