Earth’s Magnetic North Pole is shifting toward Siberia, according to updated World Magnetic Model (WMM).
About WMM
- WMM is a standard model of the core and large-scale crustal magnetic field.
- New version of model is updated every five years to address changes in Earth’s magnetic field.
- It is produced by the United States’ National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and the United Kingdom’s Defence Geographic Centre (DGC).
Shift in Earth’s Magnetic North Pole
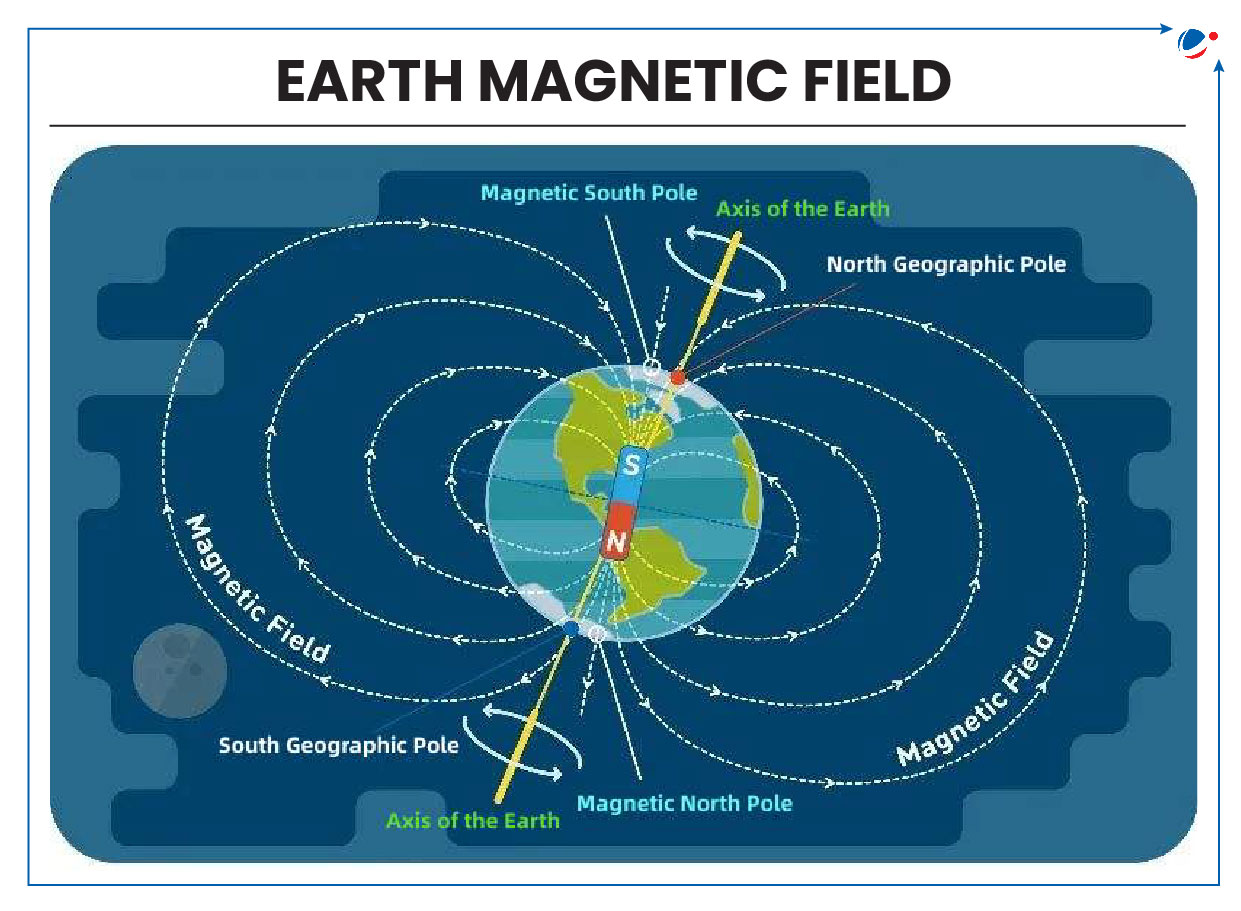
- Magnetic North is where the Earth’s magnetic field lines enter Earth in the North while Geographic North is where lines of longitude (meridians) converge in the north.
- Earth rotates on the geographic north and south poles.
- Since Earth’s Magnetic North Pole was first discovered in 1831 by explorer James Clark Ross, it has gradually shifted.
