PAC Calls for Review of GST

Parliamentary Committee on Public Accounts sought comprehensive review of GST Framework.
Key Issues Highlighting the Need for Review of GST Framework
- Issues of MSMEs: Struggle with compliance due to complexity of Inverted Duty Structure and administrative burden.
- Issues of Exporters: Face delays in input tax credit (ITC) refunds, causing cash flow issues and reducing global competitiveness.
- Issues of steel rolling mills: Pay dual taxes as scrap dealers evade GST (thus, hindering ITC claims by mills); some businesses relocate to states with GST relaxations.
- Tax evasion by Online Gaming Sector: Despite recent amendments to the GST law targeting this sector, tax evasion persists due to varied business models.
- From October 1, 2023, online gaming is taxed at 28% GST.
- Suppliers of online money gaming must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
- The Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) can direct intermediaries to block unregistered offshore gaming platforms violating the IGST Act.
Way ahead
- Simplified GST compliance framework specifically designed for MSMEs,
- Dedicated fast-track refund processing system for exporters, ensuring that ITC claims related to exports,
- A detailed independent study to understand the revenue streaming models adopted by various gaming platforms and accordingly develop a comprehensive guidelines specifically tailored to the online gaming sector.
- Tags :
- GST
UNCTAD Released ‘A World Of Debt Report 2024’
Public debt can drive development by funding critical expenditures, but excessive debt growth poses challenges, especially for developing nations.
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) ’s 2024 report warns of rising debt risks, urging immediate global action to ensure stability.
Key Findings of the Report

- Global Debt Surge: Public debt reached $97 trillion in 2023, with developing countries' debt rising twiceas fast as developed nations.
- India's public debt was recorded at 2.9 trillion US dollars.
- Debt Servicing Strains: 54 developing nations spend more on interest payments than on social sector.
- Unequal Financial System: Developing nations pay 2 to 12 times more in interest than developed countries.
Challenges Posed by the Rising Global Public Debt
- Debt Overhang: High debt levels can stifle economic growth by discouraging investment and consumption.
- Liquidity Challenge: The withdrawal of nearly $50 billion by private creditors from developing countries has worsened liquidity constraints.
- The creditor base with West-dominated institutions (private, multilateral, and bilateral creditors) makes debt restructuring expensive.
Recommendations
- Debt restructuring mechanisms to address coordination challenges.
- Expand contingency financing to prevent debt crises.
- Enhance participation of developing countries in global financial governance.
- Tags :
- UNCTAD
- public debt
Articles Sources
Largest INVIT Monetization In Roads Sector
National Highways Infra Trust (NHIT) completed largest INVIT monetization in roads sector.
- NHIT is the Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) set up by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) in 2020 to support India's Monetization programme.
Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)
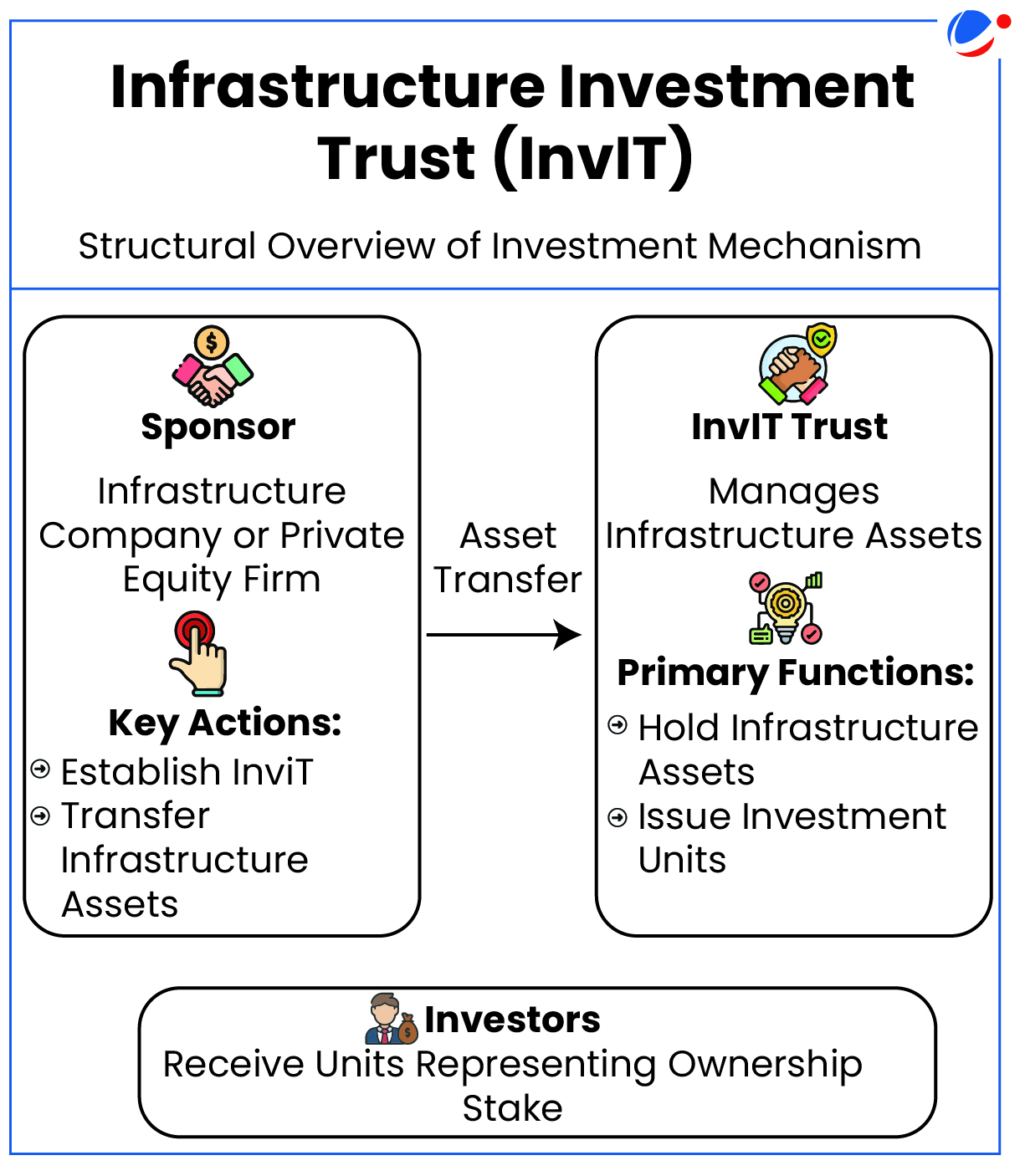
- Definition: It is an investment vehicle, like a mutual fund or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
- InvITs enable direct investment of money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects.
- Investments can be made directly or through SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle)/Holding Company by the InvIT.
- InvITs earn income through tolls, rents, interest or dividends from their investments.
- The interest, dividend, and rental income are taxable in the hand of the unitholder.
- Regulation: InvIT are regulated by the SEBI (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014.
- SEBI requires InvITs to distribute at least 90% of their income to investors.
- InvITs are recognized as borrowers under the ‘Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002’.
- Types of InvITs: Public InvITs, Private listed InvITs and Private unlisted InvITs.
- Advantages of InvITs: Access to retail investors to invest in large infrastructure projects, low ticket size, liquidity (as units are listed on stock exchanges), etc.
- AM is the process of creating new sources of revenue for the government and its entities by unlocking the economic value of unutilised or underutilised public assets.
Asset Monetization (AM)
|
- Tags :
- InvITs



