Why in the News?
Recently, on the 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, governments adopted a declaration on the empowerment of women and girls reaffirms the priciple of Women-Led Development.
Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (BPfA)
- It was originally adopted in 1995 at the Fourth World Conference on Women, stressing on upholding all human rights and fundamental freedoms for every woman and girl, without exception.
- On its 30th anniversary, Beijing + 30 Action Agenda, with 6 priority actions were released.
- Digital Revolution: Access to new skills, bridging Digital Gender Gap, etc.
- Freedom from Poverty: Social protection and high-quality public services for health, education and care.
- Zero Violence: Comprehensive national action plans involving community-led organizations.
- Full and Equal Decision-making Power: In both private and public domains.
- Peace and Security: Gender-responsive humanitarian actions
- Climate Justice: Prioritising rights of women from Indigenous communities, promoting green jobs, etc.
Women's Development vs. Women-led Development
Women's Development | Women-led Development |
|
|
Why Women-Led development is important for Society?
- Women as Agents of Empowerment: Shifting the narrative from women as mere recipients of welfare.
- Gender Equality: Tackles generational inequality (Global Gender Gap Index 2024: India ranked 129th out of 146 countries) by breaking gender stereotypes and rejecting norms that sustain gender disparity.
- Economic Empowerment: Indian women, despite constituting 48% of the population, contribute only 18% to the GDP (NFHS-5). Bridging the gender gap in employment could potentially lead to a 30% increase in the country's GDP.
- Rural Development and Poverty Alleviation: Women-led initiatives transform villages.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) mobilised a total of 8.01 Crore women from poor and vulnerable communities in self-help groups, increasing household incomes by 22%.
- Inclusive growth: It channelizes potential of women for actively shaping and driving economic, social, and political progress at all levels of governance.
- Sustainability: Empowering women in climate-related decision-making strengthens community resilience and allows them to adapt to the changing environment.
- The Deccan Development Society collaborates with nearly 5,000 Dalit and Indigenous women small farmers to restore thousands of hectares of farmland through sustainable agricultural practices.
Obstacles on the Path to Women-Led Development
- Patriarchal Social Norms: Deep-rooted patriarchy limits women's decision-making rights, reinforcing gender inequality.
- NFHS-5 (2019-21) states only 3% of women make decisions independently.
- Women shoulder a disproportionate share of unpaid care and domestic work.
- Education: Average female literacy rate throughout world is 79.9%, while India lags behind at 62.3%
- Workplace Discrimination: Women face harassment, unequal pay, and limited career growth due to glass-ceiling effect.
- Women earn 20% less than men for equal work (WEF Gender gap report, 2023).
- Gender digital divide: Only 15% of women in India have access to internet (Mobile Gender Gap 2021 Report).
- Early Marriage and Motherhood Penalty: Early marriage and childbirth reduce women's educational and career prospects.
- NFHS-5 states 23% of women aged 20-24 were married before 18.
- Women safety: Increasing violence restricts women's mobility and freedom.
- NCRB (2022) reported 4.5 lakh crimes against women.
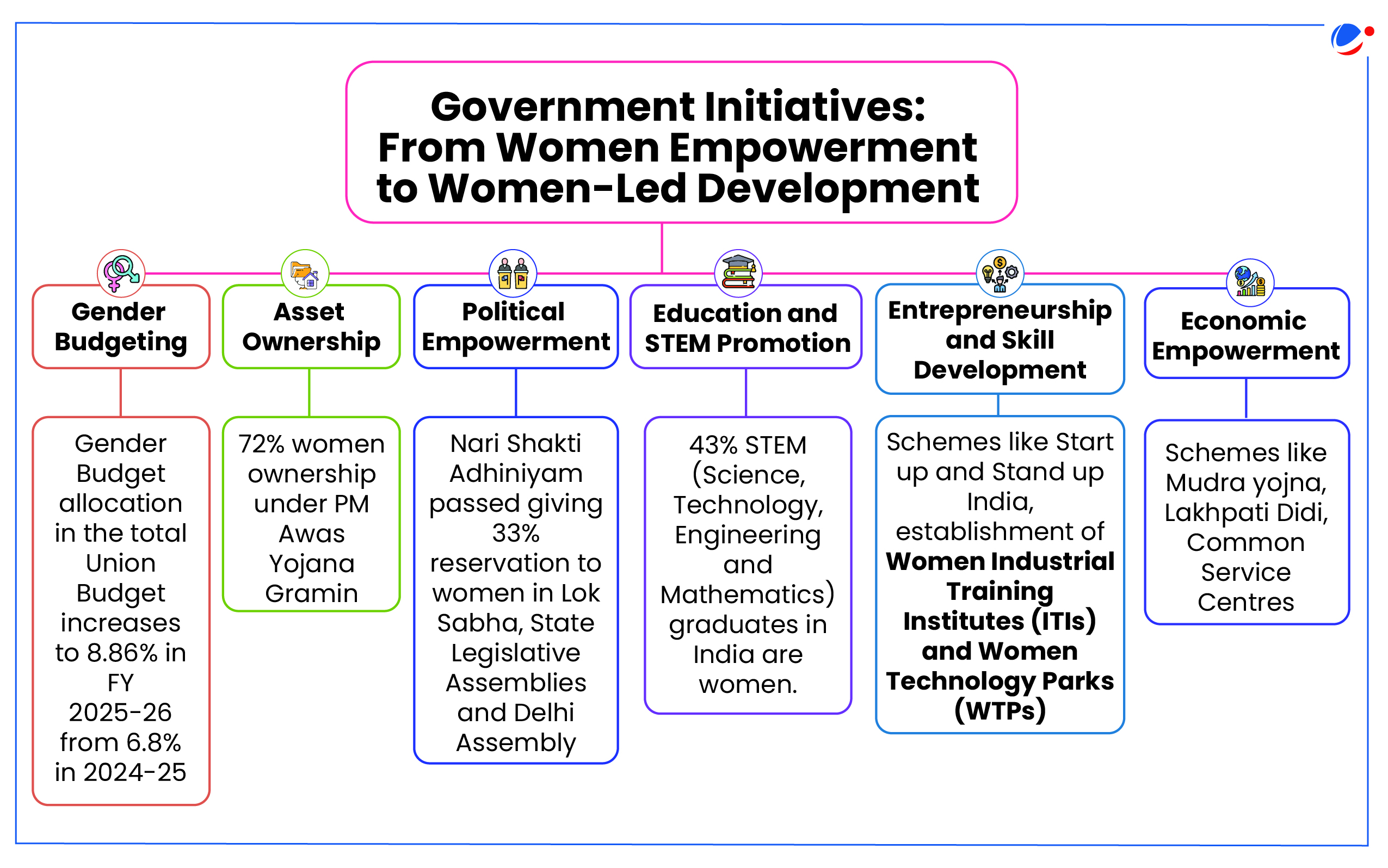
Global Initiatives to ensure Women-Led Development
|
Conclusion
Empowering women as equal participants in development fosters inclusive growth. Through political, economic, and social reforms, women are transforming from welfare recipients to active change-makers. Ensuring equal rights, opportunities, and representation paves the way for sustainable progress and a truly women-led development model in India.