- Over past century, its movement from Canada toward Siberia (Russia) has accelerated reaching a peak of 31 miles annually by 2000s but rate of movement has slowed in last five years.
- Positions of Earth’s Magnetic North and South Poles gradually change due to variations in Earth’s magnetic field over time.
- Magnetic declination – the angle between magnetic North and Geographic North – at a given location also changes over time.
- Sometimes, Magnetic Poles also undergo Pole Reversal i.e. swapping of magnetic north and south poles.
- According to Paleomagnetic records, Earth’s magnetic poles have reversed 183 times in the last 83 million years.
- Potential Implications: Errors in navigation systems, impact on migratory species, risks from solar storms to satellites and power grids etc.
Department of Consumer Affairs notifies Draft Legal Metrology (Indian Standard Time) Rules, 2025.
- These landmark rules aim to standardize and mandate use of Indian Standard Time (IST) across all sectors in India.
About Draft Legal Metrology (Indian Standard Time) Rules, 2025
- Mandatory time reference: Would be IST across all sectors, including commerce, transport, public administration, legal contracts, and financial operations.
- Prohibition: No person/entity shall use, display, or record time other than IST for official/commercial purposes.
- Provided that any law/government direction/guidelines permits same.
- Adoption of Time Synchronization Protocols: Such as Network Time Protocol and Precision Time Protocol etc. by government offices is required.
- Cybersecurity: To ensure resilience, cybersecurity measures and alternative reference mechanisms are prescribed.
- Authorized Deviations: Use of alternative timescales (GMT, etc.) is permitted for specific purposes e.g. astronomy, navigation, scientific research, etc. subject to prior permission.
Significance of New Draft Rules
- Strengthens national security by improving the synchronization of critical infrastructure
- Synchronization of digital devices and public services ensures reliable and efficient services
- Will ensure accurate financial transactions and consistency in record-keeping
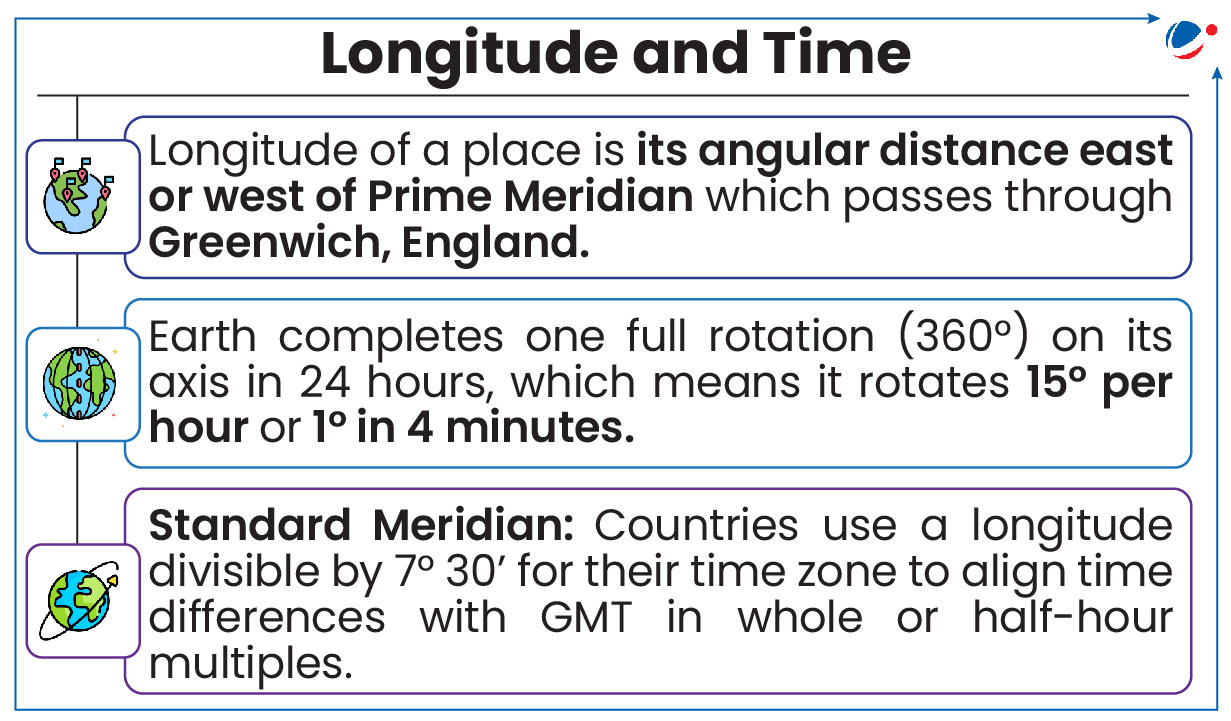
About IST
- Central meridian of country (i.e. 82°30’E meridian passing through Mirzapur) is taken as Standard Meridian or IST (Maintained by CSIR-NPL).
