Why in the News?
The human enhancement industry was worth $125 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to $348.5 billion by 2033, according to a recent report by IMARC.
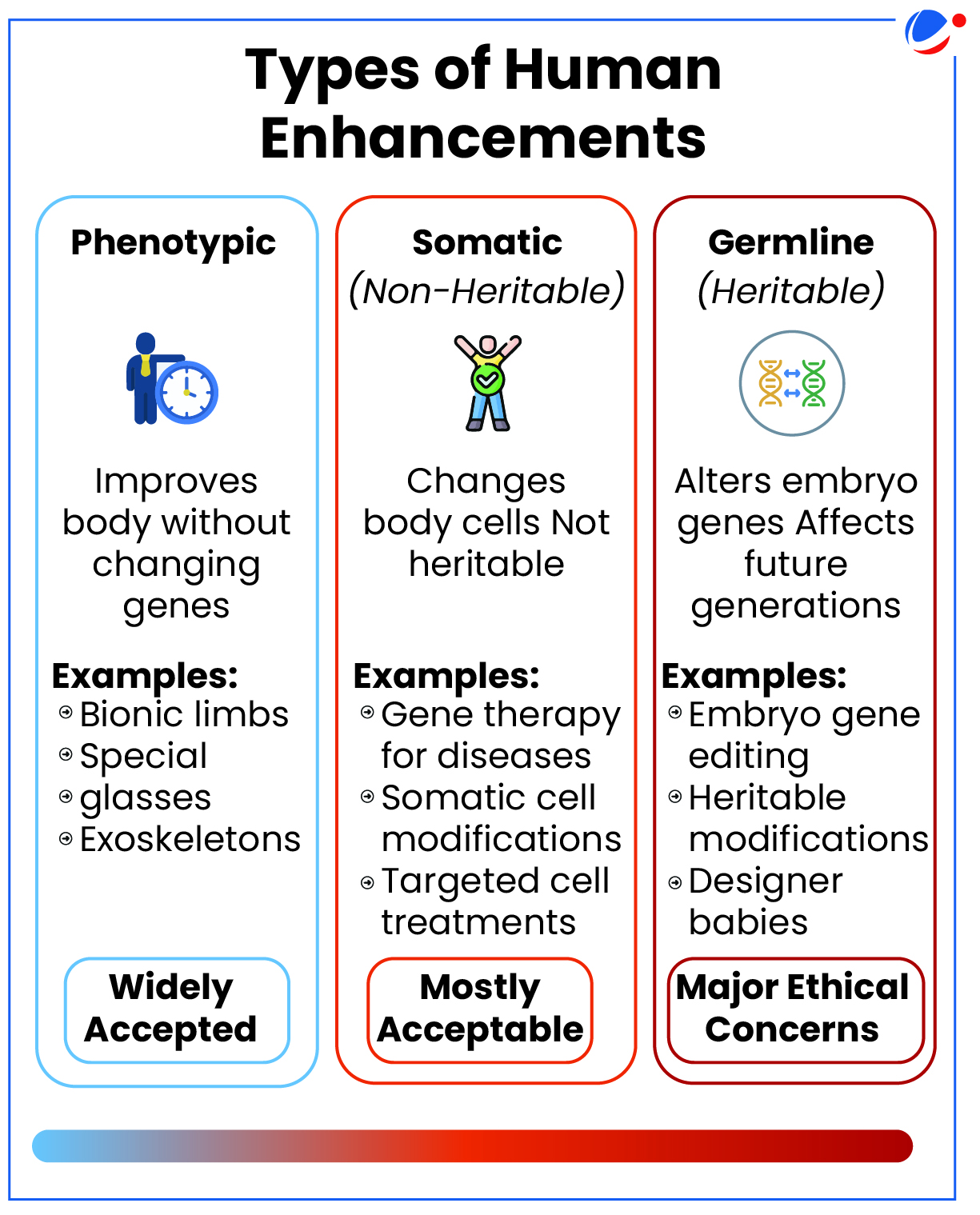
What is Human Enhancement?
- Human enhancement refers to a natural, artificial, and technological alteration of the body to enhance cognitive and physical capabilities and functions of individuals.
- It is undertaken using drugs, hormones, implants, genetic engineering to dietary supplements and cosmetic surgeries for self-improvement.
- Unlike traditional medicine, which seeks to treat or cure illness, human enhancement focuses on surpassing typical human limits.
- For example, advances in human enhancement technologies provide resistance against diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and Lyme.
- Unlike traditional medicine, which seeks to treat or cure illness, human enhancement focuses on surpassing typical human limits.
- The debate around human enhancement is shaped by two key views:
- Transhumanists: Support using advanced technologies to radically enhance human abilities and extend life.
- Bioconservatives: They believe in preserving the natural human condition and oppose using technology to drastically change or extend human life, fearing it may harm our human essence.
Concerns Associated with Human Enhancement
- Equity: Access to enhancements may be limited, increasing social inequality.
- Identity: Changing core human traits may challenge our sense of being human raising concerns about the loss of identity.
- Consent: Forced or non-consensual enhancements threaten individual freedom.
- Social Pressure: Widespread use could create discrimination against those who remain unenhanced.
- Health Risks: Long-term effects of genetic or neural modifications are still unknown.
- Environment: Longer lifespans could add pressure on resources and ecosystems.
- Genetic Diversity: Genetic engineering might reduce diversity, raising disease vulnerability.
- Regulation: Effective regulation is needed to ensure safe, fair, and ethical use of these technologies.
Conclusion
Human enhancement technologies can boost abilities, extend life, and drive progress, but they raise ethical, social, and environmental concerns. Responsible regulation, equitable access, and awareness of long-term impacts are essential to preserving core human values.



