Why in the News?
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has conducted liquidity infusion operations to curb the high liquidity deficit, which has hit its lowest level in nearly 15 years.
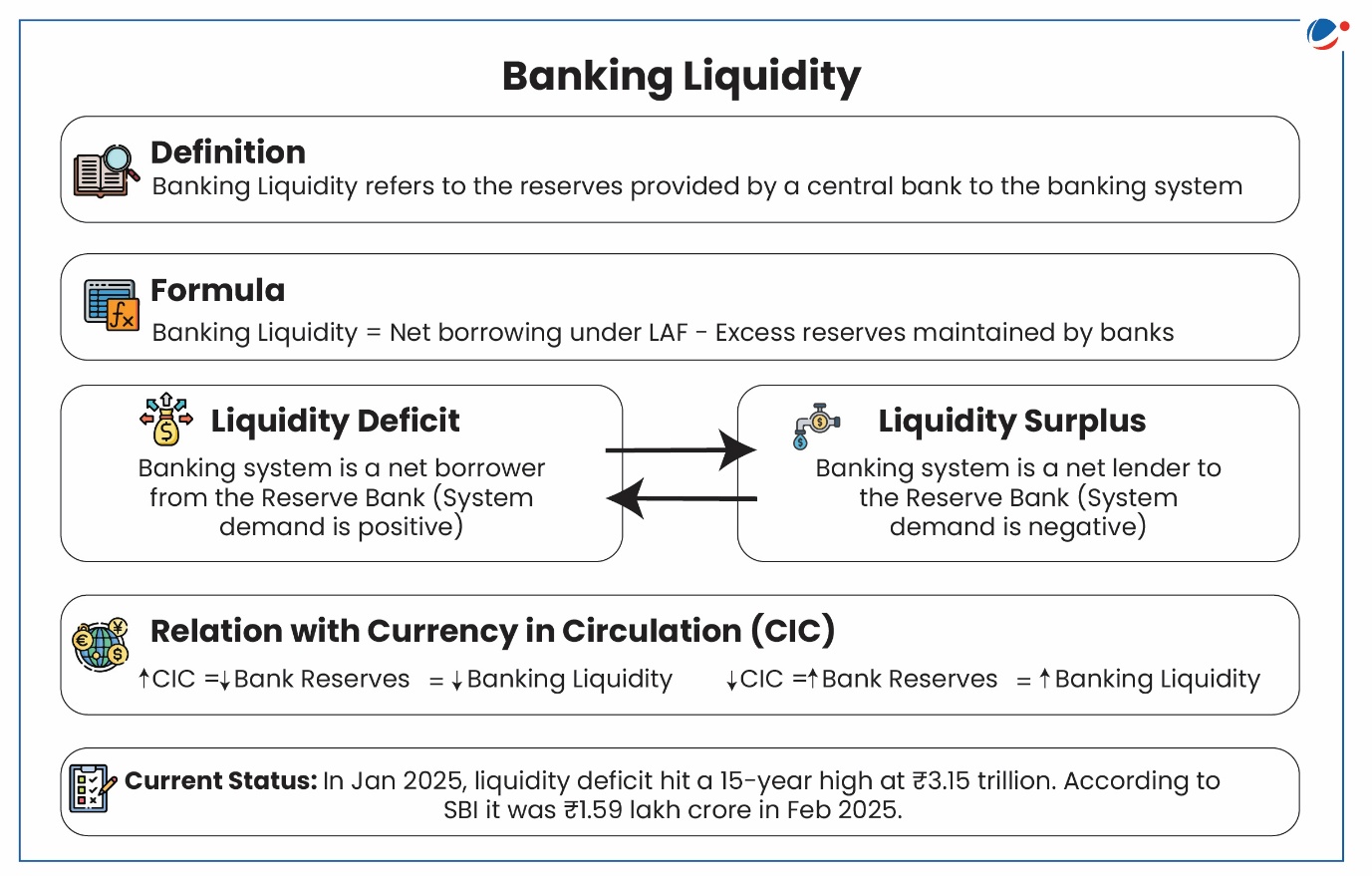
More on the News
RBI injected liquidity into the banking system through:
- OMO (Open Market Operation) purchase auctions of Government Securities for an aggregate amount of ₹1,00,000 crore in two tranches of ₹50,000 crore each.
- USD/INR Buy/Sell Swap auction of USD 10 billion for a tenor of thirty-six months.
- The swap is in the nature of a simple buy/sell foreign exchange swap from the Reserve Bank side.
- A bank shall sell US Dollars to the Reserve Bank and simultaneously agree to buy the same amount of US Dollars at the end of the swap period.
Factors leading to Liquidity Deficit
- Tax outflows: In December 2024, corporations paid over ₹3 trillion in advance taxes, significantly reducing available liquidity.
- Since these funds are transferred to the government's account with the RBI, they temporarily exit the banking system, tightening liquidity conditions.
- Just-in Time (JIT) SNA-SPARSH Transition: With the implementation of JIT, systemic liquidity has been impacted through movements in government cash balances.
- Transfer through SNA-SPARSH results in shorter intermediate halt of funds in the banking system, affecting liquidity.
- Foreign exchange (Forex) Market
- Volatility in capital flows:Sell-offs by Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) pushed the total capital outflows.
- RBI intervention in Forex market: When the RBI sells dollars, it helps prevent excessive rupee depreciation but absorbs rupees from the system, reducing liquidity.
- Festive Season Withdrawals: Withdrawal of significant amount of cash occurs during major festivals like Diwali, Christmas, which continued to Mahakumbh 2025.
Impact of Liquidity Deficit
- Higher Borrowing Cost: Lower liquidity in the banking system can lead to higher borrowing costs for banks, which may pass on those costs to borrowers including NBFCs thus affecting finances of key sectors like housing and MSMEs.
- Delay in Monetary Policy Transmission: Liquidity Deficit negatively impacts monetary policy rate transmission i.e. rate cuts cannot be effective until there is surplus liquidity.
- For example, the latest data released by the RBI shows that the impact on lending and deposit rates was minimal despite a 25 bps cut in policy repo rate, mainly due to tight liquidity conditions.
- Credit Availability: Banks tighten lending during liquidity crunch, making it harder to access credit, slowing down investment and spending.
- Profit Squeeze for banks: With banks paying more to secure liquidity, their margins are under pressure, resulting in lower profitability.
- Market Volatility: Liquidity stress shakes market confidence, fuelling uncertainty, impacting stock prices and other asset classes.
RBI's Tools for Managing Liquidity Deficit
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF): LAF is the principal instrument of liquidity management with repo rate as the policy rate.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): OMOs refer to the buying and selling of government securities by the RBI to inject or absorb liquidity in the banking system.
- Market Stabilisation Scheme (MSS): Typically used as a short-term measure to address temporary surges in liquidity.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): CRR is a mandatory reserve that banks must maintain with the RBI and it serves as a liquidity buffer without earning any interest.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): SLR is a regulatory mandate that requires commercial banks to maintain a minimum percentage of deposits in the form of liquid assets, such as gold, cash, and approved securities.
- Forex Swaps: To inject liquidity, RBI uses US Dollar/Indian Rupee buy/sell swaps, where RBI buys dollars from banks in exchange for rupees, with the commitment to sell those dollars back at a later date.