- It is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) (now Universal Coordinated Time (UTC)).
- Local time at Prime Meridian (0° longitude) is known as GMT.
- Several tea gardens in Assam follow an informal ‘Chaibagan’ or ‘Bagan time’ ('Tea Garden Time'), which is one hour ahead of IST.
- It was introduced by the British tea companies to increase daylight work hours and productivity.
In a rare event, massive methane plumes emitted from volcano Mount Fentale (Ethiopia).
- Mount Fentale is a stratovolcano which last erupted in 1820.
About Stratovolcano
- A stratovolcano is a large, steep-sided volcano built up by alternating layers of lava flows and volcanic ash, often associated with explosive eruptions.
- E.g., Mount Fuji (Japan), Mount Vesuvius (Italy), Mount Etna (Italy), Mount Rainier (USA), Krakatoa (Indonesia), etc.
About Methane Plumes
- It’s the release of large quantities of methane from super-emitter sites like gas drilling sites.
- Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with 80 times the Global Warming Potential (GWP) of carbon dioxide over a 20-year period.
Recently, a volcano erupted at Mount Dukono in Indonesia.
About Mount Dukono
- About: With a height of 1,087 metres above sea level, it is one of Indonesia’s 127 active volcanoes.
- Location: on Halmahera Island
Other major volcanoes erupted recently in Indonesia
- Mount Merapi: Located near the city of Yogyakarta.
- Mount Ruang: It is a stratovolcano located in the Sulawesi Islands.
- Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki: Located in Flores island
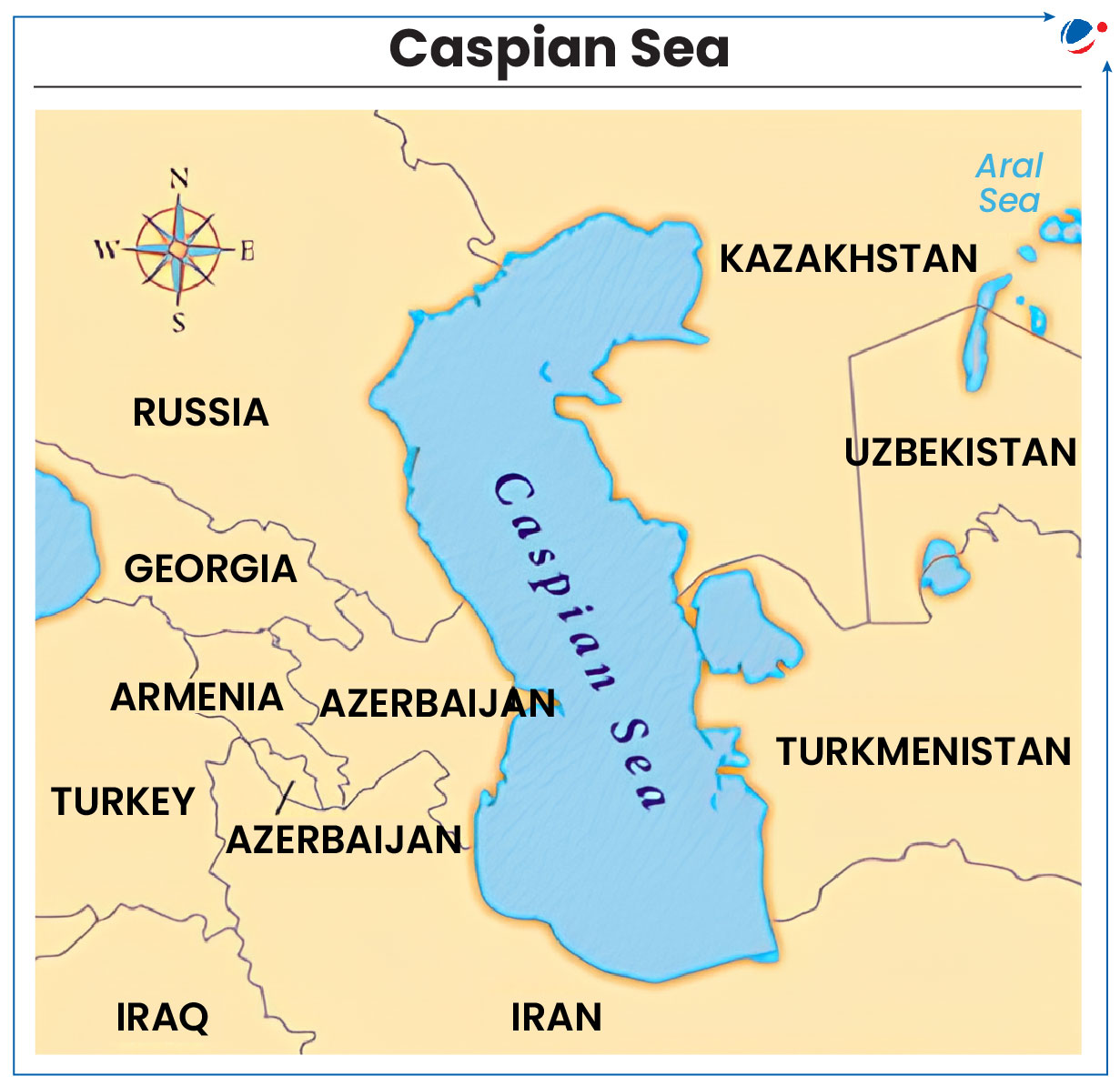
Environmental activists raised concerns over the rapidly declining water levels in the Caspian Sea.
- It has already lost nearly 31,000 square km since 2005.
About Caspian Sea
- It is the largest enclosed water body in the world.
- The sea is bordered by five countries: Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Iran.
- Kazakhstan has the longest coastline along the Caspian Sea.
