Why in the news?
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) notified Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme.
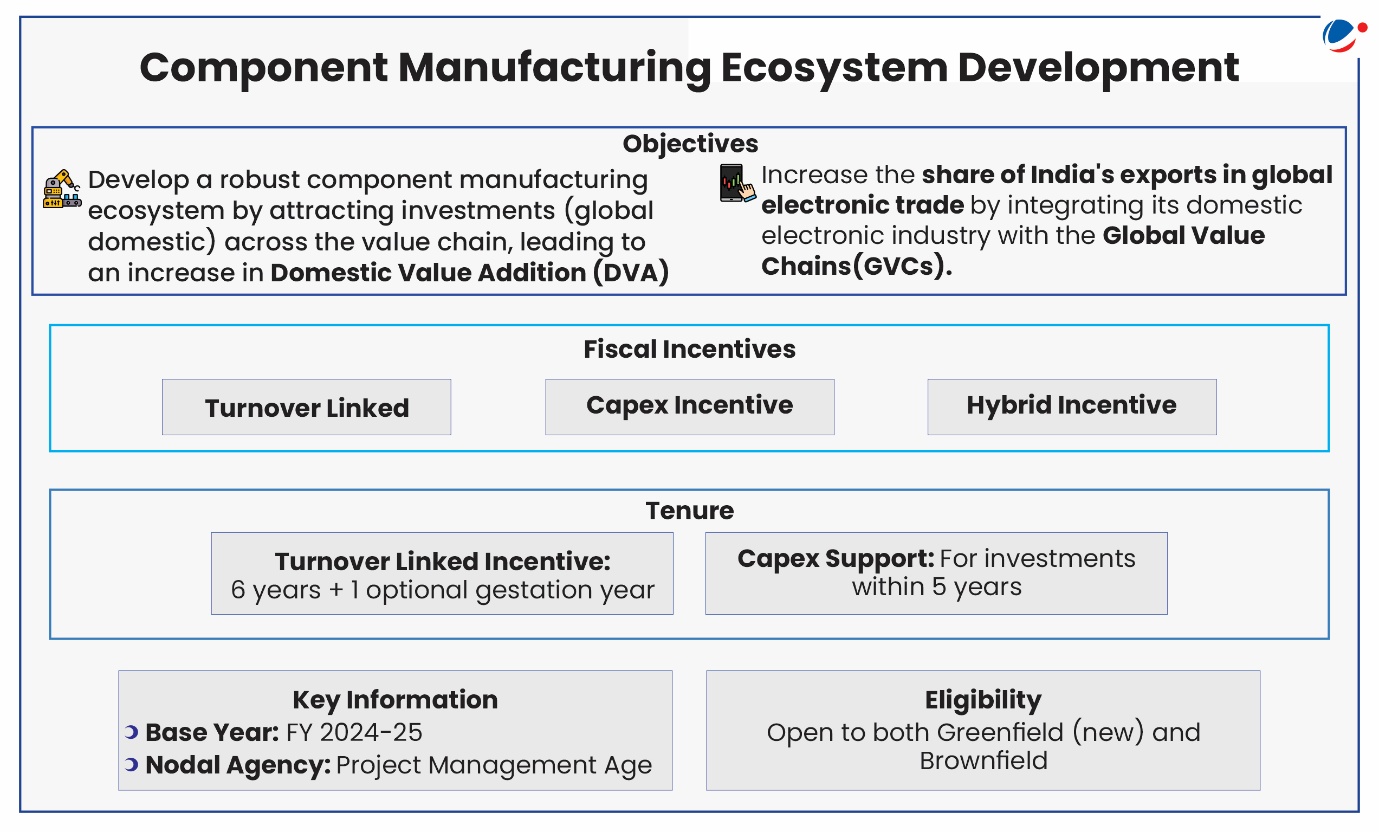
About the scheme
- Based on Production, Electronics Value Chain can be divided into 4 categories: Design, Components, Assembly, Original Equipment Manufacturing.
- The scheme focuses on Components section (Passive components or non-semiconductor components) like resistors, capacitors, sensors, films, lenses, etc.
- The scheme provides differentiated fiscal incentives on target segment products, depending on the specific challenges being faced by the industry.
India's Electronics Sector: An Overview
Key Initiative to Boost Electronics Manufacturing In The Country
|
Why Does India Need to Achieve Self-Reliance in Manufacturing of Electronic Components?
- National Security: Dependence on foreign-made electronic components, especially in defense and critical infrastructure, poses risks such as data breaches and supply chain disruptions.
- China, Hong Kong account for 56% of India 's total imports of electronics, telecom, electrical products (GTRI)
- Rising Imports, Despite Domestic Production of End Products: With then rise of electronics production, imports of components have also increased.
- They major reason for this is local capacity for component manufacturing remained underdeveloped.
- Strategic Opportunity (China+1 Shift): With global firms looking beyond China, India has a strong opportunity to attract investments in component and sub-assembly manufacturing.
- Leveraging India's Competitive Advantage: India is among the most cost-effective electronic component manufacturing destinations globally.
- According to the PWC, India's minimum monthly wage is just 46% of Thailand's and its labour force is 12 times larger than Thailand's.
Electronics is one of the fastest-growing global industries, driven by digitization. However, Despite the need for self-reliance and India's strengths in electronics, domestic manufacturing remains underdeveloped.
Challenges for Electronic Component Manufacturers in India
- High Logistics Costs: India has longer lead times and higher transport costs than countries like China and Vietnam.
- For example, Shipping a premium smartphone cost $0.80 from China vs $8 from India (PWC).
- Global Oligopoly in Components: Component markets are dominated by a few countries with natural or policy-driven advantages.
- For example, Japan benefits from strong R&D infrastructure. Taiwan advanced through US support and knowledge transfer.
- Underdeveloped Supporting Industries: Industries like chemicals are not yet equipped to supply high-quality raw materials for electronics.
- For example, India can potentially supply chemicals for semiconductors, but needs to upgrade to meet industrial standards.
- Limited Access to Critical Minerals: Critical minerals are essential but often scarce or controlled by other countries. For example, China dominates exports of gallium and germanium (used as silicon alternatives).
- In 2023, India identified 30 critical minerals it heavily depends on from abroad, increasing supply chain risks.
- Shortage of Skilled Workforce: Lack of trained workers for specialized systems like SMT lines limits local manufacturing capabilities.
Conclusion
To position India as a global hub for electronic component manufacturing, NITI Aayog recommends a multi-pronged strategy. This includes incentivizing R&D and design, rationalizing tariffs, enhancing skill development, enabling technology transfers, and upgrading infrastructure. Together, these efforts can help build a strong and self-reliant electronics manufacturing ecosystem in India.



