Why in the News?
Six sites have been added to India's Tentative List by UNESCO's World Heritage Centre in 2025.
More on the News

- A tentative list is an "inventory" of properties a country believes deserves to be a World Heritage Site.
- Process: After inclusion in Tentative List, the country has to prepare a nomination document that will be considered by UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
- In India, Indian National Commission for Co-operation with UNESCO (INCCU), and Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) play a key role in this regard.
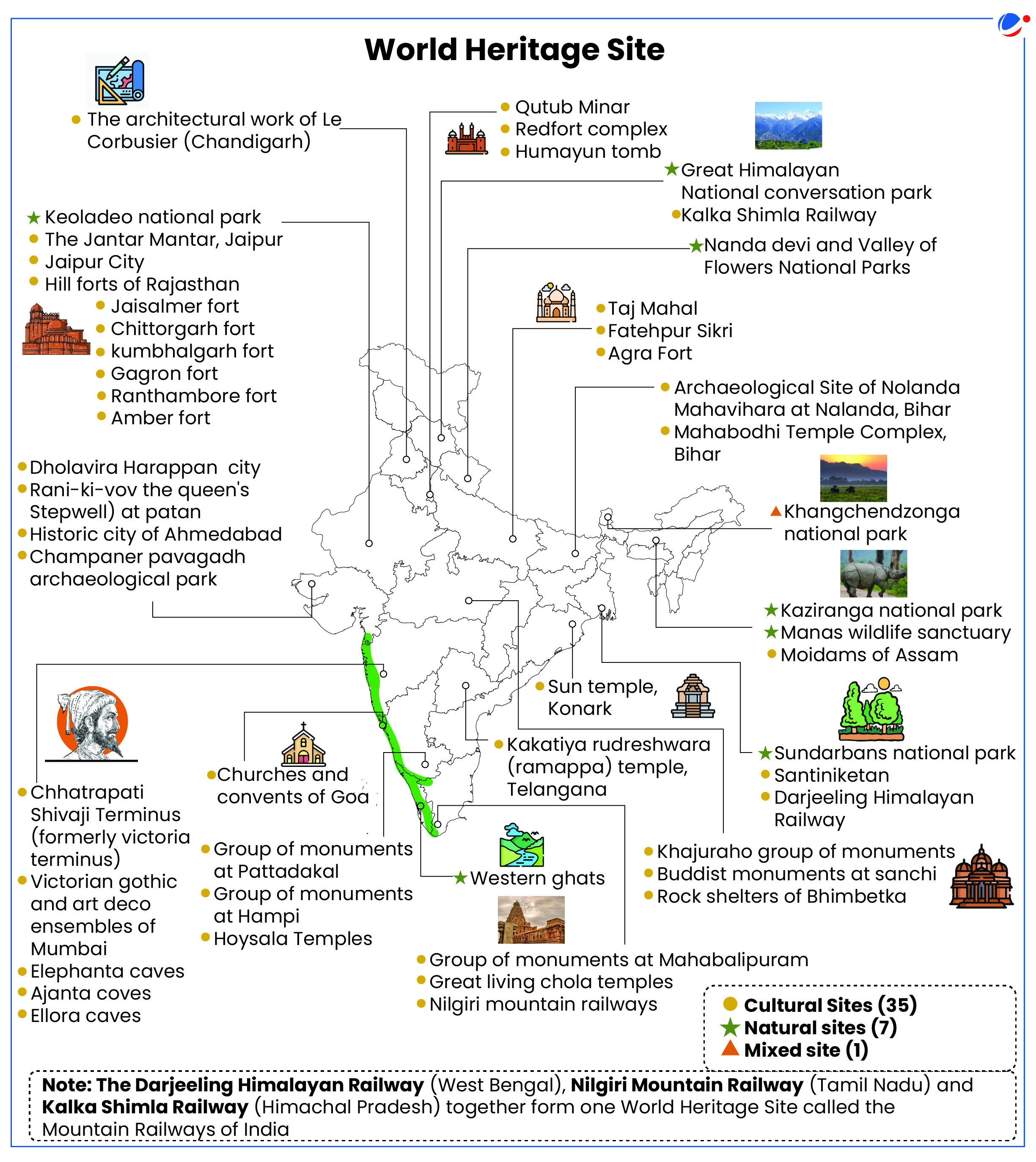
- In India, 62 sites are listed on UNESCO's Tentative List.
- The 6 sites are
- Mudumal Menhirs of Telangana
- Kanger Valley National Park in Chhattisgarh
- Ashokan Edict Sites in multiple states
- Chausath Yogini Temples in Madhya Pradesh and Odisha
- Gupta Temples in multiple states
- Palace-Fortresses of the Bundelas in Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
What are UNESCO World Heritage Sites (WHS)?
- A World Heritage Site is a location recognised by UNESCO for its "outstanding universal value".
- It is guided by Convention Concerning Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage(called World Heritage Convention).
- Three categories: Cultural heritage, Natural heritage, and Mixed heritage (cultural as well as natural).
Criteria for selection
- A site must meet at least one of these criteria: represent human creative genius, showcase cultural or historical significance, exemplify architectural, ecological, or geological importance, or contain exceptional natural beauty and biodiversity. It should contribute to human heritage, on-going natural processes, or conservation efforts.
- Other considerations: The protection, management, authenticity and integrity of properties.
World Heritage Convention (Adopted in 1972 by General Conference of UNESCO)
- It came in to effect in 1975 and defines kind of natural or cultural sites which can be considered for inscription on World Heritage List.
- World Heritage Committee (WHC) was constituted based on Convention within UNESCO.
- List of World Heritage in Danger and World Heritage Fund were established in 1975 under the Convention.
- India ratified the World Heritage Convention in 1977.
UNESCO World Heritage Committee (Intergovernmental Committee for Protection of the Cultural and Natural Heritage of Outstanding Universal Value)
- Composition: Members selected from amongst 196 States Parties. (India is currently a member)
- Term of office: 6 years (Most States Parties voluntarily choose to be Members for only 4 years)
- Functions:
- It meets at least once a year, to deliberate addition, removal, or modification of items on WHSs list.
- Performs regular audits of designated Sites, Can List a threatened site as World Heritage in Danger.
- To remove a propertyfrom list whose Outstanding Universal Value is lost or destroyed.
- India for 1st time hosted 46th World Heritage Committee Meeting in July 2024 in New Delhi. It was organized by ASI on behalf of Ministry of Culture.
- 'Moidams' The Mound-Burial System of Ahom Dynasty Inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage List as India's 43rd Entry.
- World Heritage Fund (Fund for Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage of Outstanding Universal Value): It was established in 1977 under WHC.
- Resources: Contributions from States Parties, voluntary contributions by governments, foundations, private sector, or the public.