- Its oil reserves are estimated at 48 billion barrels.
- Reasons for declining water level: The climate crisis, excessive water use for agriculture, and pollution from nuclear waste, industry and poor urban planning, etc.
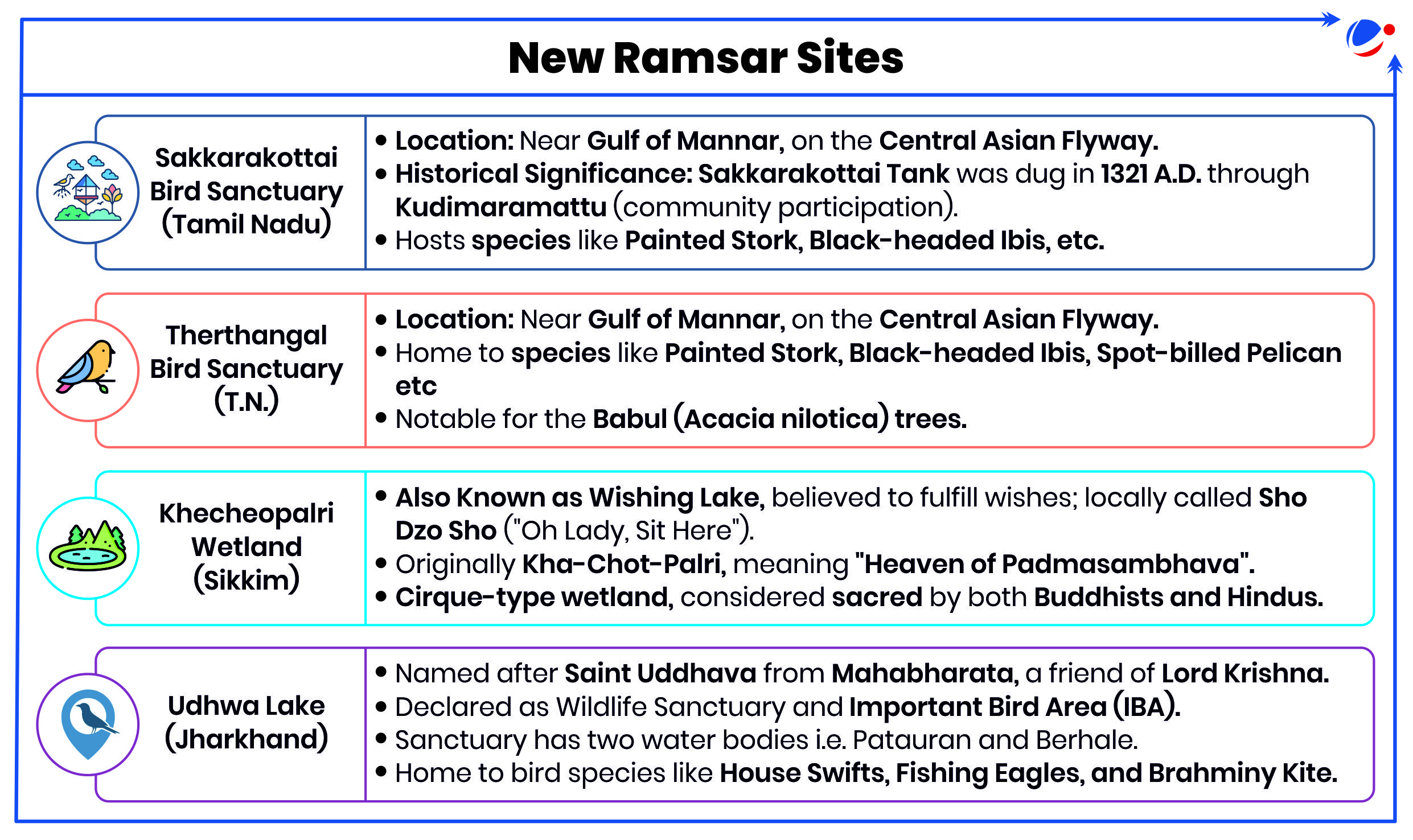
Indore and Udaipur have become the first two Indian cities to make it to the global list of accredited wetland cities under Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- Indore: Sirpur Lake (Ramsar Site) recognised for water bird congregation and is being developed as a bird sanctuary.
- Udaipur: Surrounded by five major wetlands, namely, Pichola, Fateh Sagar, Rang Sagar, Swaroop Sagar, and Doodh Talai.
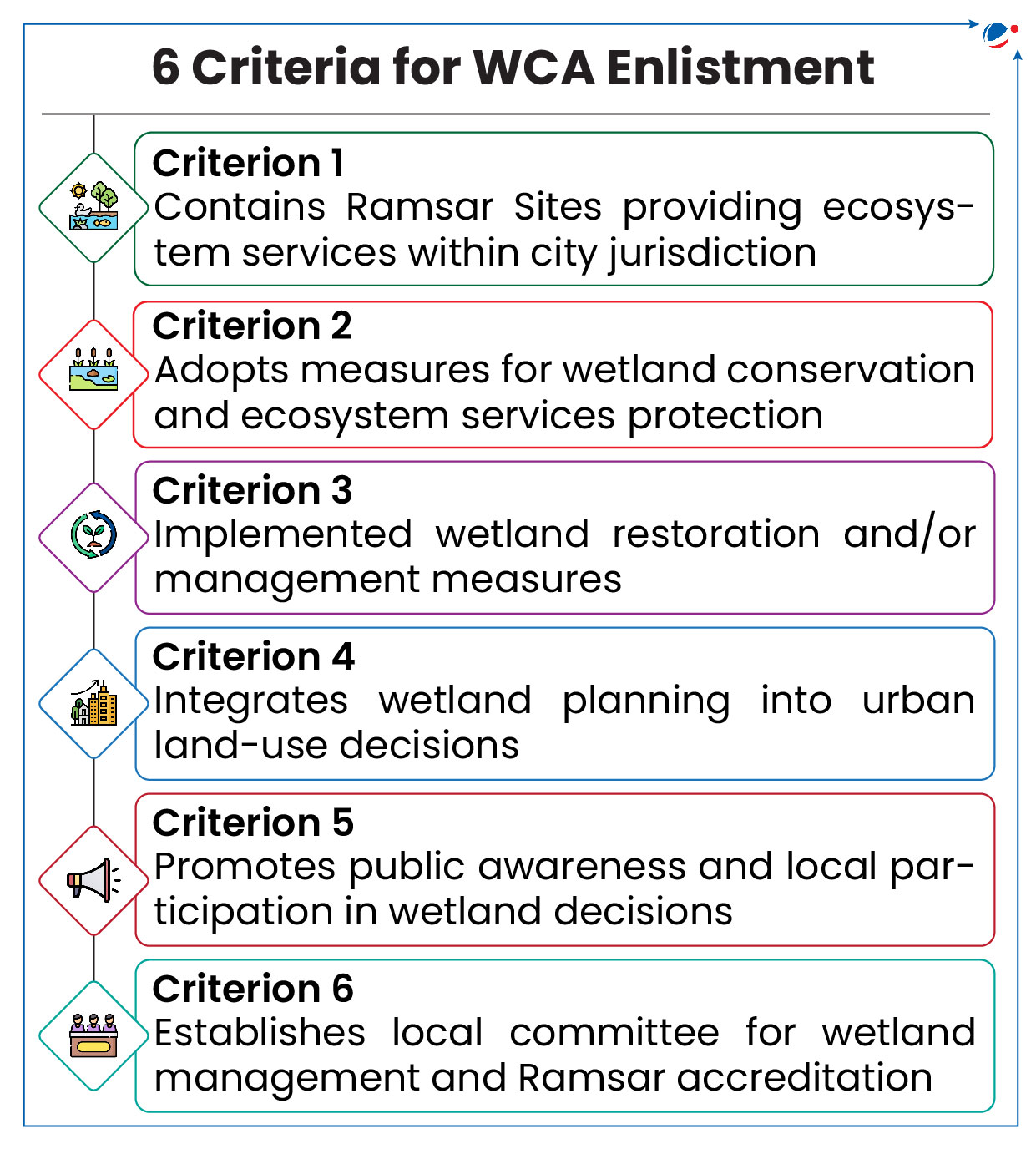
About Wetland City Accreditation (WCA)
- It is a voluntary Accreditation system that provides an opportunity for cities that value their natural or human-made wetlands to gain international recognition and positive publicity for their efforts.
