Why in the News?
The U.S. President signed an executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve (SBR) and the U.S. Digital Asset Stockpile to have a Strategic Crypto Reserve (SCR).
More on the news
- It aims to include cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP, Solana's SOL and Cardano's ADA in efforts to elevate America's crypto industry.
- It also aims at addressing the crypto management gap as the US will have a strategic advantage to being among the first nations to create an SBR.
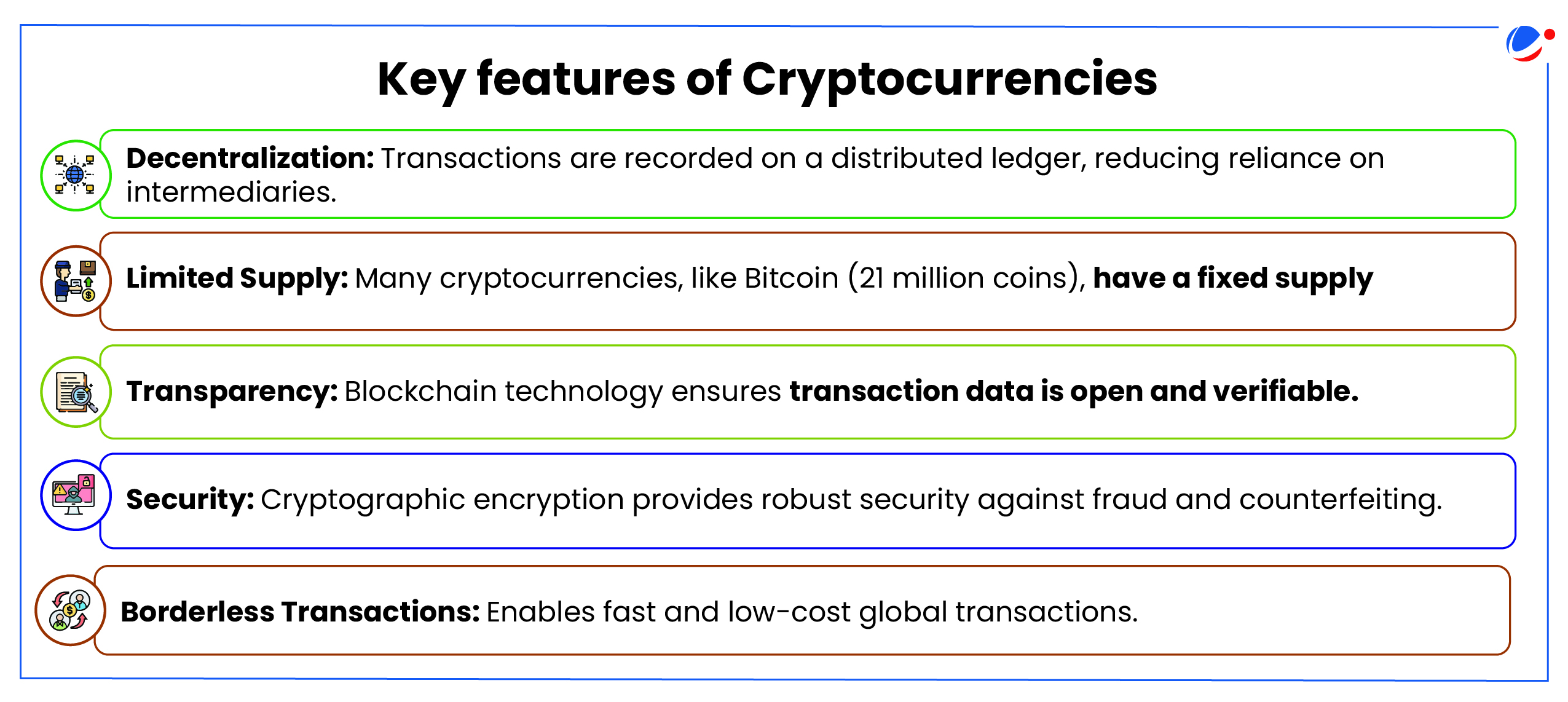
What is Cryptocurrency?
- Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates on decentralized blockchain technology.
- Unlike traditional fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies are not controlled by any central authority such as a government or central bank.
- Examples: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Ripple (XRP), Tether (USDT).
About Strategic Crypto Reserve (SCR)
- SCR is a government-held stockpile of cryptocurrencies maintained as part of national financial reserves to hedge against economic uncertainties, enhance financial sovereignty, and leverage blockchain technology for economic resilience.
- Functions as a digital alternative to traditional reserves such as foreign exchange (forex) and gold.
- The operational mechanics of a strategic cryptocurrency reserve remain to be fully defined,
- Some see similarities to the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, which serves as a way for the government to limit the impacts of petroleum supply disruptions.
Should India have a Strategic Cryptocurrency Reserve?
Arguments in favour
- Diversification of National Reserves: Cryptocurrencies exhibit low correlation with traditional assets like gold, bonds, and equities, reducing portfolio risk.
- Hedging Against Economic Shocks: Acts as a hedge against US dollar fluctuations and global monetary instability.
- Example; Reduces vulnerability to geopolitical shifts (e.g., sanctions, trade wars).
- Cost-Efficient Remittances: Crypto transactions could slash remittance fees from 6.4% (global average) to less than 1%, saving India billions annually.
- Technological Leadership: Leverages India's tech talent pool to innovate in blockchain and DeFi (Decentralized Finance).
- High Return Potential: Historical crypto returns outpace traditional assets, offering asymmetric growth opportunities.
- Example: Bitcoin's 200X growth over a decade outperformed stocks like NVIDIA (50X) and Apple (10X).
- Financial Sovereignty: Reduces reliance on external financial systems (e.g., SWIFT) and strengthens economic independence.
Arguments Against
- Volatility and Market Risks: Extreme price swings (e.g., Bitcoin's 80% drop in 2022) could destabilize reserves.
- RBI's Reservations and Policy Stance: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has repeatedly warned against the risks of cryptocurrency, citing financial instability.
- RBI favors a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) over decentralized cryptocurrencies, seeing them as a threat to monetary sovereignty.
- Regulatory Challenges: Conflicts with existing financial laws and the uncertainty of future regulations.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Cyberattacks on crypto wallets or exchanges could lead to massive losses.
- Example: $600M Poly Network hack (2021).
- Environmental Impact: Energy-intensive mining (e.g., Bitcoin's proof-of-work) conflicts with climate goals.
- Adoption Barriers: Public scepticism and limited institutional trust in crypto as a reserve asset.
- Liquidity challenges in converting large crypto holdings to fiat currency.
Way forward for India
- Start Small: Can allocate 1-2% of forex reserves ($6–12 billion) to crypto for controlled experimentation.
- Build Regulatory Frameworks: Can learn from Singapore and Japan's balanced models to mitigate risks while encouraging innovation.
- Leverage Tech Expertise: Can develop secure custody solutions and blockchain infrastructure using domestic talent.
- Focus on Utility: Can prioritize crypto use cases like remittances and DeFi to drive real-world adoption.
- Monitor Global Trends: Can align with evolving international standards (e.g., US Bitcoin ETFs, EU's MiCA regulations).