- It was approved at Uruguay in COP12 of Ramsar Convention (2015).
- It is valid for 6 years, after which it must be renewed, providing that it continues to fill each of the 6 criteria (refer image).
Significance of WCA
- Promote conservation and wise use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, as well as sustainable socio-economic benefits for local populations.
- Help in implementation of Amrit Dharohar initiative of MoEF&CC.
This has increased wetlands tally from 85 to 89, highest in Asia, third globally. Wetlands have been added from Tamil Nadu, Sikkim and Jharkhand.
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar sites, the highest among Indian states.
- Sikkim and Jharkhand have added their first Ramsar sites.
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
- Intergovernmental treaty adoptedin Ramsar (Iran) in 1971 (came into force in 1975).
- Objective: Provides a framework for national and international efforts to conserve and wisely use wetlands.
- World Wetlands Day is celebrated on 2nd February.
Gujarat has notified "Inland Mangrove of Guneri" in the District of Kutch as a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS).
- It is Gujarat’s first Biodiversity Heritage Site.
- Notified in accordance with the Biodiversity Act, 2002.
About Inland Mangrove of Guneri
- Guneri mangroves grow 45km from Arabian Sea and 4km from Kori Creek, representing a rare inland ecosystem.
- Unlike conventional mangrove ecosystems, this site does not receive tidal water inflow and lacks muddy or swampy conditions.
- It is reportedly one of only eight of its kind across the world.
- Area houses around 20 migratory and 25 resident migratory avifaunal species.
C40 Cities & UN-Habitat have announced a landmark partnership to transform urban planning.
- It will launch an Urban Planning Accelerator to cut city emissions by 25% by 2050 while promoting safer, fairer, & inclusive urban spaces.
About UN Habitat
- Launch: 1978
- Mission: To promote socially & environmentally sustainable towns and cities, ensuring adequate shelter for all.
- Role: Through initiatives like New Urban Agenda, it seeks to make cities inclusive, safe, resilient, & sustainable.
About C40
- C40 is a global network of nearly 100 mayors of world’s leading cities that are united in action to confront climate crisis.
- Six Indian cities are currently members of C40: Bengaluru; Chennai; Delhi NCT; Jaipur; Kolkata and Mumbai.
Article Sources
1 source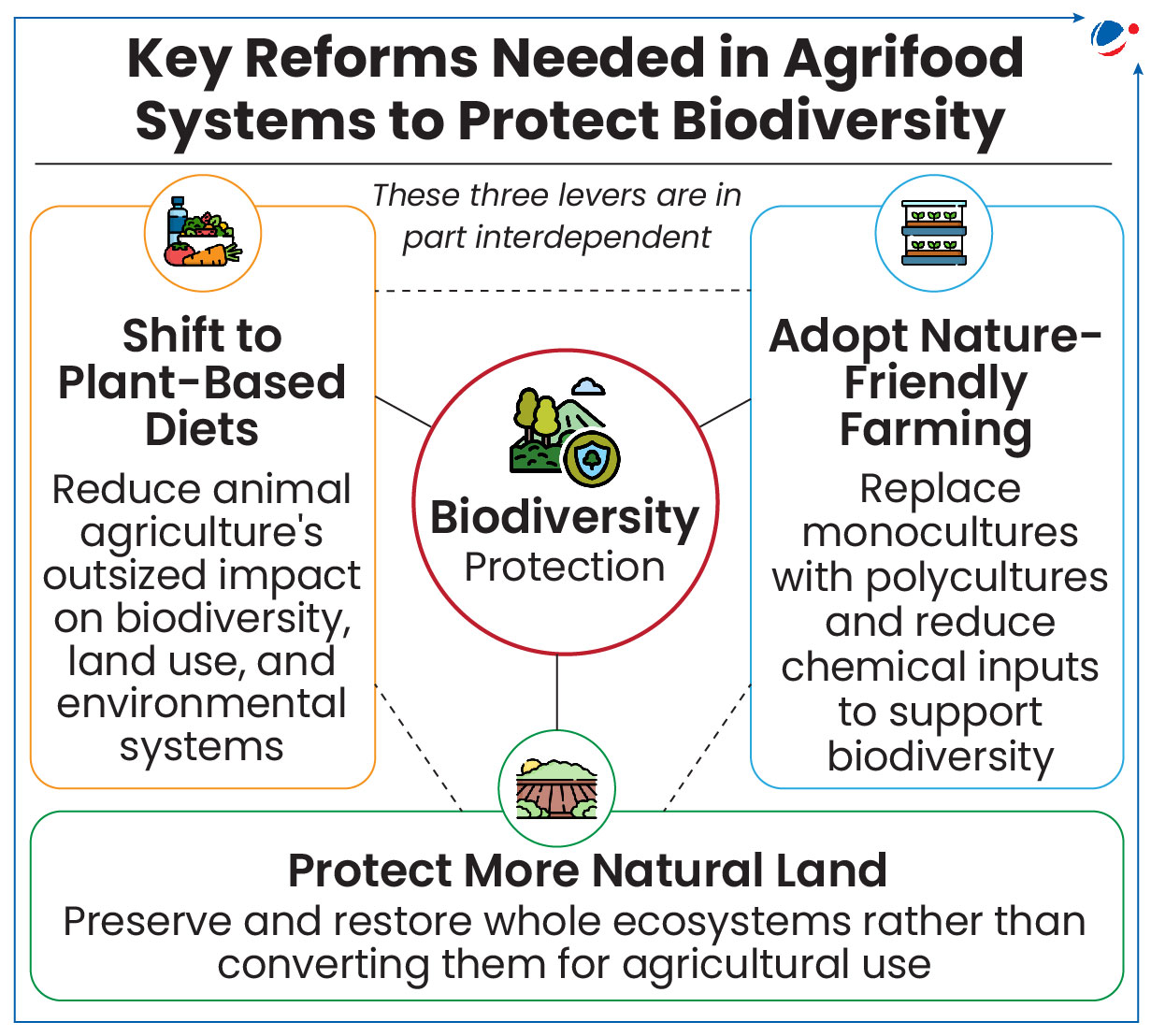
UN Biodiversity Conference (CBD COP 16.2) in Rome builds on COP16 momentum in Colombia, where FAO launched Agri-NBSAPs with the Colombian government and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
About Agri-NBSAPs
- Agri-NBSAP aims to assist governments in integrating Four More Wetlands into National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs) and their implementation.
- An agrifood system encompasses all stages of food production, from farm to fork.
- NBSAP provides a framework for biodiversity conservation, enables sustainable use of biological resources.
- Countries frame NBSAP under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF) which aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- It provides a collective mechanism to help governments build capacity, identify and implement strategic levers across AFS to achieve their NBSAP targets.
Why should AFS be Integrated into NBSAPs?
- Meeting KM-GBF Goals: Over half of 23 targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF) are directly or indirectly related to agriculture.
- Cutting Emissions: Agrifood systems produce nearly 1/3 of global greenhouse gases driving climate change, which further degrades habitats and causes biodiversity loss.
- Protecting Food Security: Biodiversity supports pollination, soil fertility, and pest control.
- Biodiversity decline threatens 3 billion lives with 75% of food crops depend on pollinators.
Article Sources
1 sourceAWBI will honour Champions of Animal Protection under two major categories Prani Mitra and Jeev Daya Award.
- This initiative aims to recognize outstanding individuals and organizations for their remarkable contributions to animal welfare and protection.
About AWBI
- Prevention of Cruelty to Animal Act (PCAA) 1960 established the AWBI in 1962 as a statutory advisory body on Animal Welfare Laws and promotes animal welfare.
- It was started under the stewardship of Rukmini Devi Arundale, well known humanitarian.
- It consists of 28 Members including 6 Members of Parliament (2 from Rajya Sabha and 4 from Lok Sabha).
A recent study discovered F11 bacteria (Labrys portucalensis) that degrades at least 3 types of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
About F11 Bacteria
- It is an aerobic bacteria from the Xanthobacteraceae family.
- It may aid Bioaugmentation in wastewater treatment etc.
- Bioaugmentation is the addition of microorganisms that can biodegrade recalcitrant molecules in a polluted environment.
About PFAS
- PFAS are toxic chemicals that resist grease, oil, water, and heat. They are called ‘forever chemicals’ due to their almost indestructible nature.
- Uses: Nonstick cookware, grease-resistant food packaging, and waterproof and firefighting clothing etc.
Article Sources
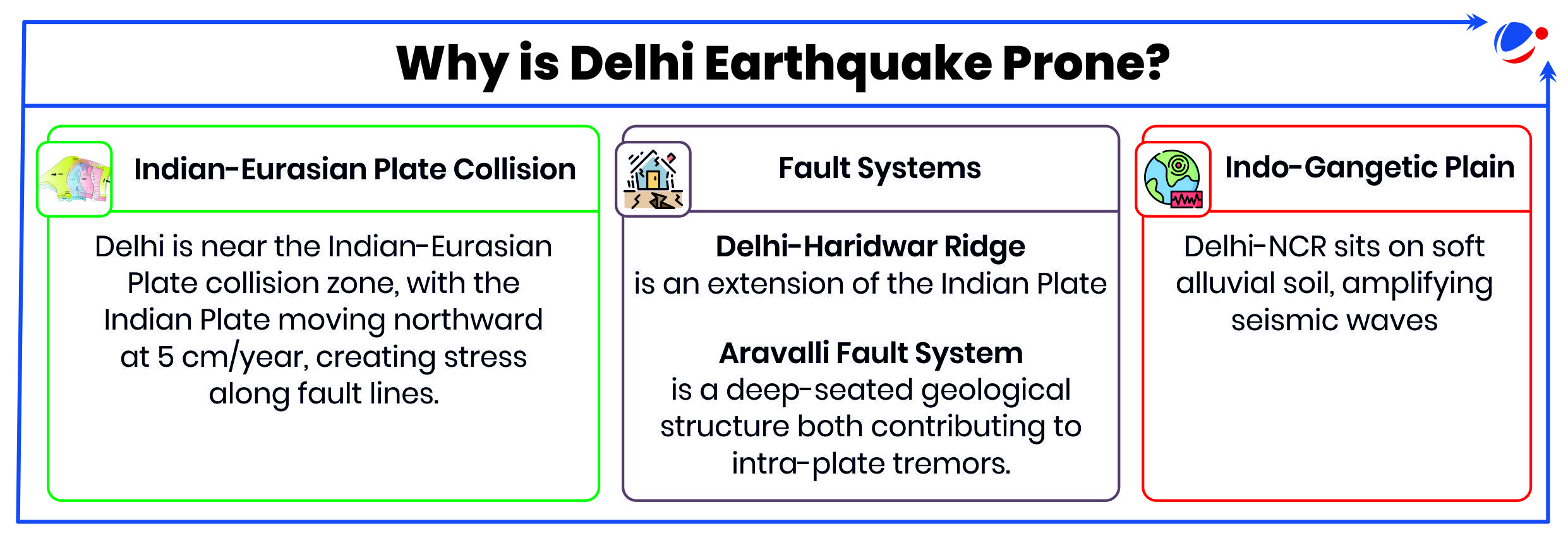
1 sourceEarthquake Measuring 4.0 in richter scale shakes Delhi-National Capital Region (NCR).
- Unlike Himalayan quakes caused by plate tectonics, this earthquake was an intra-plate event, resulting from "in situ material heterogeneity”.
- Tremors were more intense due to the epicentre (point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake) located within Delhi and the earthquake's shallow depth of 5 km (See box).
Earthquakes Due to In-Situ Material Heterogeneity
- Definition: It refers to seismic activity caused by the inherent variability in the physical properties of the Earth's crust. E.g., Rock type, presence of fluids in rock pores, etc.
- Formation: Variations in physical properties (heterogeneities) can cause stress concentration, which eventually increase the likelihood of earthquakes.
- Influence on Faults: ‘In-situ heterogeneity’ creates stress buildup in fault zones, increasing the chances of earthquakes.
- Delhi is placed in seismic zone IV in the seismic zoning map of India, the second highest in the country.
About Shallow Earthquake
|




